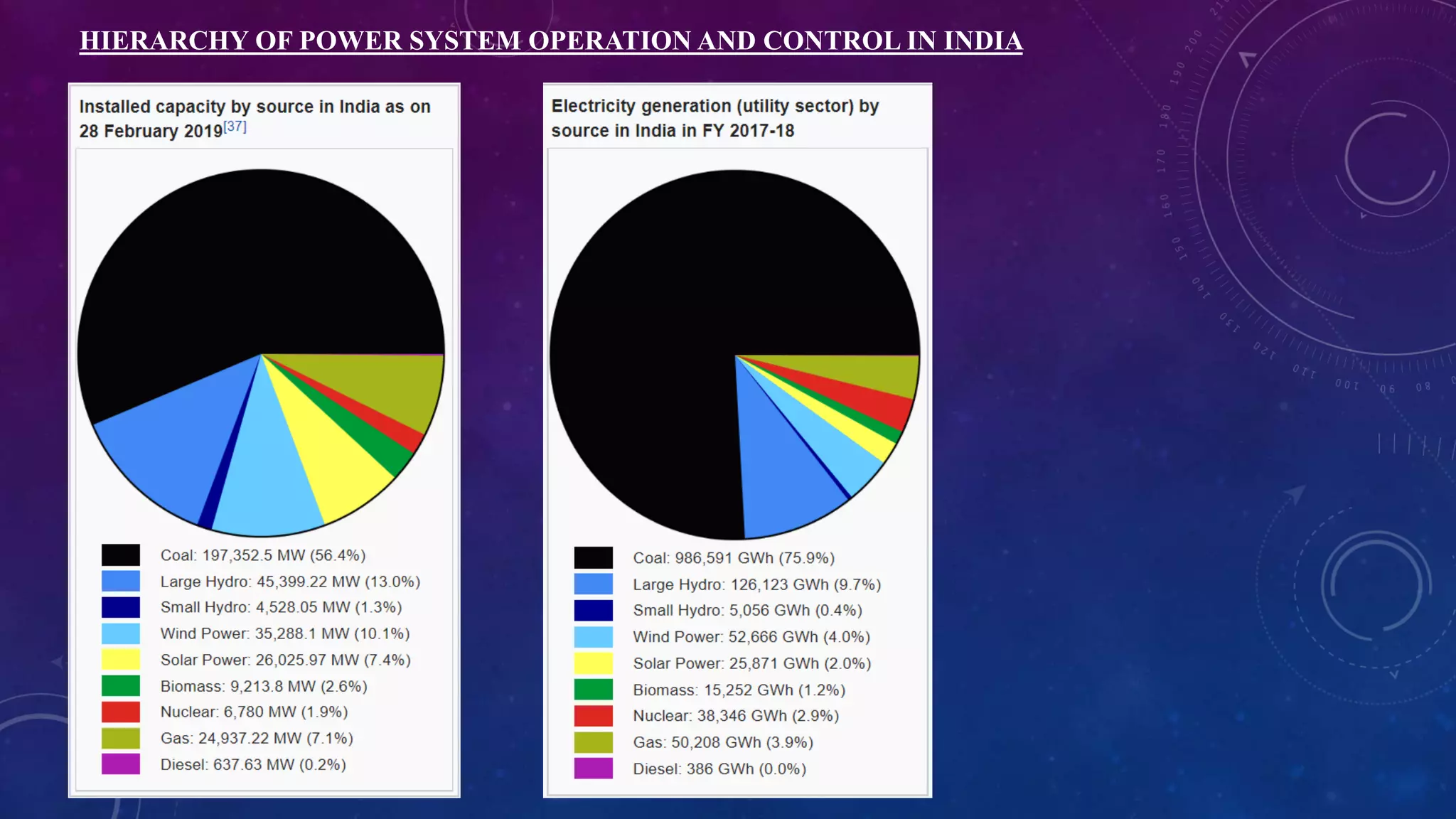
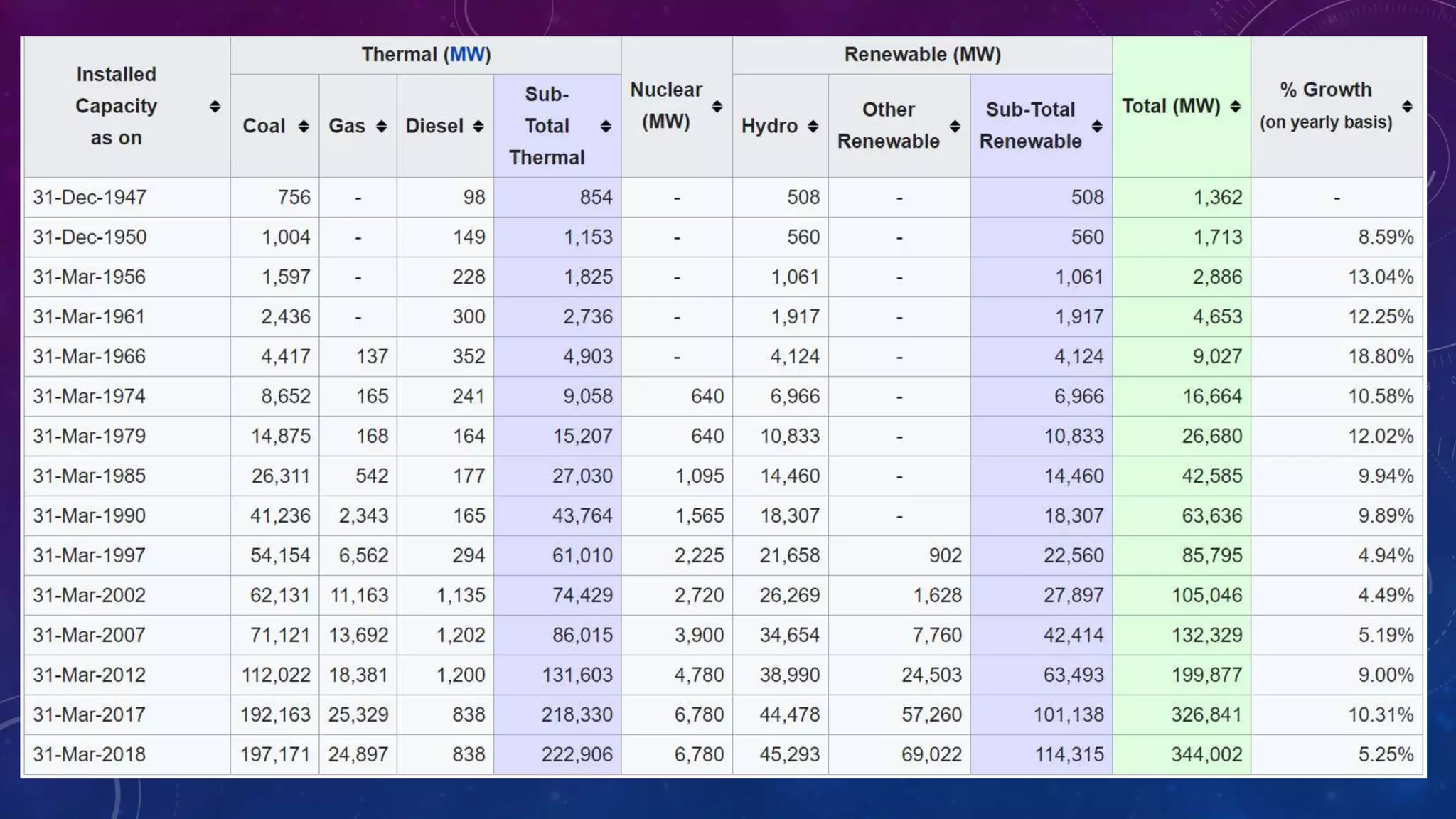
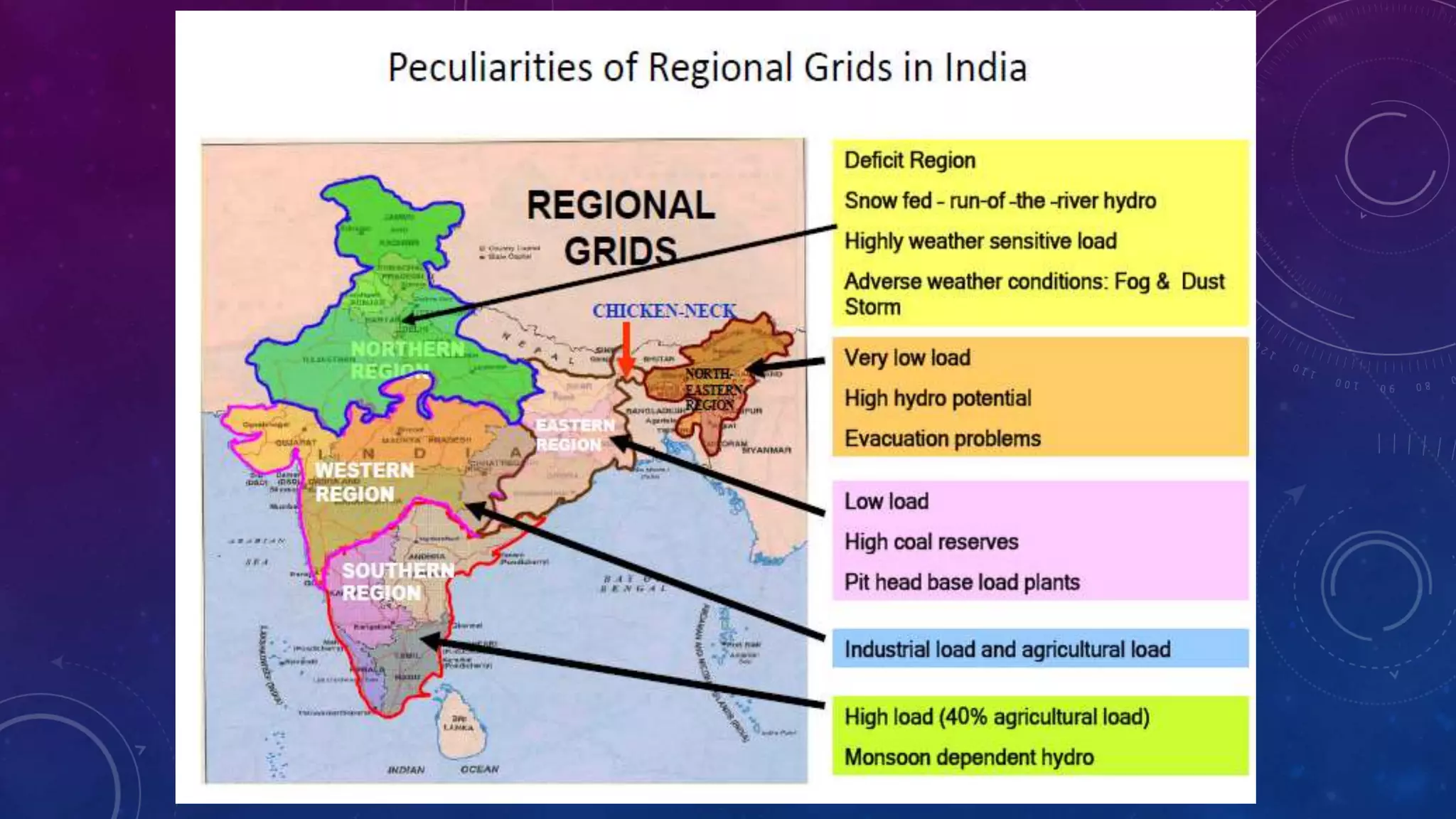
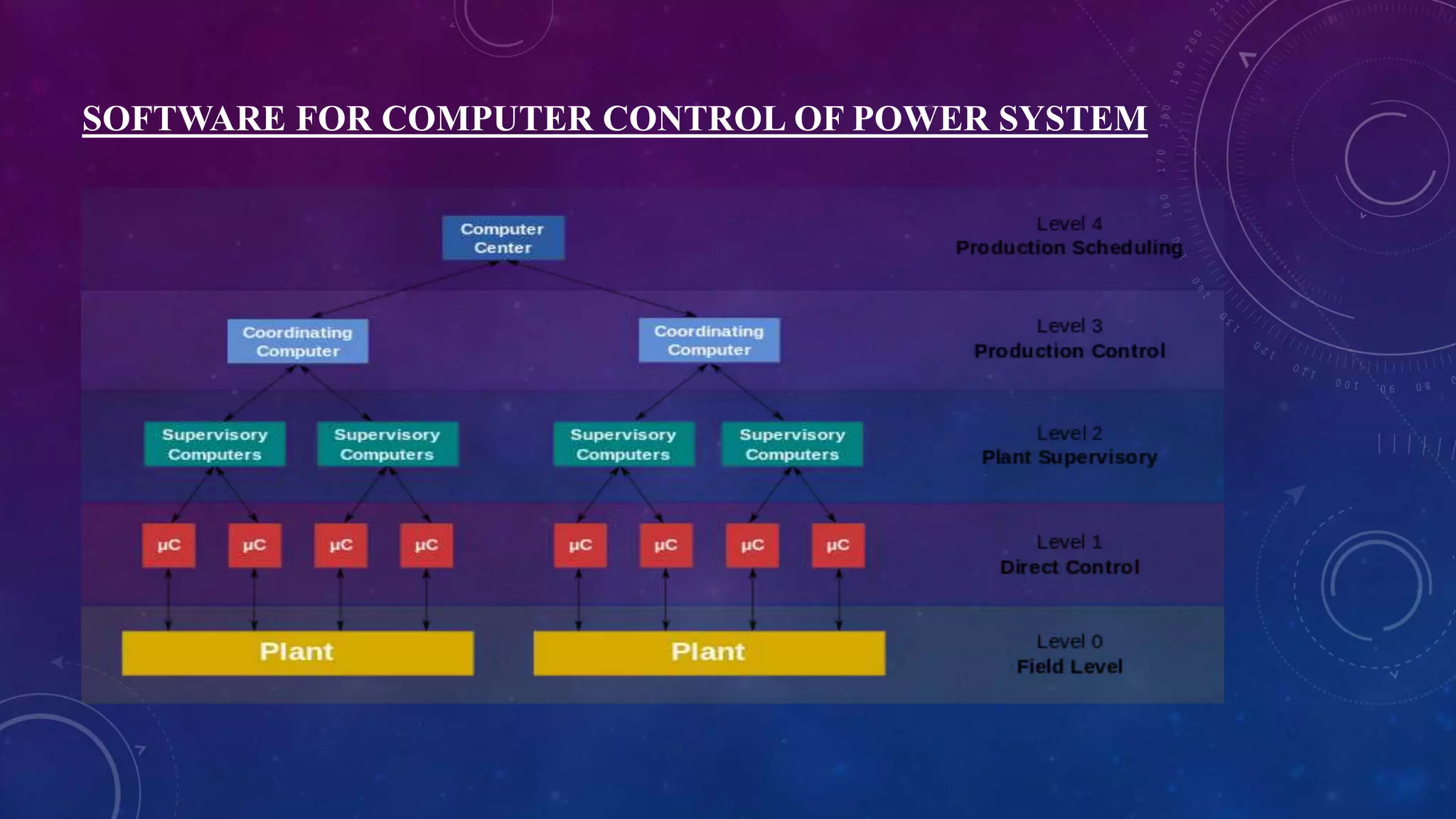
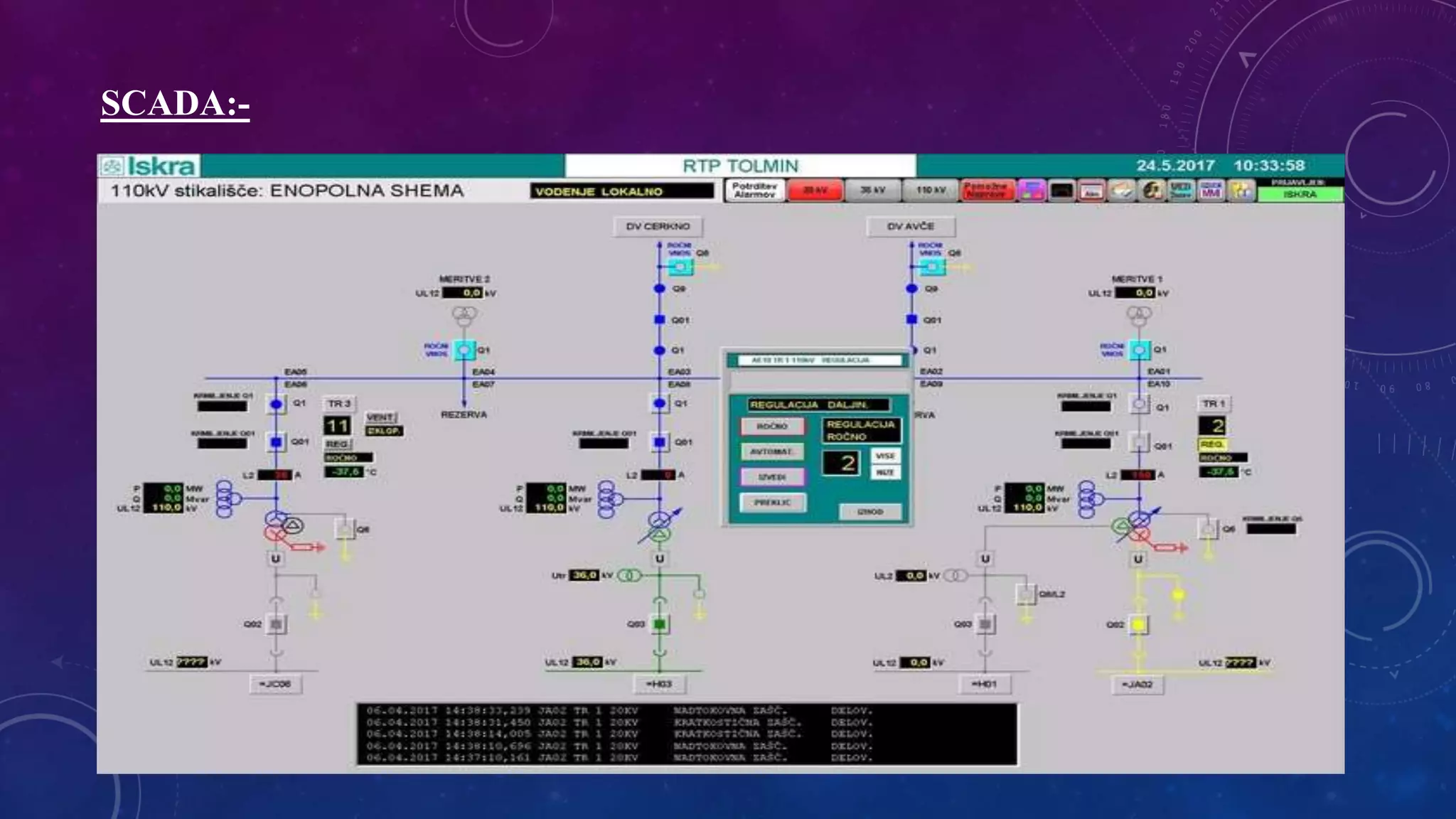
This document discusses computer control of power systems and SCADA systems in India. It provides statistics on India's power sector, including installed capacity, sources of energy, transmission losses, and peak load. It also outlines challenges in power systems like storage limitations and varying demand. The roles of an energy control center are summarized, including load forecasting, capacity planning, system monitoring, and economic dispatch. Finally, it introduces the hierarchy of power system operation in India and key components of SCADA systems, such as sensors, RTUs, master units, communication links, and software.