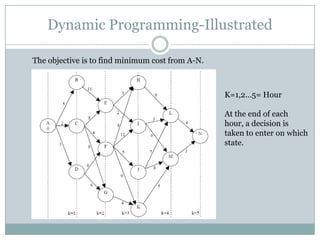
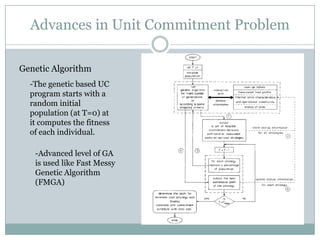
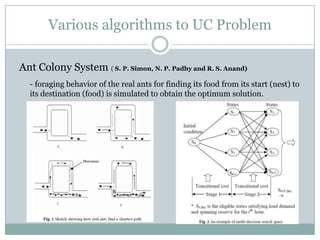
This document discusses optimization of power system operation through techniques like unit commitment and economic dispatch. It begins with an introduction to meeting varying electricity demand. It then outlines the steps of optimization including long-term planning, unit commitment for hourly/monthly decisions, and economic dispatch for instantaneous dispatch. Unit commitment deals with deciding which generation units to operate to satisfy demand while considering constraints. Common solution methods for unit commitment include priority lists, heuristics, mixed integer programming and dynamic programming. The document provides examples of advances in these areas and practical software used for optimization.



![Economic Dispatch- Covered EarlierEnergy Policy Act defines “Economic Dispatch” to mean “the operation of generation facilities to produce energy at the lowest cost to reliably serve consumers, recognizing any operational limits of generation and transmission facilities.” [EPAct 2005, Sec. 1234 (b)] Actually, For Power System Economic Operation, the installed generating capacity should be greater than the load at any specific momentThis topic is covered in earlier presentation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizationofpowersytem-110823160035-phpapp01/85/Optimization-of-power-sytem-4-320.jpg)