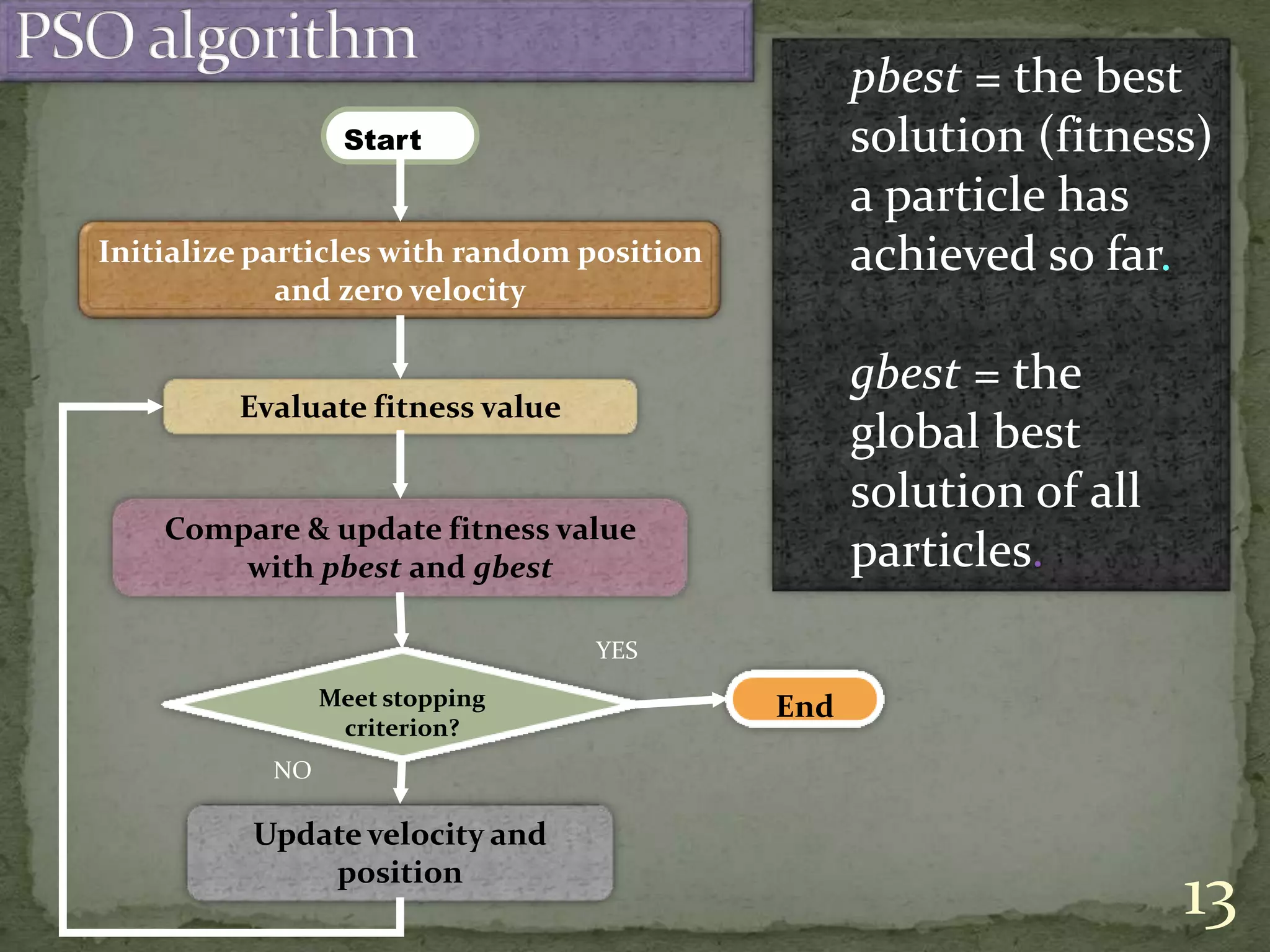
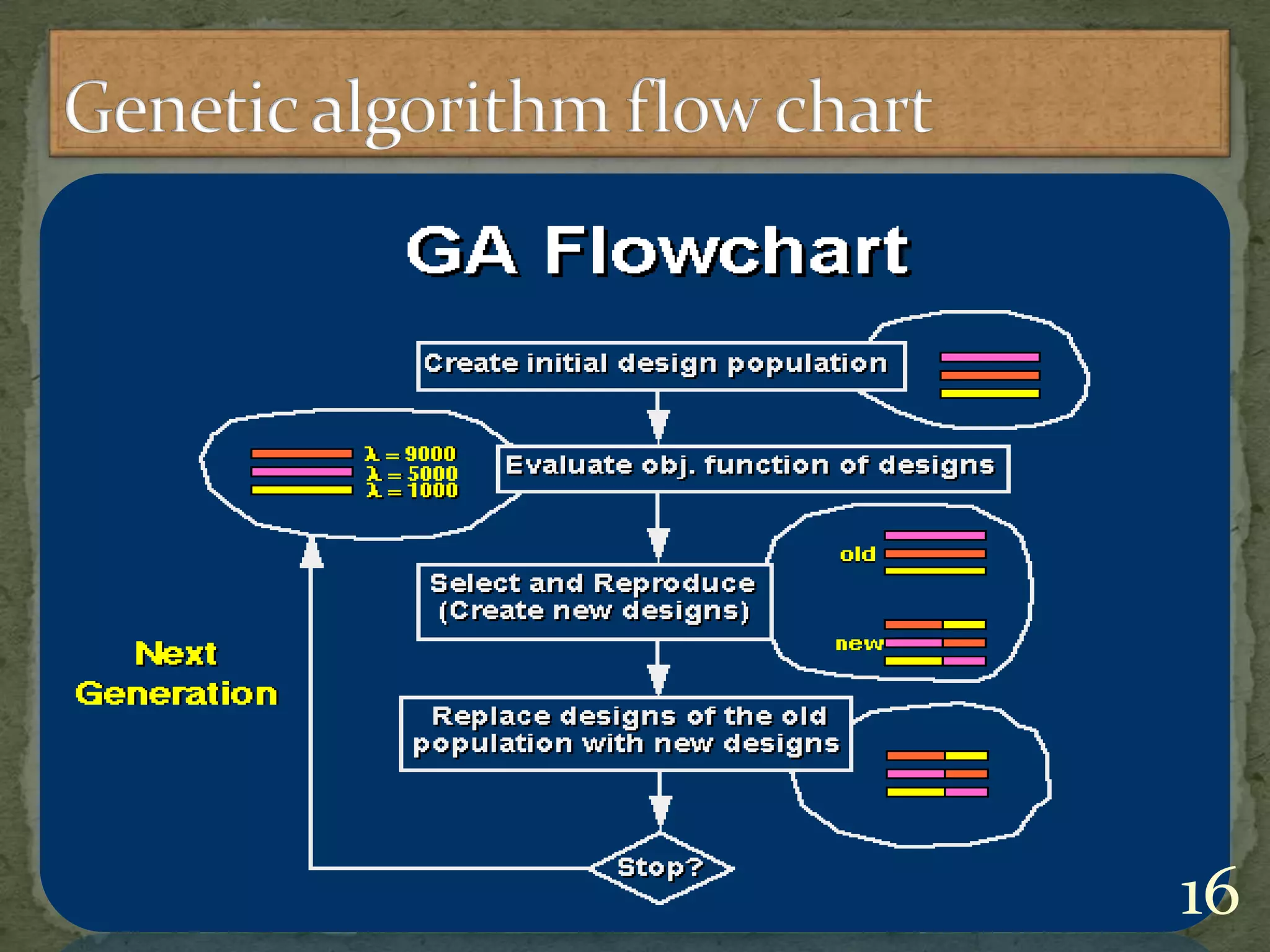
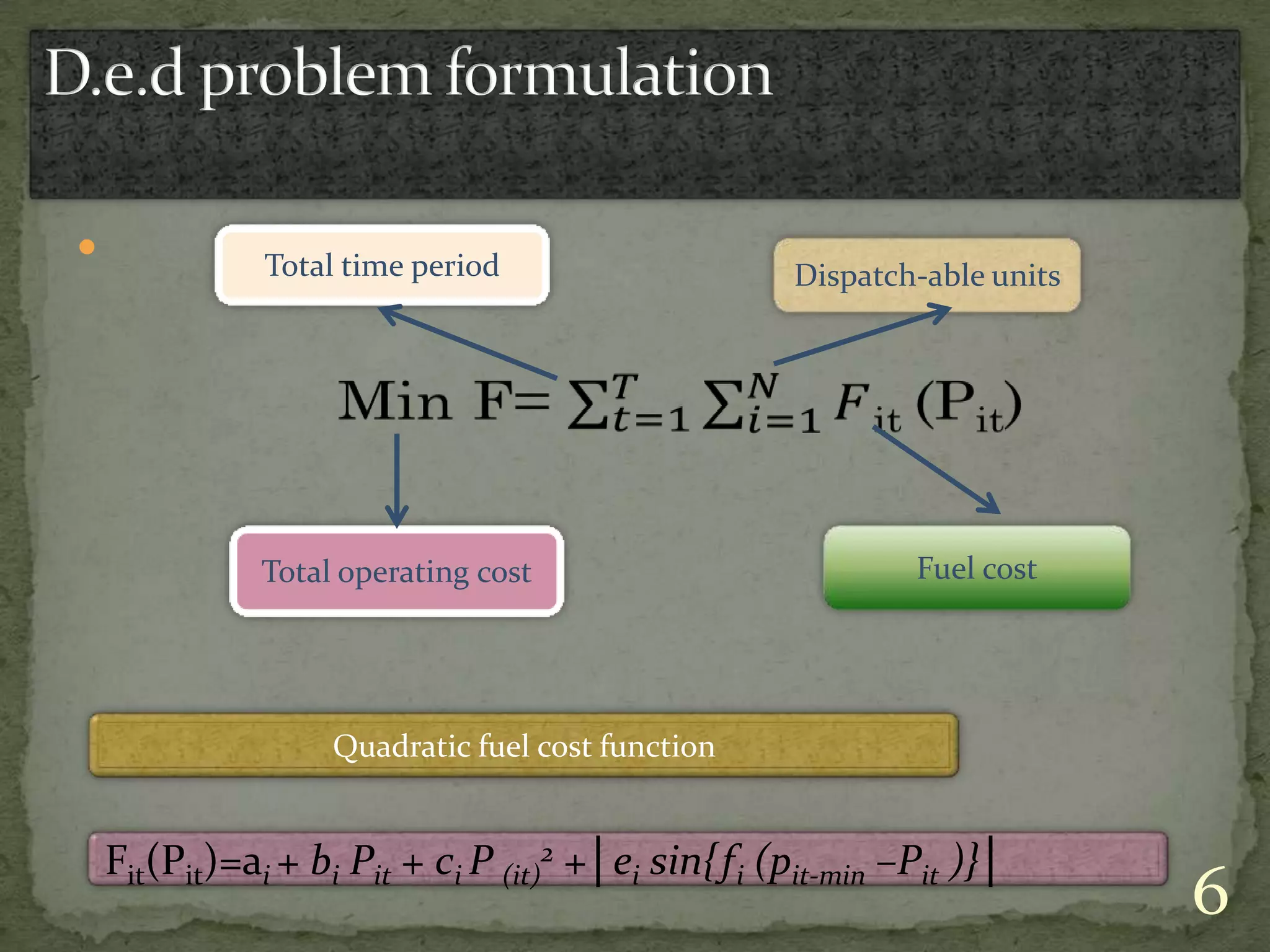
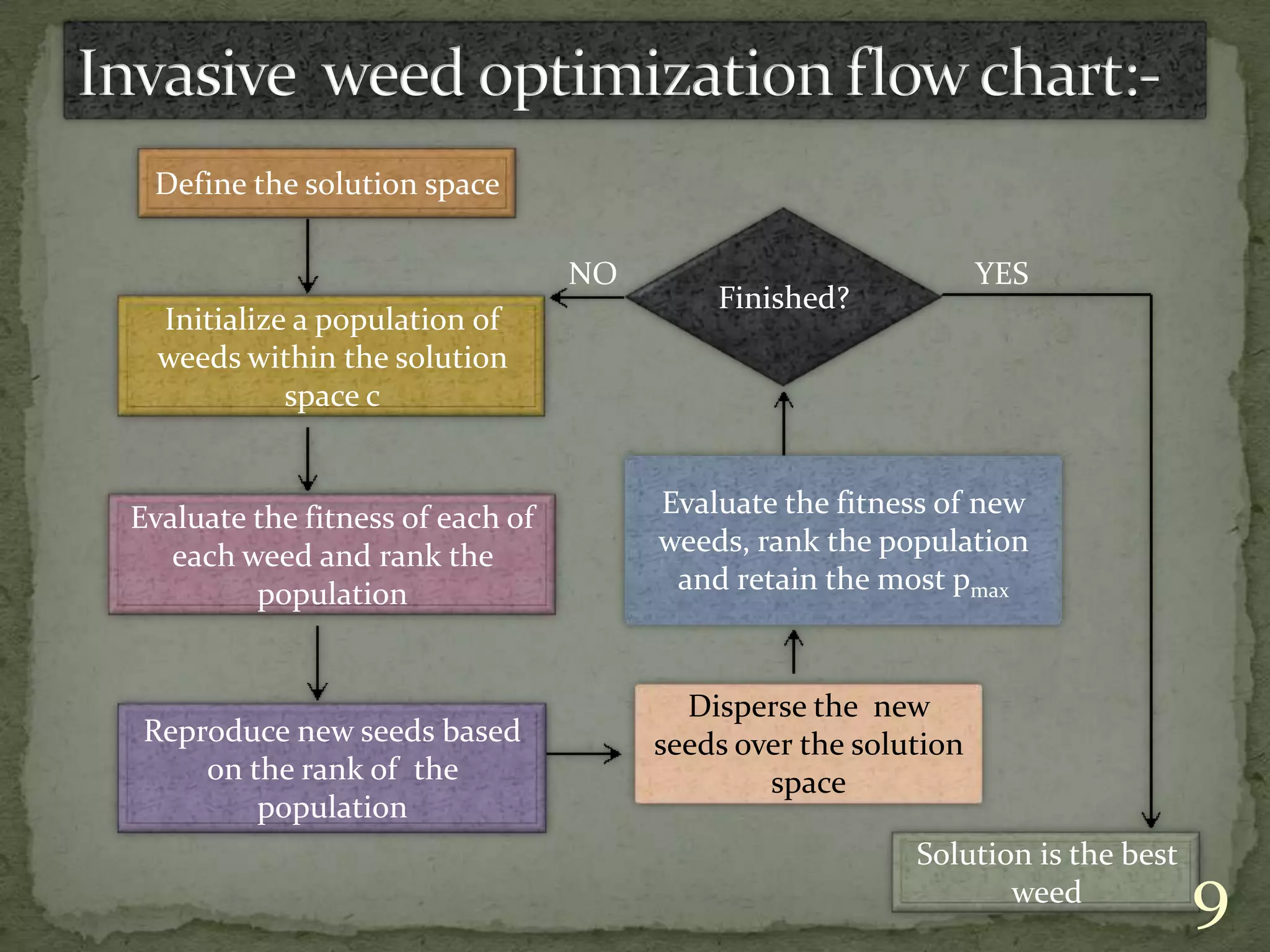
This document discusses various solution techniques for the economic load dispatch (ELD) problem in power systems. It first defines ELD and explains why it is important for minimizing generation costs while meeting load demands. The document then outlines different ELD formulation and solution methods like invasive weed optimization, particle swarm optimization, genetic algorithms, and simulated annealing. It provides flowcharts to illustrate the processes. The document also discusses the limitations of classical optimization methods for dynamic ELD problems and concludes with references used.





![1. Xi G=[X1,i,G,X2,i,G,X3,i,G…………….XD,i,G]
2. SiG
= [{Fmax
, G-F(XiG )}{Smax - Smin }]/[{Fmax , G – Fmin ,G}]
3. =[{(Gmax -G)÷Gmin}n * ( max - min )+ min ]
4. = G(S, Xi )/ G(Si , x )
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamiceconomicloaddispatch-areviewofsolutionmethodologies48-130524092704-phpapp01/75/Dynamic-economic-load-dispatch-a-review-of-solution-methodologies48-10-2048.jpg)