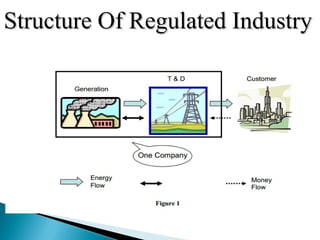
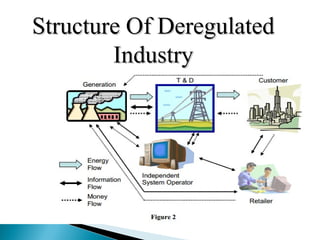
The document discusses electricity deregulation and the requirements for a deregulated electricity market. It outlines the benefits of deregulation such as more efficient use of generation capacity, improved consumer choice, and potentially lower prices. In a deregulated market there are different entities like generators, transmitters, distributors, retailers, and customers. Regulation is still needed to prevent monopoly behavior and ensure reliability. The document compares regulated versus deregulated industry structures and different market models for electricity trading. It also discusses issues in deregulated markets like network congestion, supply shortages, defaults, and lack of experience with risk hedging tools. The objective of India's Electricity Act of 2003 was to introduce competition while protecting consumers and ensuring universal access to electricity