Types of movement across the cell membrane
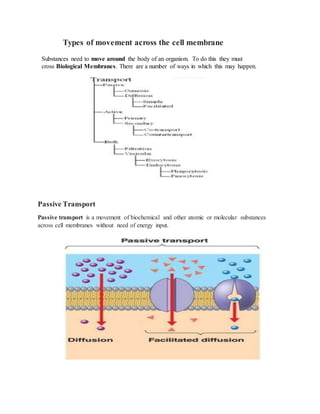
- 1. Types of movement across the cell membrane Substances need to move around the body of an organism. To do this they must cross Biological Membranes. There are a number of ways in which this may happen. Passive Transport Passive transport is a movement of biochemical and other atomic or molecular substances across cell membranes without need of energy input.
- 2. Kinds of Passive Transport There are three main kinds of passive transport. 1- Osmosis 2- Diffusion 3- Facilitated diffusion Osmosis Osmosis is defined as the diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis involves movement of water from regions in which there are relatively more water molecules per volume, i.e. "high water potential", to regions where there are fewer water molecules per volume "lower water potential". Plasma membrane is permeable to water but not to solute o Solute = dissolved particle o Solvent = liquid medium in which particles may be dissolved Water moves from solution with lower concentration of dissolved particles to solution with higher concentration of dissolved particles Water moves from dilute solution to concentrated solution Osmotic potential is the total of all dissolved particles Osmosis Produces a PhysicalForce
- 3. Movement of water into a cell can put pressure on plasma membrane Animal cells will expand and may burst o Some cells, such as Paramecium have organelles called contractile vacuoles which are basically little pumps which pump excess water out of cell o You can alter the rate of contractile vacuole pumping by placing it in increasingly hypotonic solutions Organisms with a cell wall, such as plants, do not burst o Cell membrane pushes against cell wall o The rigid cell wall resists due to its own structural integrity o These opposing forces create turgidity, which keeps plants upright o If you don't water a plant, it wilts (this is called plasmolysis). Water it, the leaves will come back up do to the reestablishment of turgidity. Solution Types Relative to Cell Hypertonic Solution: Solute concentration higher than cell o More dissolved particles outside of cell than inside of cell o Hyper = more (think hyperactive); o Tonic = dissolved particles o Water moves out of cell into solution o Cell shrinks Hypotonic Solution: Solute concentration lower than cell o Less dissolved particles outside of cell than inside of cell o Hypo = less, under (think hypodermic, hypothermia); o Tonic = dissolved particles o Water moves into cell from solution o Cell expands (and may burst) Isotonic Solution:
- 4. Solute concentration equal to that of cell o No net water movement Diffusion Spontaneous movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Does not require energy Occurs via random kinetic movement Net diffusion stops when concentration on both sides equal (if crossing a membrane) or when there is a uniform distribution of particles o Equilibrium is reached o Molecules continue to move, but no net change in concentration (hence the phase "net diffusion" above o Diffusion of one compound is independent to diffusion of other compounds
- 5. Factors Affecting Diffusion across a Plasma Membrane Several factors that affect the rate of diffusion include temperature, density of the diffusing substance, medium of diffusion and concentration gradient. Diffusion directly through lipid bilayer o The greater the lipid solubility of the diffusing particle, the more permeable the membrane will be o All else being equal, smaller particles will diffuse more rapidly than larger particles. o O2, H2O, CO2 rapidly diffuse across lipid bilayer. Diffusion of Hydrophilic Molecules Across a Plasma Membrane o Plasma membrane is semipermeable. o Water, while polar, is small enough to freely move across the plasma membrane. o Larger hydrophilic uncharged molecules, such as sugars, do not freely diffuse. o Charged molecules cannot diffuse through lipid bilayer. o Ion channels and specific transporters are required for charged molecules and larger, uncharged molecules. Temperature As temperature increases the average kinetic energy of particles increases. Greater kinetic energies lead to increased velocities. The increased velocity means that there is a greater chance of collisions between particles, resulting in an increased rate of diffusion. Generally, the rate of diffusion increases with temperature. Density of Diffusing Substance
- 6. Density is defined as the amount of material that exists within a given volume. Regions of high density contain a greater number of particles per unit volume than regions of lower density. An increased number of particles leads to a greater chance of collisions, and this leads to an increased rate of diffusion. A lower number of particles leads to a reduced chance of collisions and this lowers the rate of diffusion. Therefore, high-density regions have a greater rate of diffusion than low-density regions. Medium of Diffusion Diffusion also depends upon the medium in which it takes place. Physically, the particles within the medium act as a barrier to diffusion. This means that the greater the number of molecules or larger particles within the medium, the lower the rate of diffusion. ConcentrationGradient The concentration of a substance is defined as the number of solute molecules that can be found within a given volume. A large difference in concentration leads to a greater probability of molecular collisions over the region and therefore increases the rate of diffusion. Generally, the greater the concentration gradient, the greater the rate of diffusion. FacilitatedDiffusion Allows diffusion of large, membrane insoluble compounds such as sugars and amino acids Does not require energy (passive) Highly Selective Substance binds to membrane-spanning transport protein Fully reversible - molecules may enter the cell and leave the cell through the transport protein. Particles move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. How to Cheat - Glucose Enters the Cell by Facilitated Diffusion Glucose binds to transport protein Transporter changers conformation and
- 7. glucose is released into cell Intracellular glucose is immediately phosphorylated o phosphorylated glucose does not diffuse out (remember that the transport protein is very specific) o internal glucose (unphosphorylated) concentration remains low providing large concentration difference. Regulationof Glucose Uptake by Insulin Insulin stimulates increase in number of glucose transporters at membrane surface o Increase number of transporters increases diffusion rate o Driving force (phosphorylation) remains the same Low insulin levels decrease the number of glucose transporters at membrane surface o Portions of membrane with transporters endocytose, trapping the transport protein in a vesicle o Vesicle cannot refuse with membrane until insulin levels increase Diabetes Type I - Juvenile Diabetes - cannot make insulin o Autoimmune disease o Insulin-secreting pancreatic cells destroyed Type II - Adult Onset Diabetes - loss of ability to respond to insulin o Lack of membrane receptors for insulin o Therefore, cannot mobilize enough facilitative transport proteins to surface References: