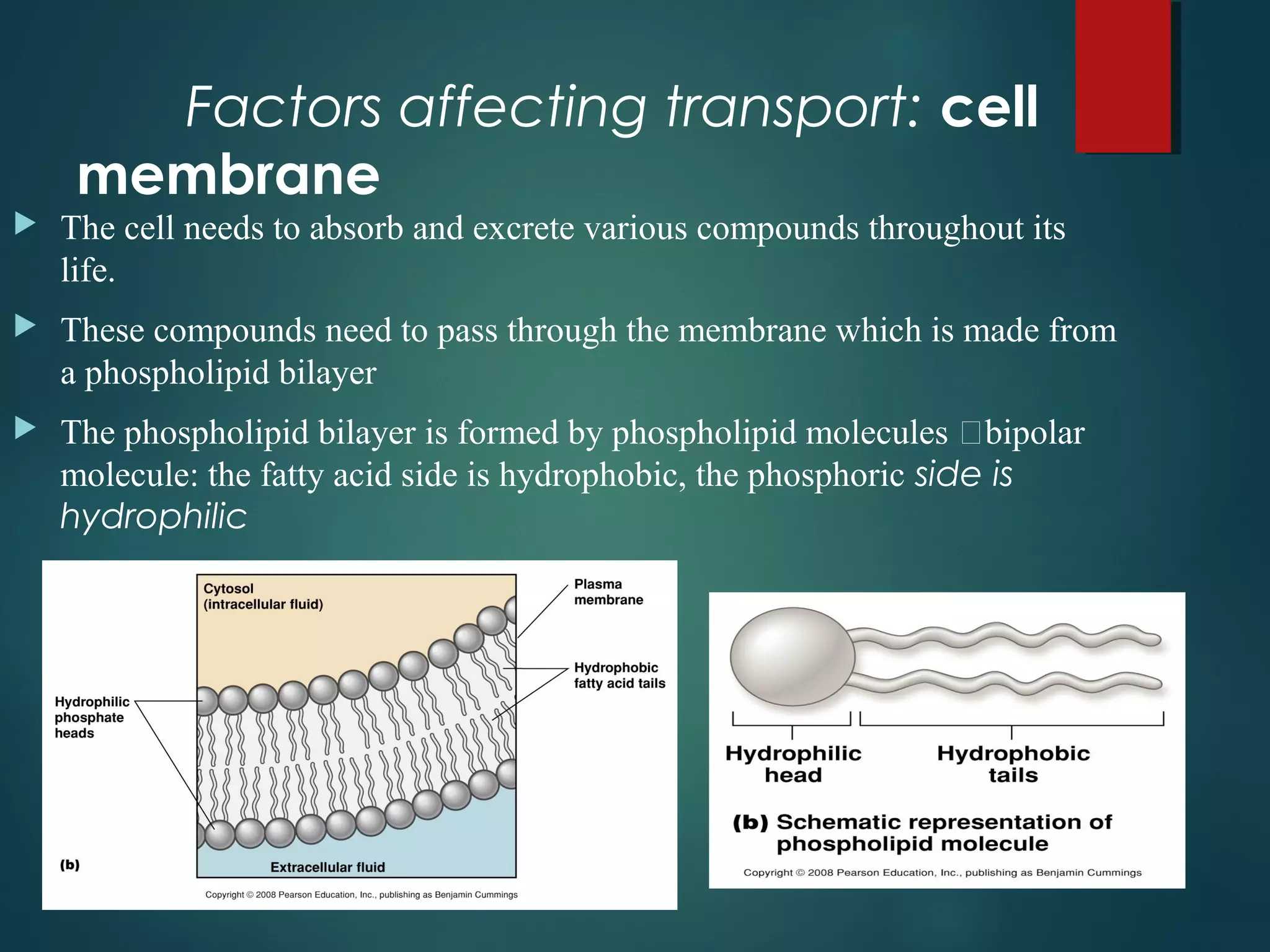
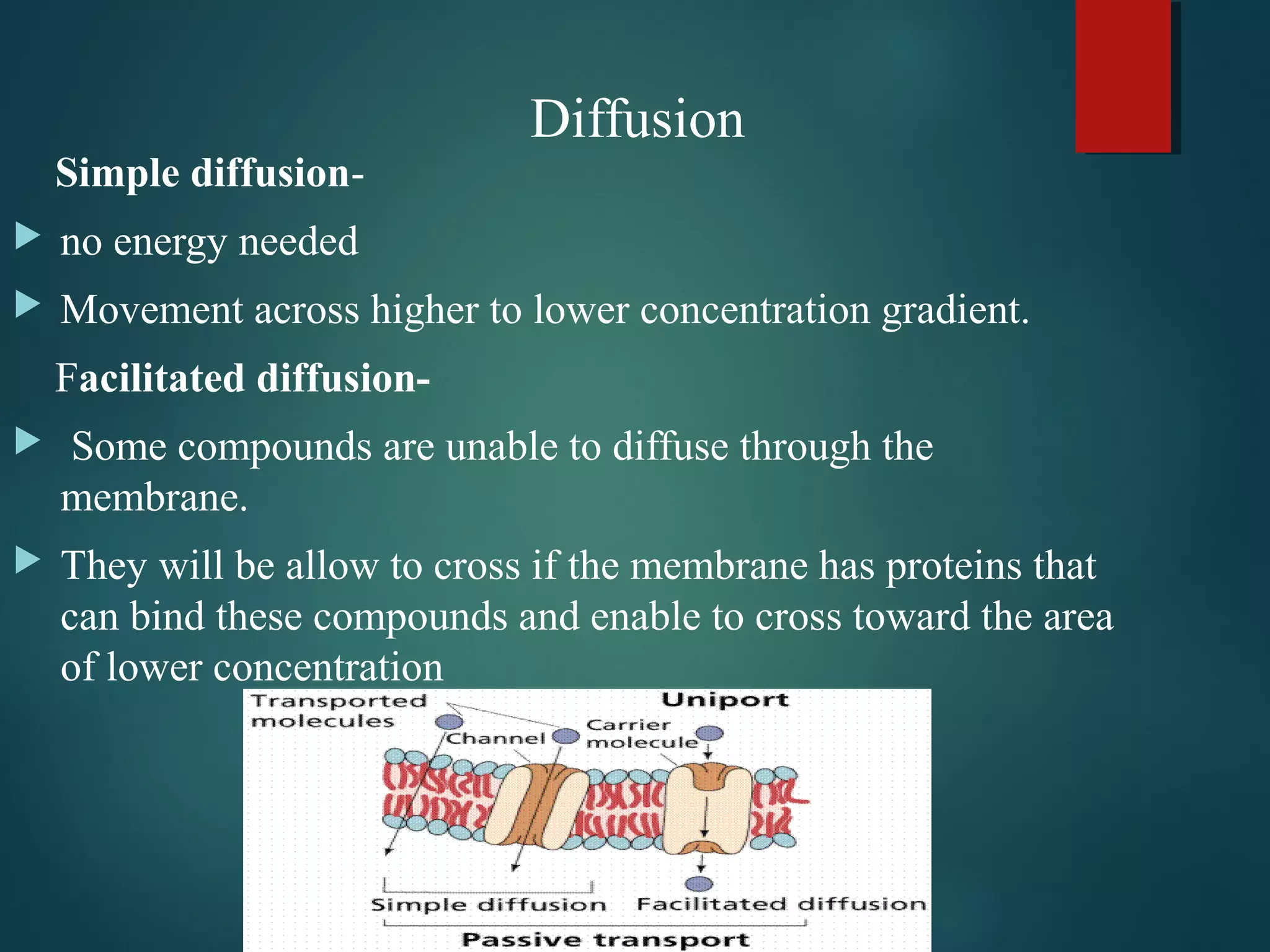
This document discusses various types of cell membrane transport. It describes passive transport mechanisms like diffusion and osmosis that move molecules from high to low concentration without ATP. Diffusion can occur through simple diffusion or facilitated diffusion using transport proteins. Osmosis is diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane. Active transport uses ATP and transports molecules against their concentration gradient using pumps, phagocytosis, or endocytosis and exocytosis. Various factors like concentration gradients and molecule properties affect the rate of transport. Membrane transport proteins include aquaporins, ion channels, and solute carriers.