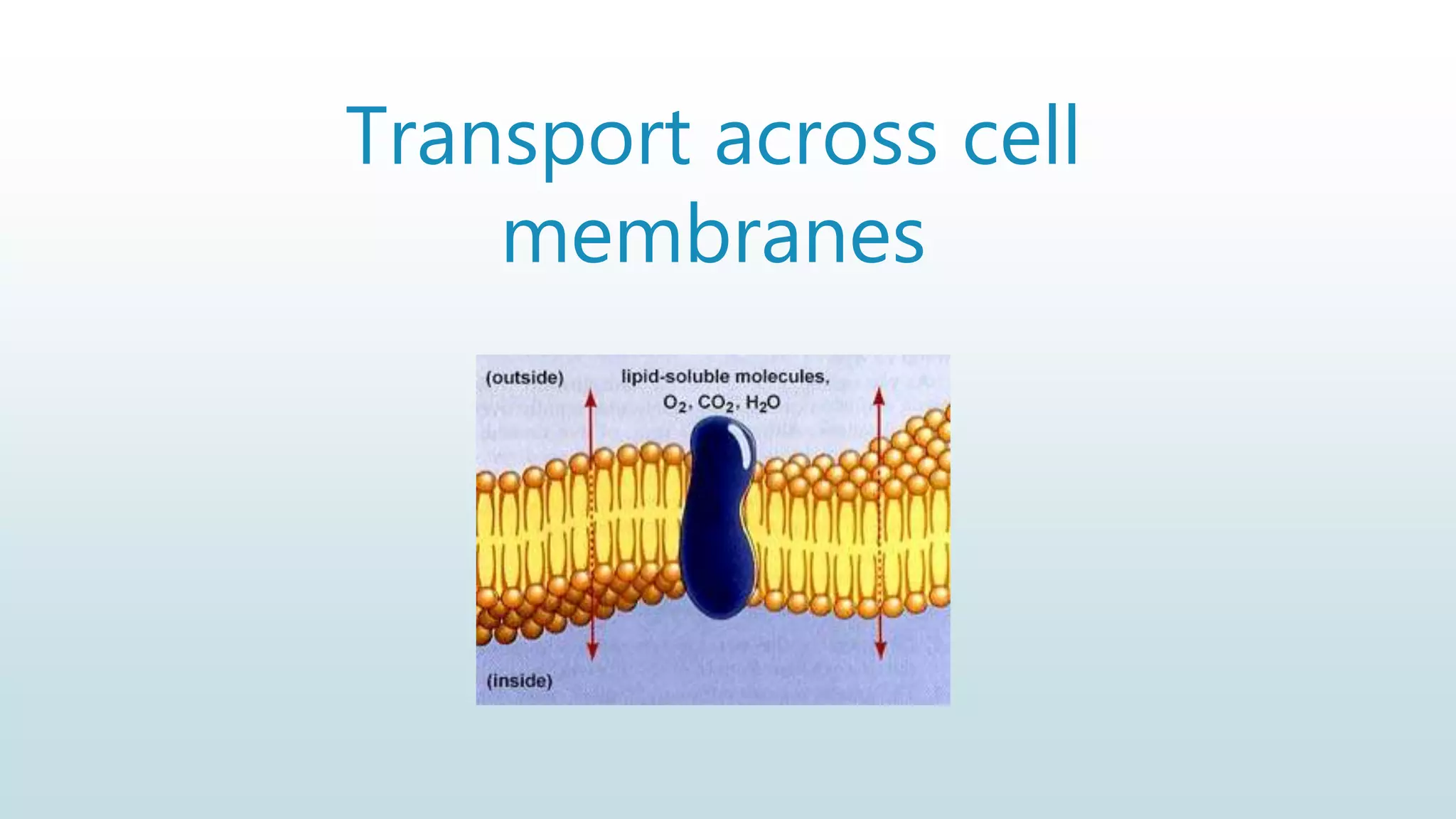
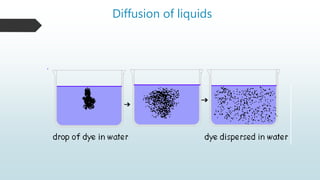
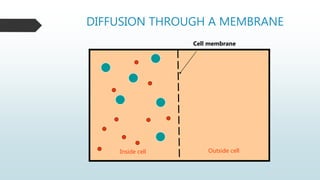
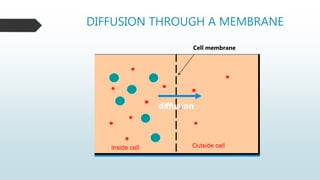
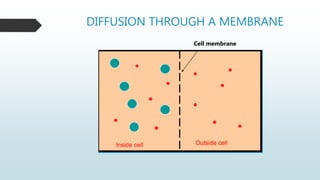
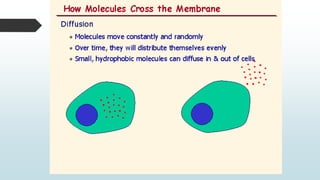
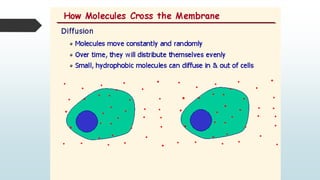
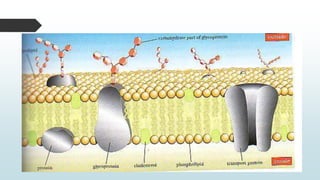
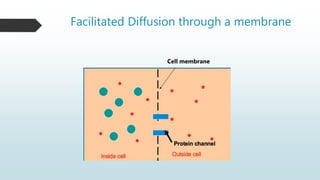
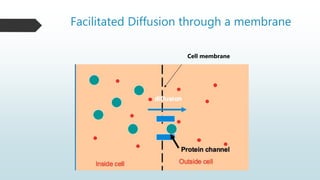
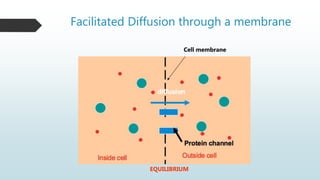
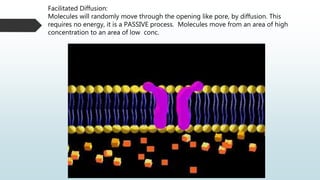
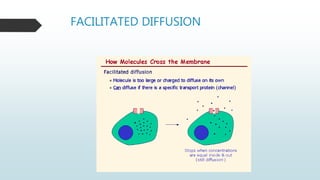
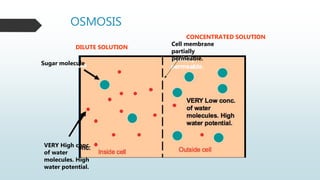
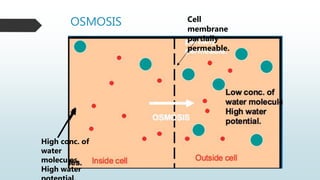
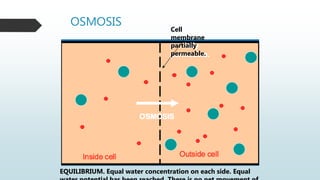
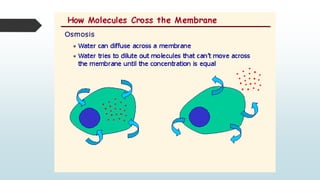
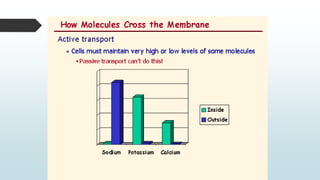
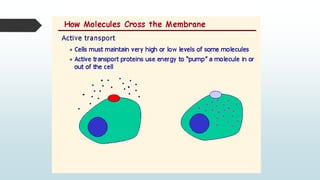
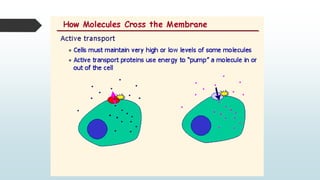
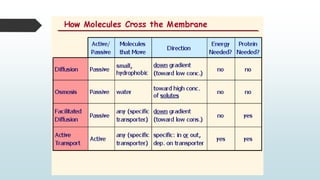
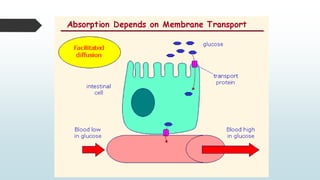
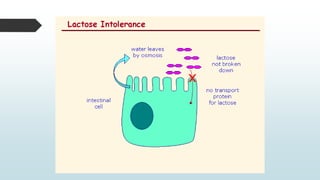
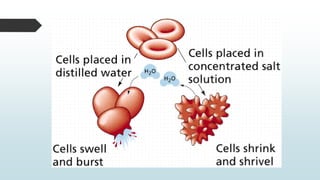
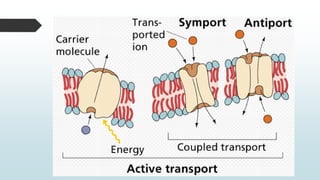
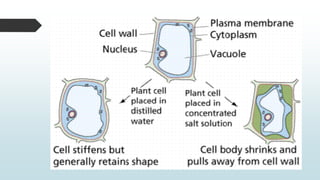
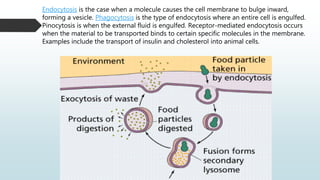
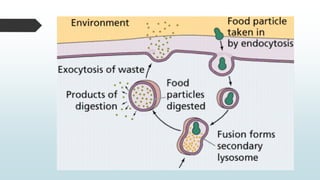
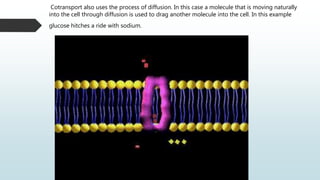
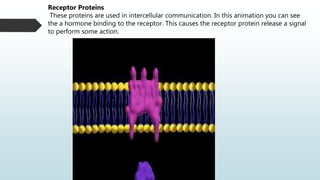
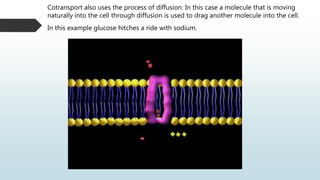
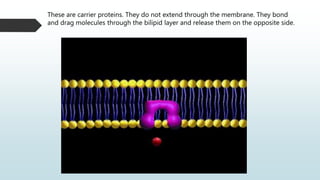
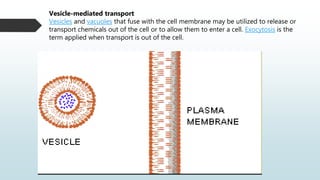
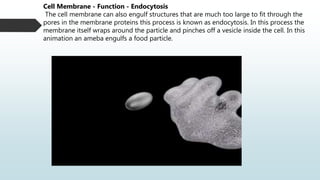
The document summarizes four basic mechanisms of transport across cell membranes: diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. Diffusion is the passive movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration down a gradient. Facilitated diffusion uses protein channels to transport molecules that cannot diffuse directly through the membrane such as glucose. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a partially permeable membrane to equalize water concentration. Active transport requires energy and transports molecules against a concentration gradient using carrier proteins.