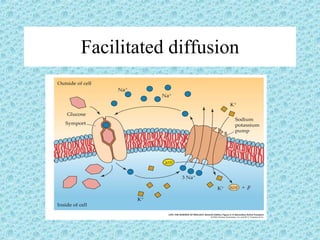
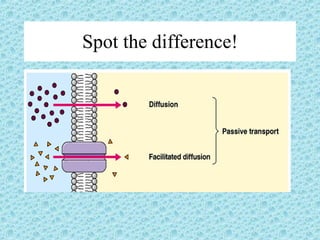
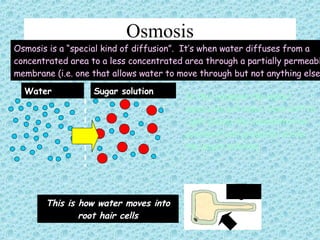
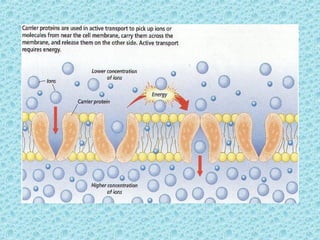
Facilitated diffusion is the passive transport of molecules across a cell membrane using carrier proteins. There are two main types of carrier proteins: carrier proteins that bind to specific molecules and undergo a conformational change to transport them across the membrane, and ion channels that have pores lined with charged groups to transport ions. Facilitated diffusion is saturated at high concentration differences because there are a limited number of carrier proteins.