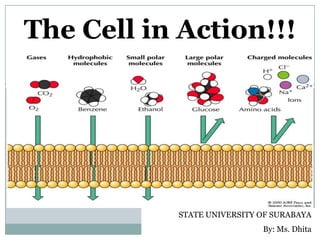
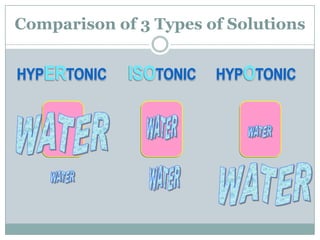
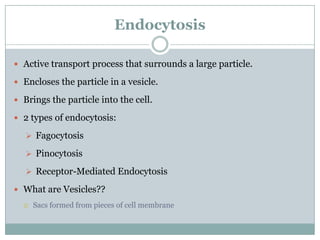
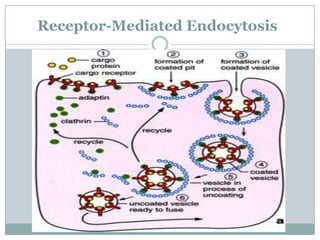
The document explains key cellular processes including diffusion, osmosis, and the mechanisms of passive and active transport. It describes how substances move across cell membranes, detailing the roles of semipermeable membranes, vesicles, and different types of solutions (hypertonic, isotonic, and hypotonic). Additionally, the document covers the processes of endocytosis and exocytosis for moving large particles into and out of cells.