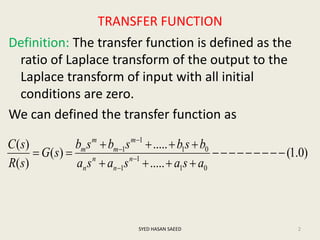
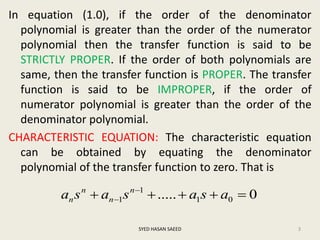
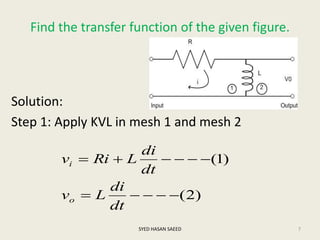
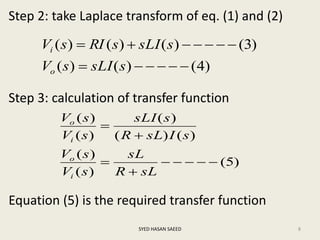
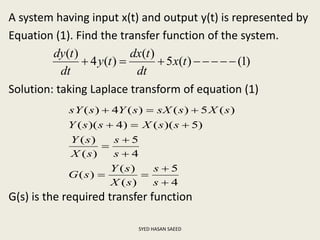
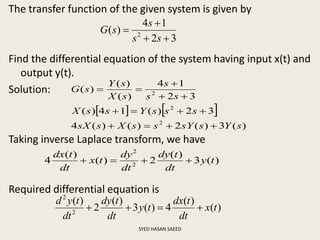
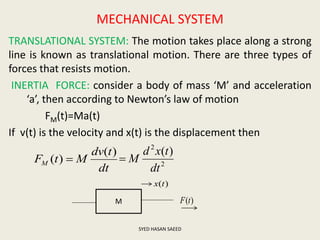
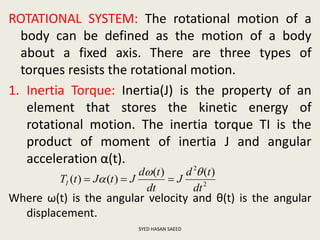
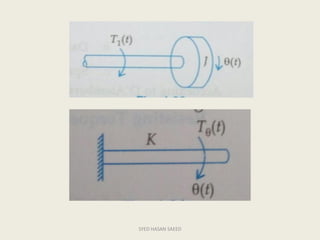
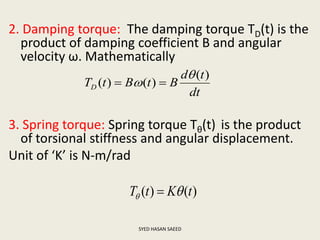
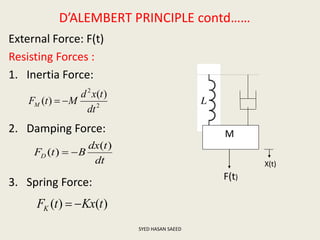
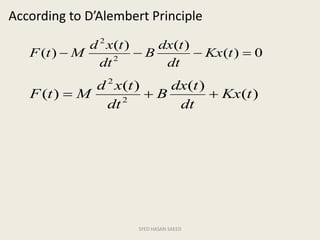
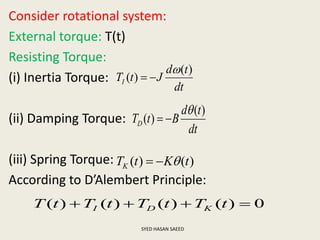
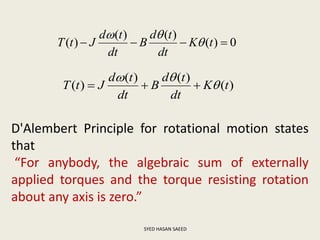
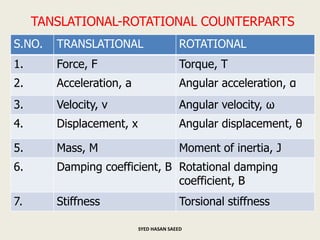
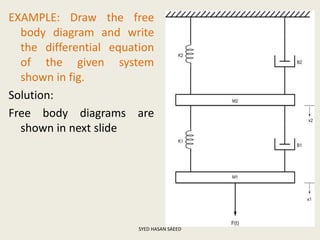
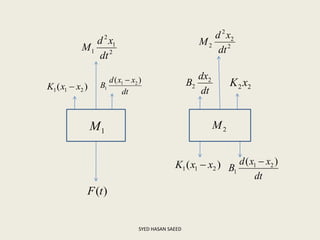
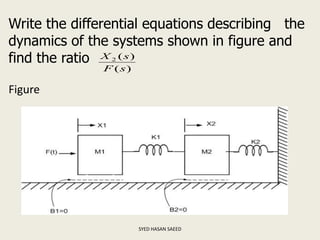
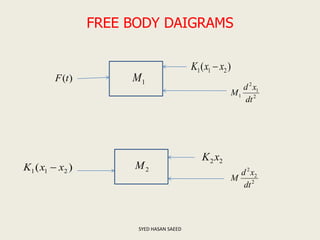
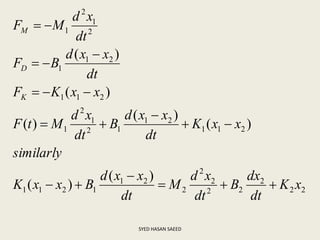The document defines transfer function as the ratio of the Laplace transform of the output to the input of a system with zero initial conditions. It discusses poles and zeros, which are values of s that make the transfer function tend to infinity or zero. Strictly proper, proper, and improper transfer functions are classified based on the order of the numerator and denominator polynomials. The characteristic equation is obtained by equating the denominator of the transfer function to zero. Advantages of transfer functions include representing systems with algebraic equations and determining poles, zeros and differential equations. Translational and rotational mechanical systems are described along with their resisting forces, and D'Alembert's principle is explained.