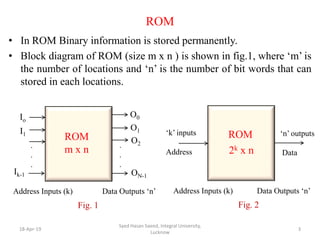
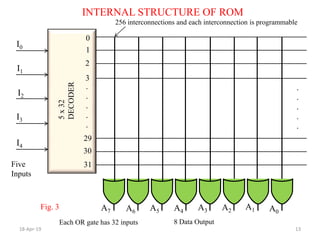
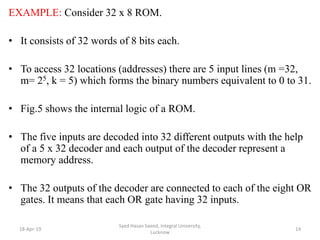
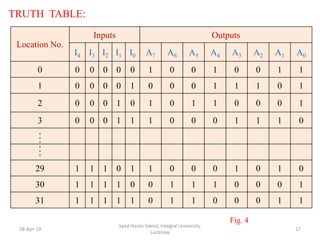
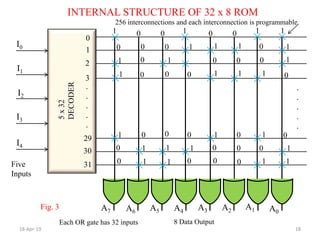
The document discusses Read Only Memory (ROM) and its characteristics. It defines ROM as memory that permanently stores binary information. ROM is programmed during manufacturing and does not allow writing. It is used to store fixed information like instructions or lookup tables. The document also provides examples to illustrate how to determine the number of address lines and input/output lines for different ROM configurations. It describes the internal structure of ROM including decoders and programmable connections to store binary data at each address.