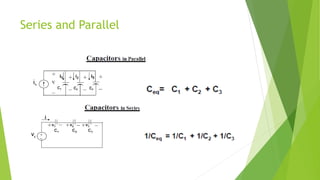
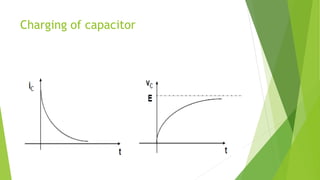
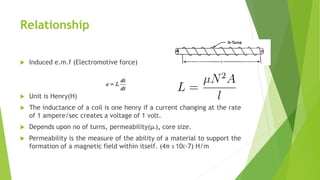
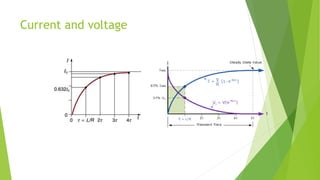
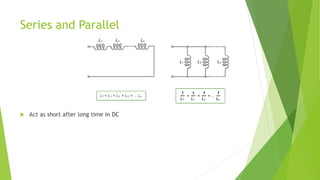
This document discusses capacitors and inductors. It provides information on their properties, behaviors, and applications. Capacitors store electric charge and act as open circuits to direct current. Inductors store energy in magnetic fields and oppose changes in current passing through them. Both are basic components in electrical and electronic circuits. They are used in applications like filters, tuned circuits for radio/TV, transformers, and switched-mode power supplies.