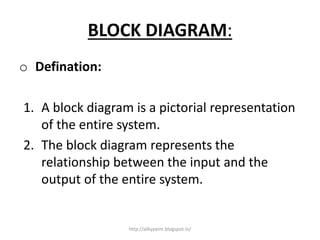
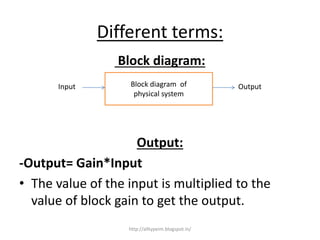
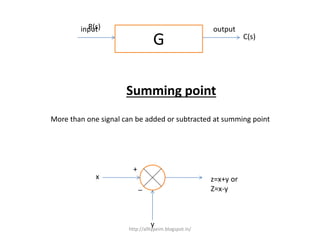
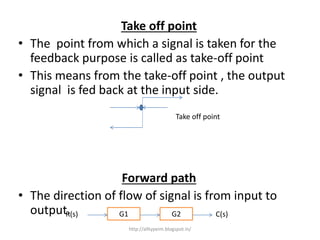
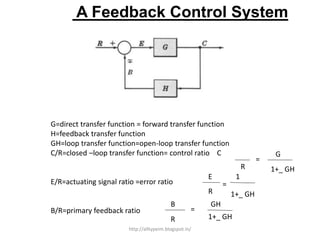
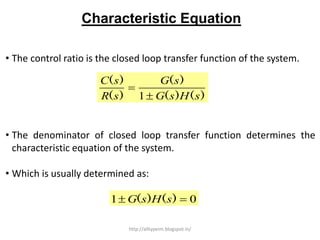
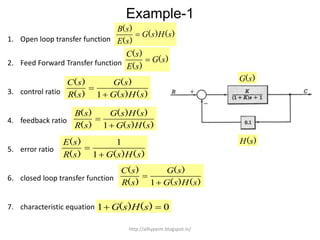
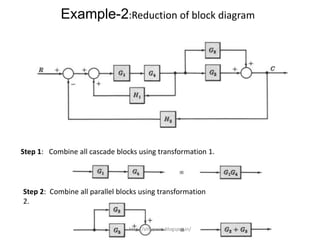
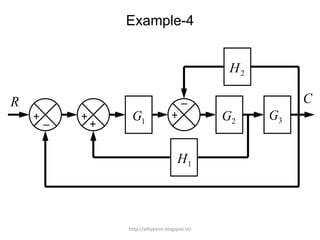
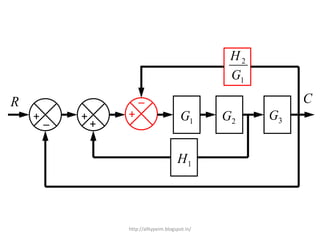
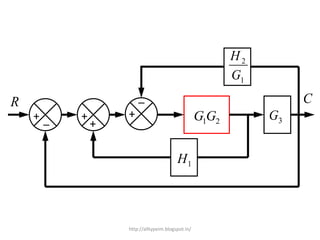
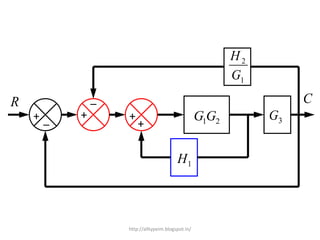
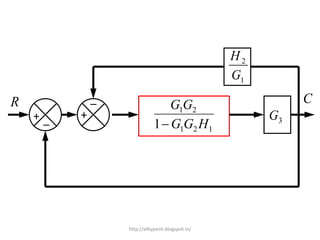
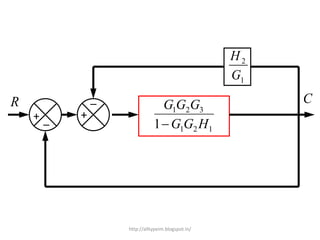
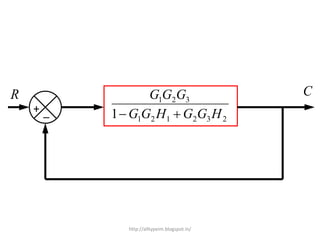
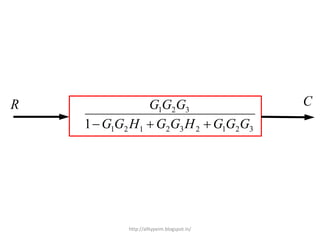
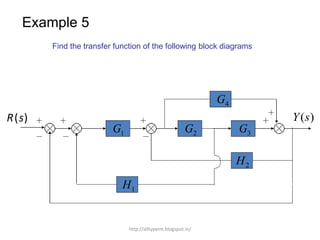
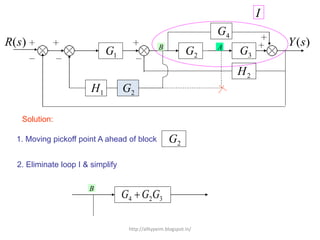
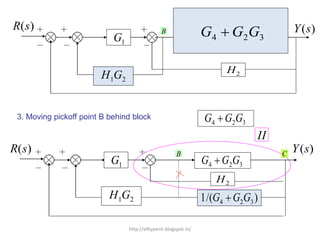
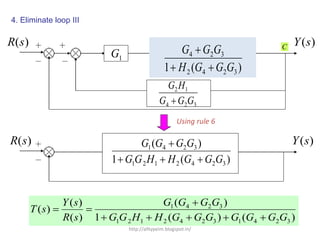
1. A block diagram is a pictorial representation of a system that shows the relationship between inputs and outputs of the entire system.
2. Block diagrams can represent physical systems and use symbols like summing points, gains, and transfer functions.
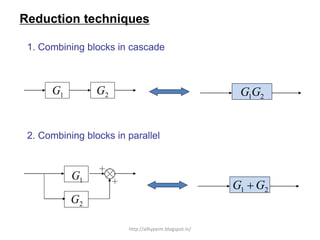
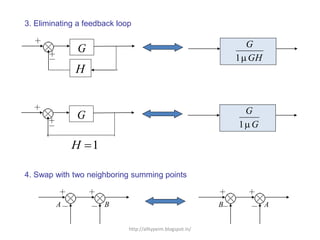
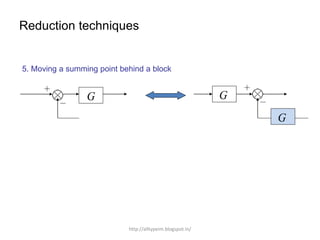
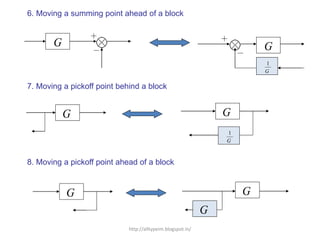
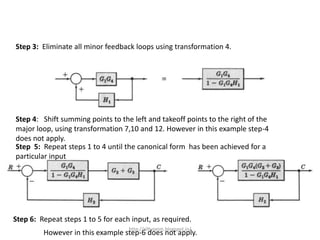
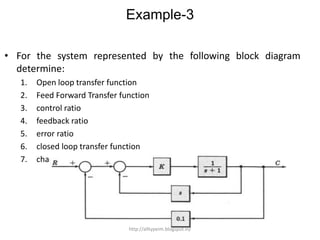
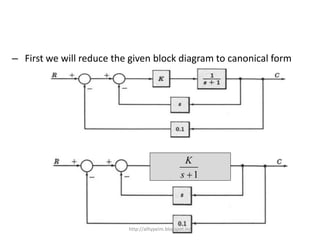
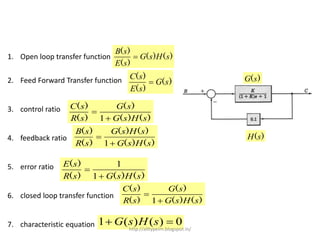
3. Reduction techniques can be used to simplify block diagrams, such as combining blocks in series or parallel or eliminating feedback loops.