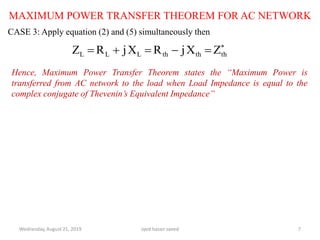
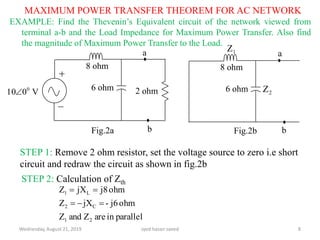
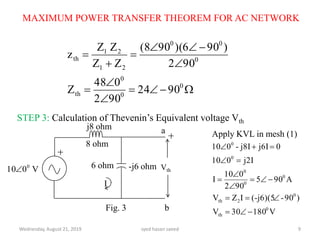
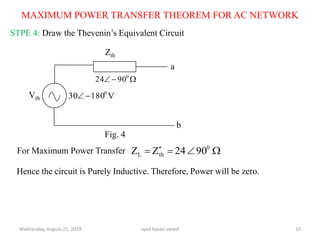
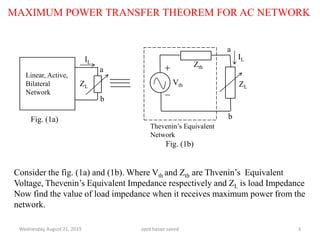
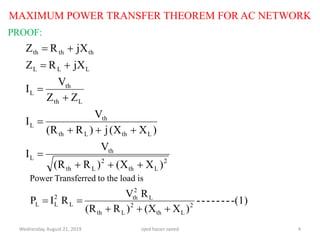
This document discusses the maximum power transfer theorem for AC networks. It defines the theorem as stating that maximum power is transferred from an AC network to a load when the load impedance is equal to the complex conjugate of the Thevenin's equivalent impedance of the network. It provides examples of calculating the Thevenin's equivalent circuit for a given network and determining the load impedance required for maximum power transfer. In the example network shown, the Thevenin's equivalent impedance is found to be purely inductive, meaning no power can be transferred to the load.

![MAXIMUM POWER TRANSFER THEOREM FOR AC NETWORK
For any network Vth, Rth and Xth are fixed.
CASE 1: When RL is constant and XL is varying:
Wednesday, August 21, 2019 syed hasan saeed 5
(2)-----------X-X
0X2(XRV-
0
)X(X)R(R
X2(XRV-[0])X(X)R(R
dX
dP
0
)X(X)R(R
RV
dX
d
dX
dP
thL
ththL
2
th
22
Lth
2
Lth
LthL
2
th
2
Lth
2
Lth
L
L
2
Lth
2
Lth
L
2
th
LL
L
Hence, the magnitude of load reactance must be equal Thevenin’s reactance but
opposite phase difference. This is the first condition. The equation (1) becomes
)3(
)R(R
RV
P 2
Lth
L
2
th
L
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maximumpowertransfertheoremforacnetwork-190821161218/85/Maximum-power-transfer-theorem-for-ac-network-5-320.jpg)
![MAXIMUM POWER TRANSFER THEOREM FOR AC NETWORK
CASE 2: When XL is constant and RL is varying
Wednesday, August 21, 2019 syed hasan saeed 6
(4)-------R)X(XR
0)R2(RRV-][V)X(X)R(R
0
)X(X)R(R
)R2(RRV-][V)X(X)R(R
dX
dP
0
)X(X)R(R
RV
dR
d
dR
dP
L
2
Lth
2
th
LthL
2
th
2
th
2
Lth
2
Lth
22
Lth
2
Lth
LthL
2
th
2
th
2
Lth
2
Lth
L
L
2
Lth
2
Lth
L
2
th
LL
L
Put Xth = -XL in equation (4)
RL = Rth - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - (5)
Hence, for maximum Power Transfer, the load resistance must be equal to the
Thevenin’s Equivalent Resistance. The equation (3) becomes
)6(
4R
V
P
th
2
th
maxL ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maximumpowertransfertheoremforacnetwork-190821161218/85/Maximum-power-transfer-theorem-for-ac-network-6-320.jpg)