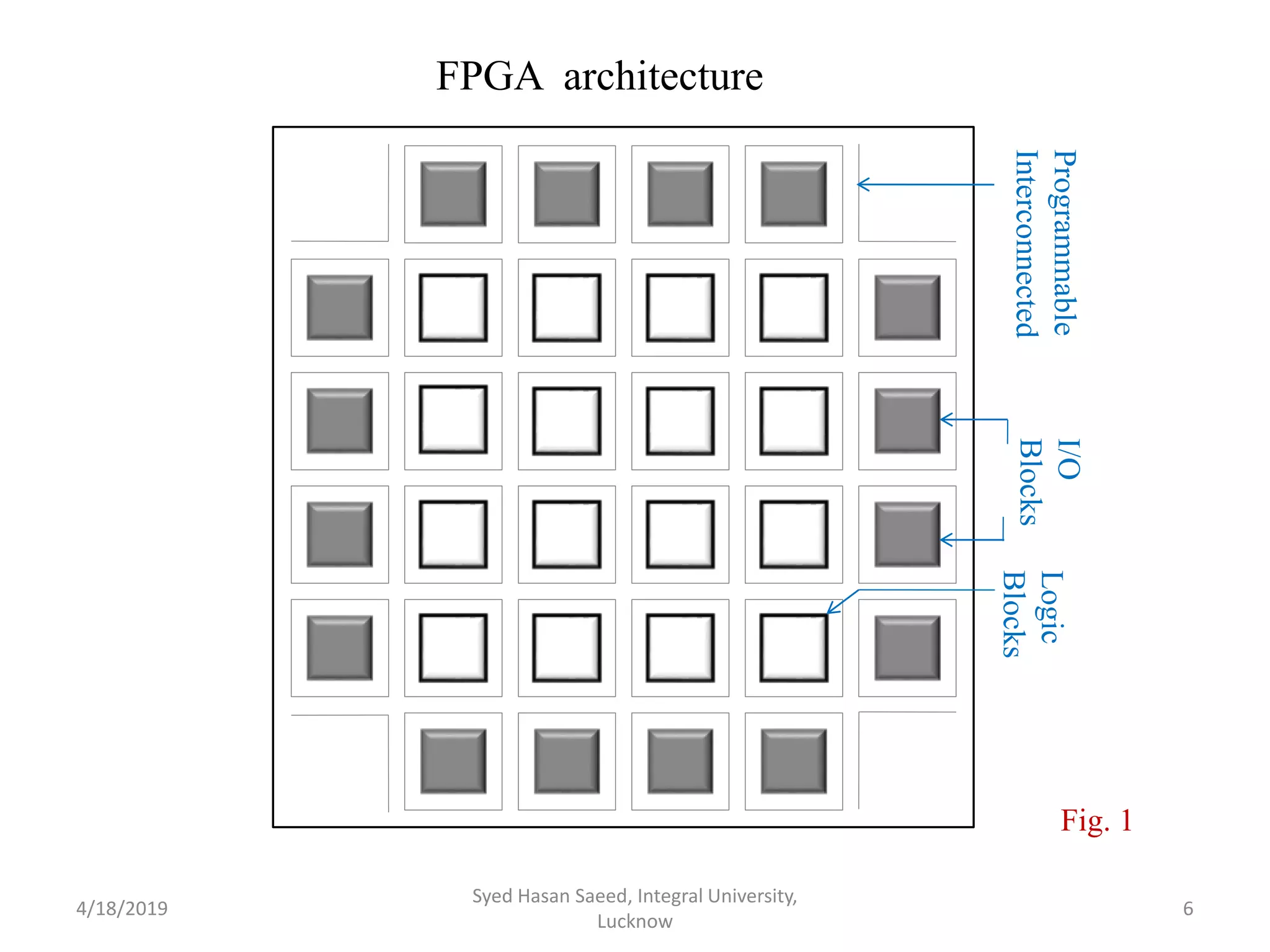
Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are programmable logic devices that enable configurations outside of the manufacturing process and consist of interconnected logic blocks and input/output pins. They are versatile and deployed in various applications such as digital signal processing, video processing, and telecommunications, but have drawbacks like complexity and higher costs. FPGAs require programming via hardware description languages and are validated through extensive testing and simulation processes.