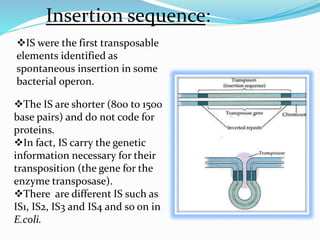
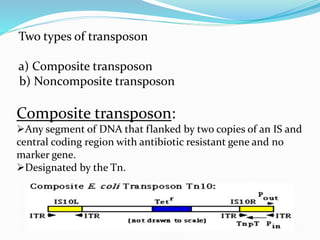
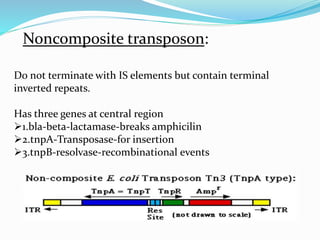
Transposable elements, first discovered by Barbara McClintock in corn, are DNA segments that can move within the genome and occupy approximately 45% of the human genome and a larger fraction in some plants. There are three main types of transposable elements found in prokaryotes: insertion sequences, transposons, and bacteriophage mu, each with unique characteristics. These elements play a crucial role in genetic variation and can influence gene expression and evolutionary processes.