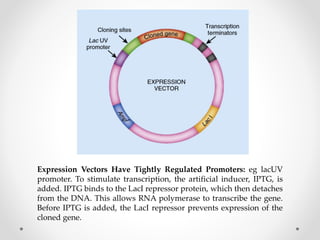
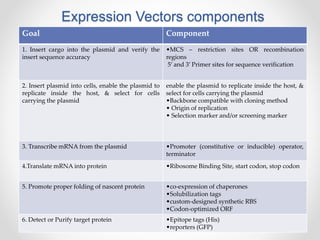
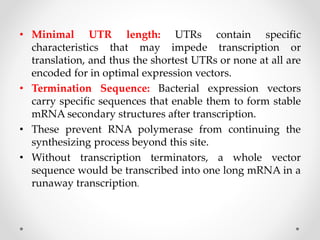
This document discusses key components of expression vectors that are important for efficiently expressing cloned genes. It explains that expression vectors contain regulatory sequences like promoters and terminators to control transcription, as well as elements like ribosome binding sites, fusion tags, and selection markers. Specifically, it provides details on tightly regulated promoters, commonly used viral and bacterial promoters, and considerations for promoters in prokaryotic and eukaryotic expression systems. The document also reviews other important vector elements and their functions.