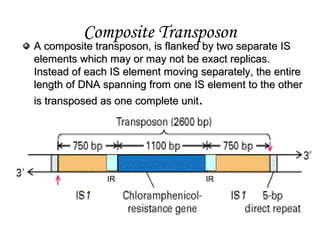
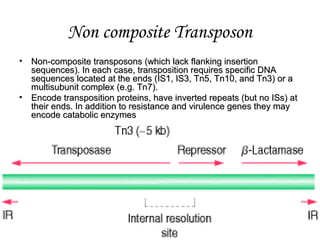
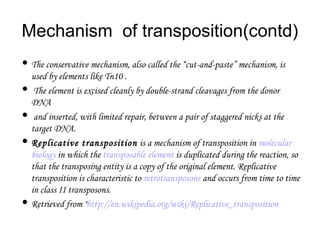
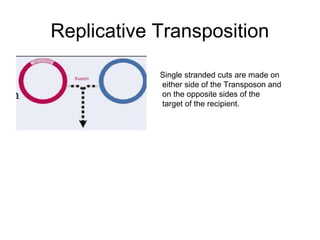
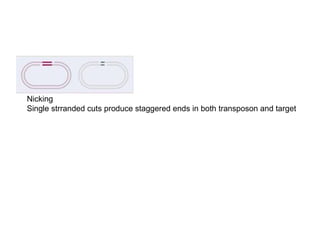
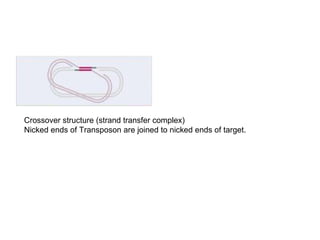
This document provides information about bacterial transposons. It defines key terms like transposons, transposase, and IS elements. It describes the two types of bacterial transposons: composite mobile genetic elements and non-composite mobile genetic elements. Composite transposons are flanked by IS elements, while non-composite transposons lack flanking IS sequences but have inverted repeats. The mechanisms of transposition, including replicative and non-replicative, are explained. General transposon structure and mechanisms of movement are illustrated.


![Bacterial Transposons
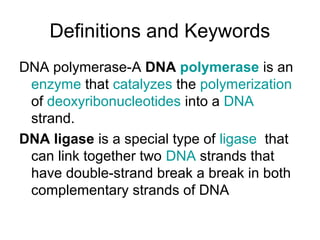
•
Bacteria contain two types of transposons
•
1]Composite mobile genetic elements that are larger than IS
elements and contain one or more protein-coding genes in addition
to those required for transposition.
•
2]Non composite mobile genetic elements are those which lack IS
elements on its ends e.g. is Tn3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e2242b65-3fa5-4c89-80c0-96ccf61fa431-161006215307/85/SBT01P0101Bacterial-Transposons-1-4-320.jpg)

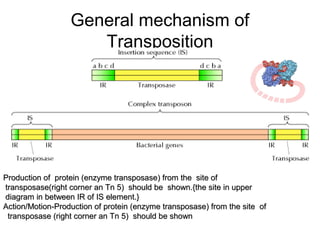








![INSTRUCTIONS SLIDE
Questionnaire to test the user
• Q1]Define tranposition?
• Transposons are sequences of DNA that can move around to different positions
within the genome of a single cell, a process called transposition.
• Q2]Give examples of non composite transposons.
• IS1, IS3, Tn5, Tn10, and Tn3) or a multisubunit complex (e.g. Tn7)
• Q3]Describe the general structure of bacterial transposons.
• Ans
1
5
2
4
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e2242b65-3fa5-4c89-80c0-96ccf61fa431-161006215307/85/SBT01P0101Bacterial-Transposons-1-22-320.jpg)

![• Q4]Explain the mobile genetic elements found in bacteria.
ANS:-
Three of the many types of mobile genetic elements found in bacteria. Each of these
DNA elements contains a gene that encodes a transposase, an enzyme that conducts at
least some of the DNA breakage and joining reactions needed for the element to move.
Each mobile element also carries short DNA sequences (indicated in red) that are
recognized only by the transposase encoded by that element and are necessary for
movement of the element. In addition, two of the three mobile elements shown carry genes
that encode enzymes that inactivate the antibiotics ampicillin (ampR) and tetracycline
(tetR). The transposable element Tn10, shown in the bottom diagram, is thought to have
evolved from the chance landing of two short mobile elements on either side of a
tetracyclin-resistance gene; the wide use of tetracycline as an antibiotic has aided the
spread of this gene through bacterial populations. The three mobile elements shown are
all examples of DNA-only transposons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e2242b65-3fa5-4c89-80c0-96ccf61fa431-161006215307/85/SBT01P0101Bacterial-Transposons-1-24-320.jpg)
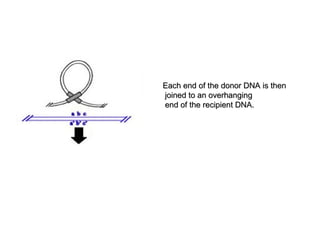
![• Q5]Illustrate the mechanism of
transposition in transposons.
• ANS:-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e2242b65-3fa5-4c89-80c0-96ccf61fa431-161006215307/85/SBT01P0101Bacterial-Transposons-1-25-320.jpg)

