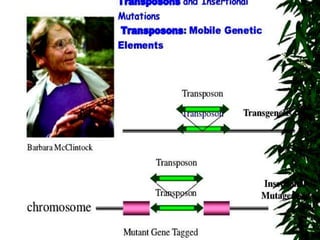
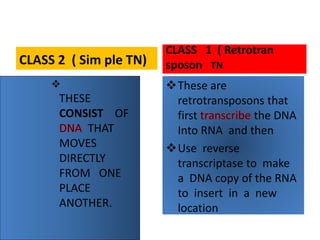
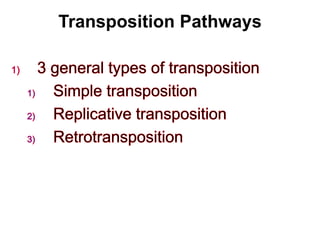
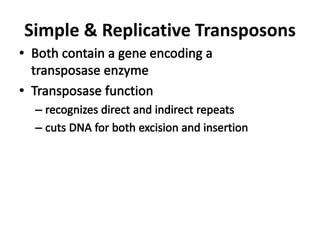
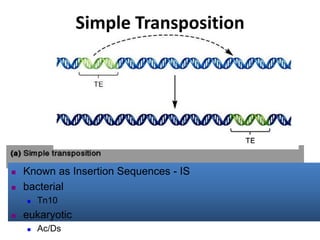
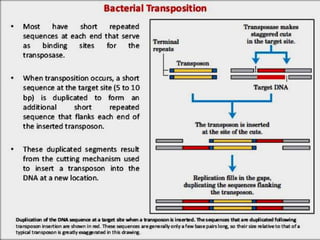
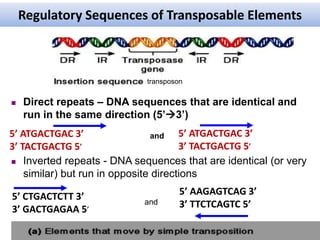
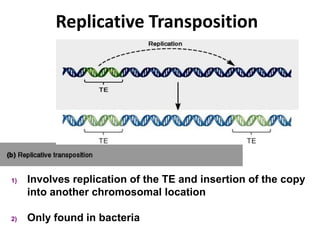
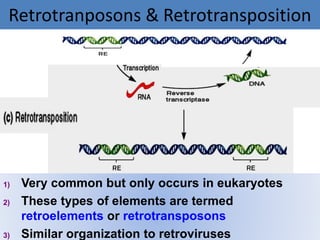
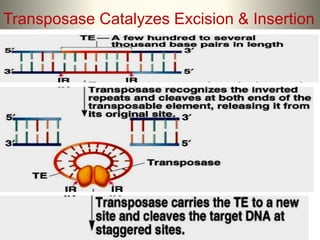
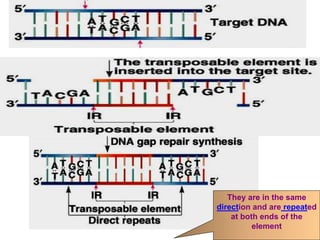
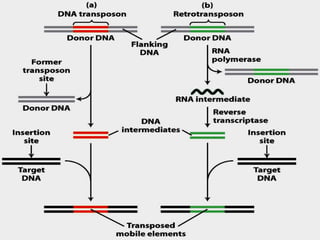
This document summarizes information about transposons. It discusses that Barbara McClintock discovered transposons in maize in 1948 and was awarded a Nobel Prize for this discovery in 1983. It describes transposons as sequences of DNA that can move to different locations within a genome. The document outlines different types of transposons, including Class 1 and Class 2, and their mechanisms of transposition. It also discusses transposons' involvement in disease.