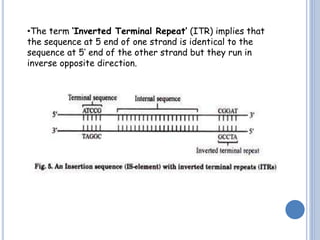
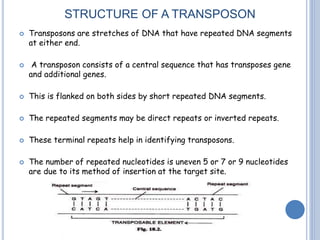
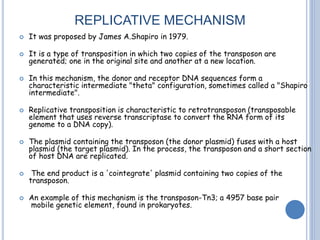
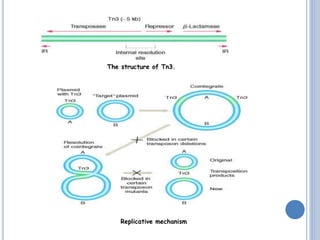
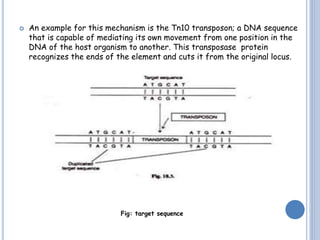
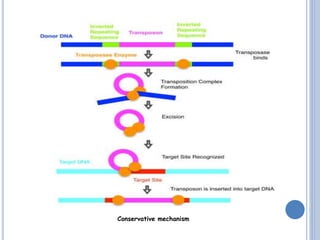
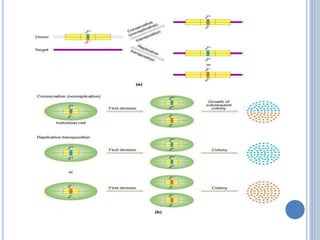
Transposable elements are DNA sequences that can change their position within a genome. They are common in bacteria and include insertion sequences (IS elements) and larger transposons. IS elements are short sequences that can insert into bacterial chromosomes, while transposons are composed of IS elements flanking additional genes. Transposition occurs via either replicative or conservative mechanisms, with replicative resulting in duplication of the transposable element. Transposition can cause mutations but also increases genome flexibility and is useful for genetic engineering applications like insertional mutagenesis.