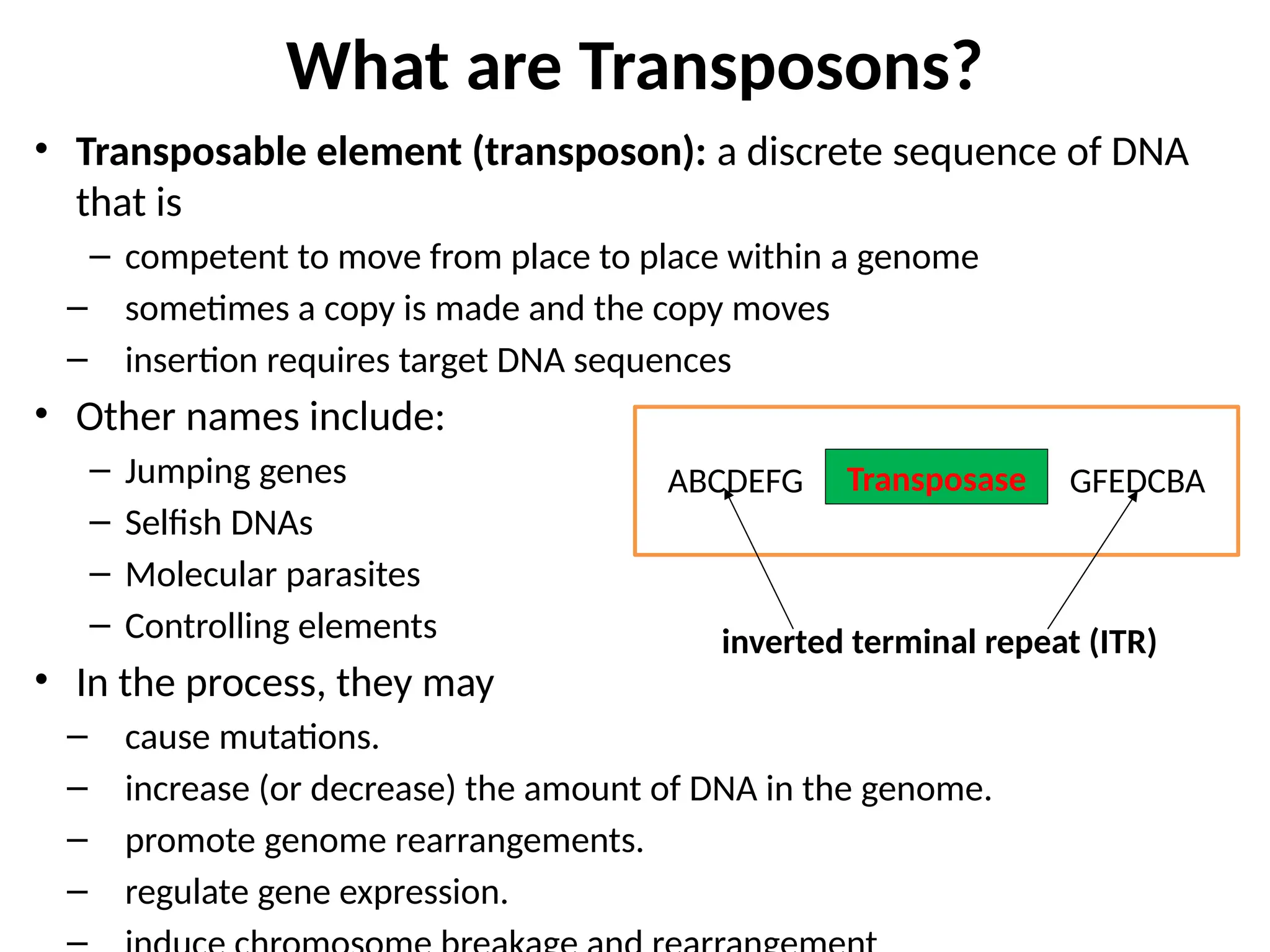
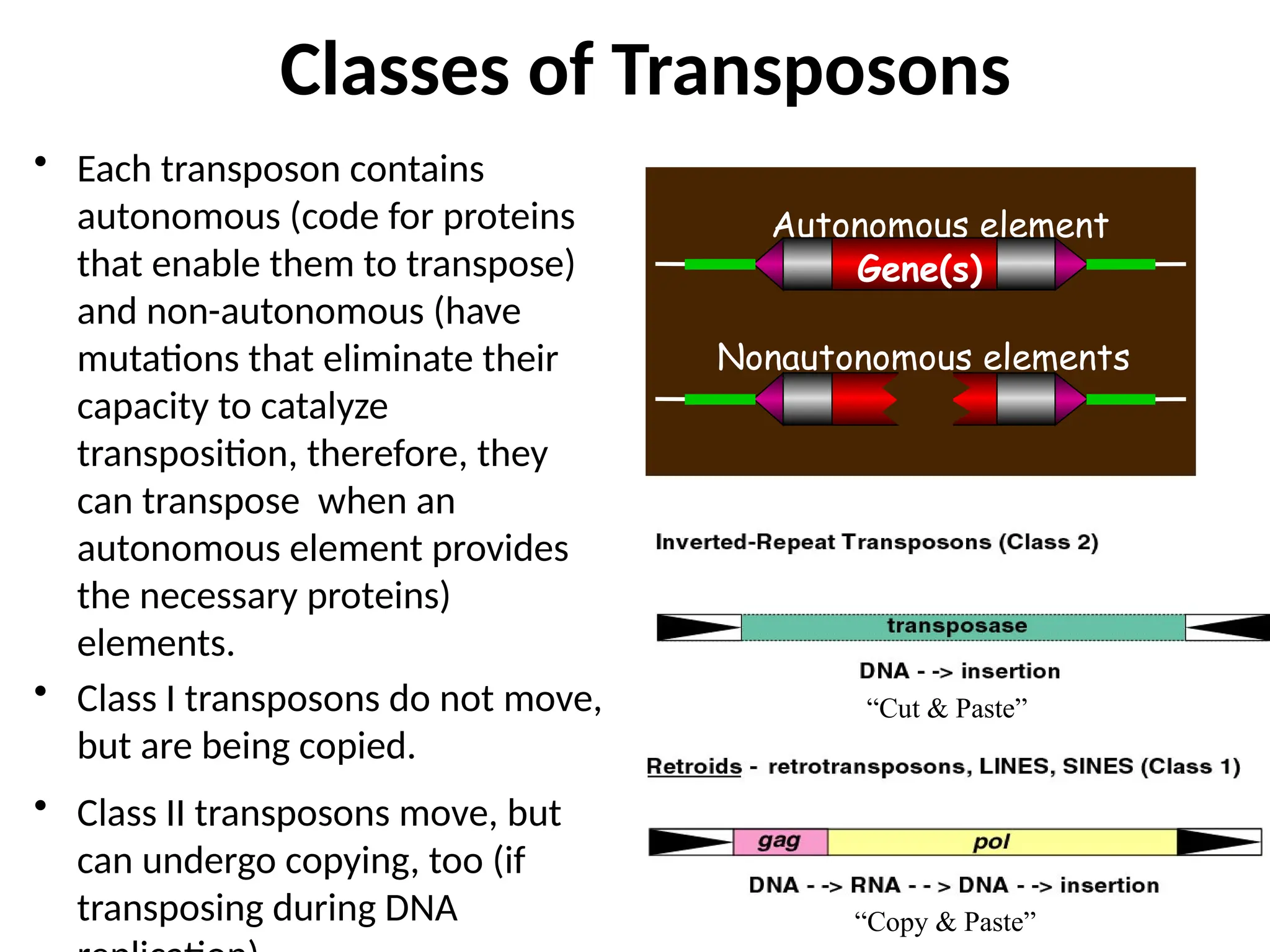
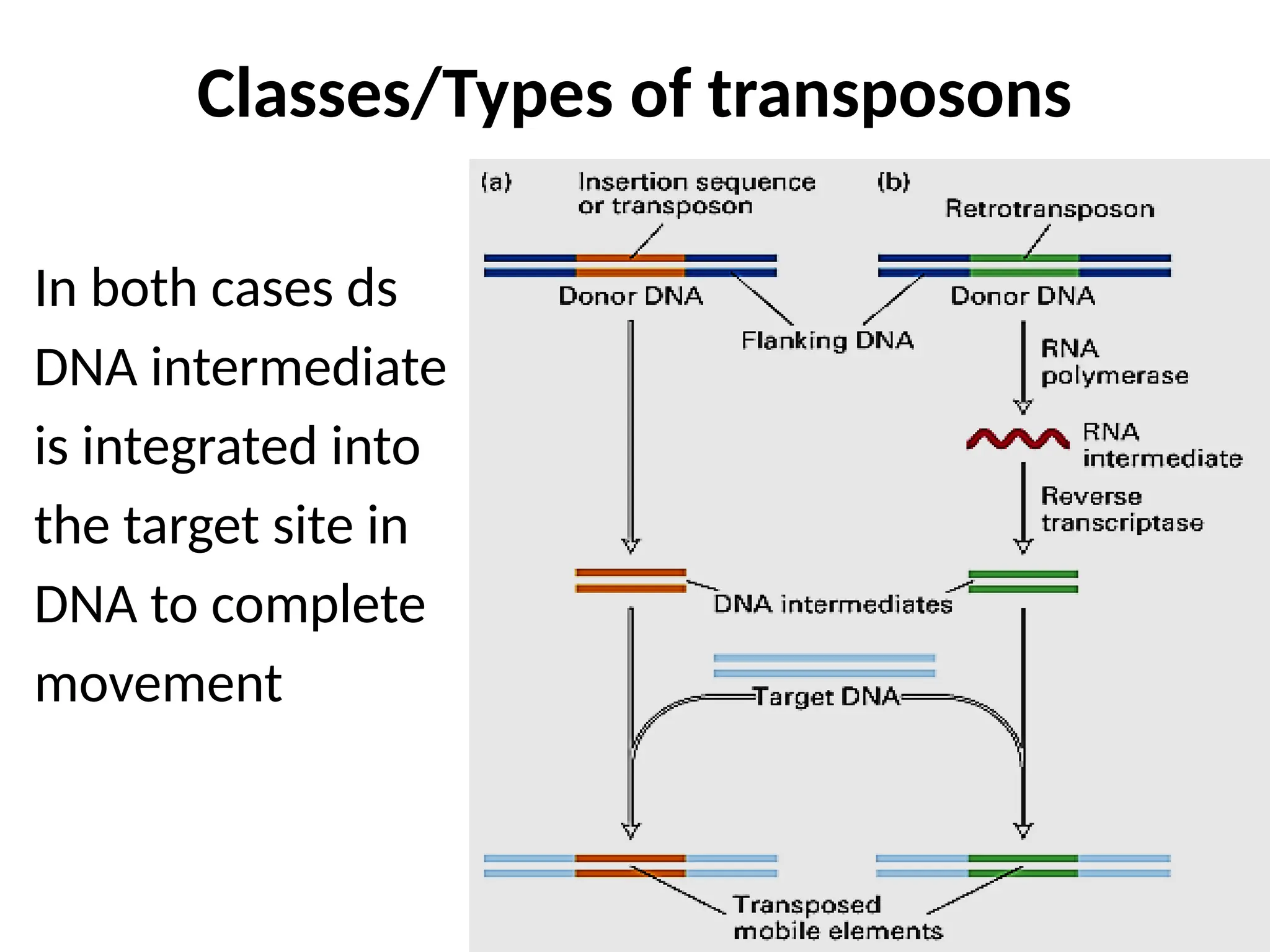
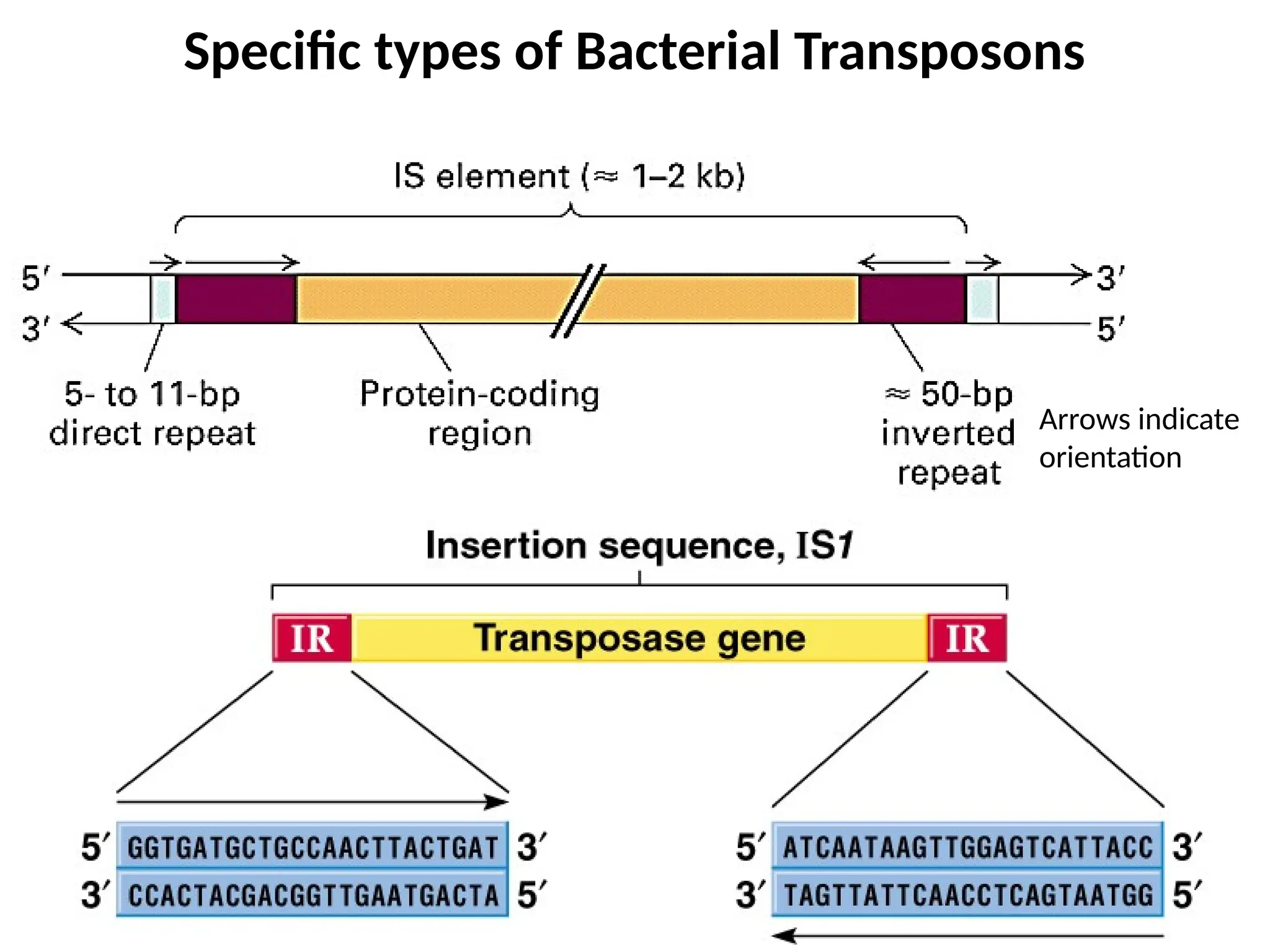
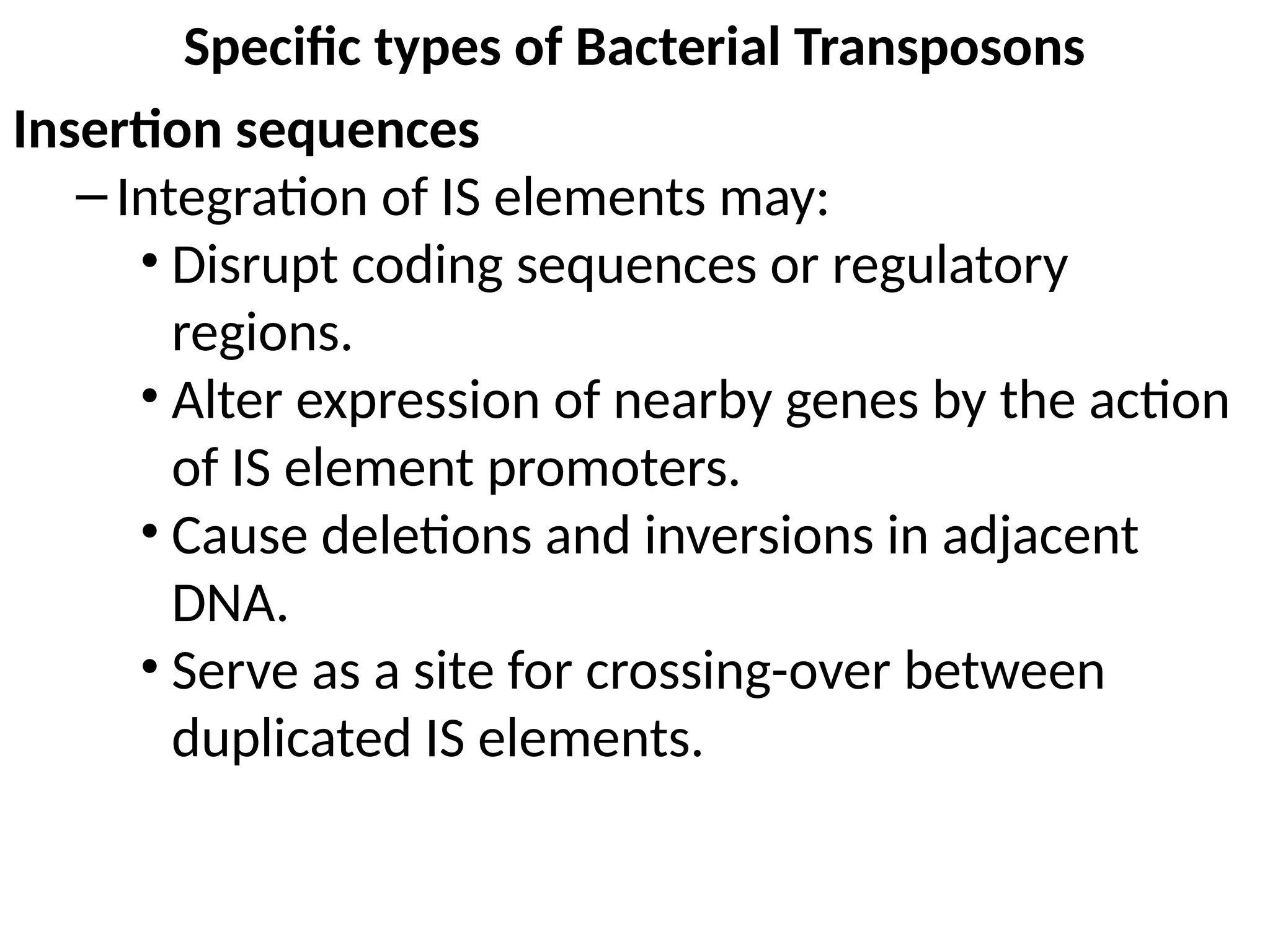
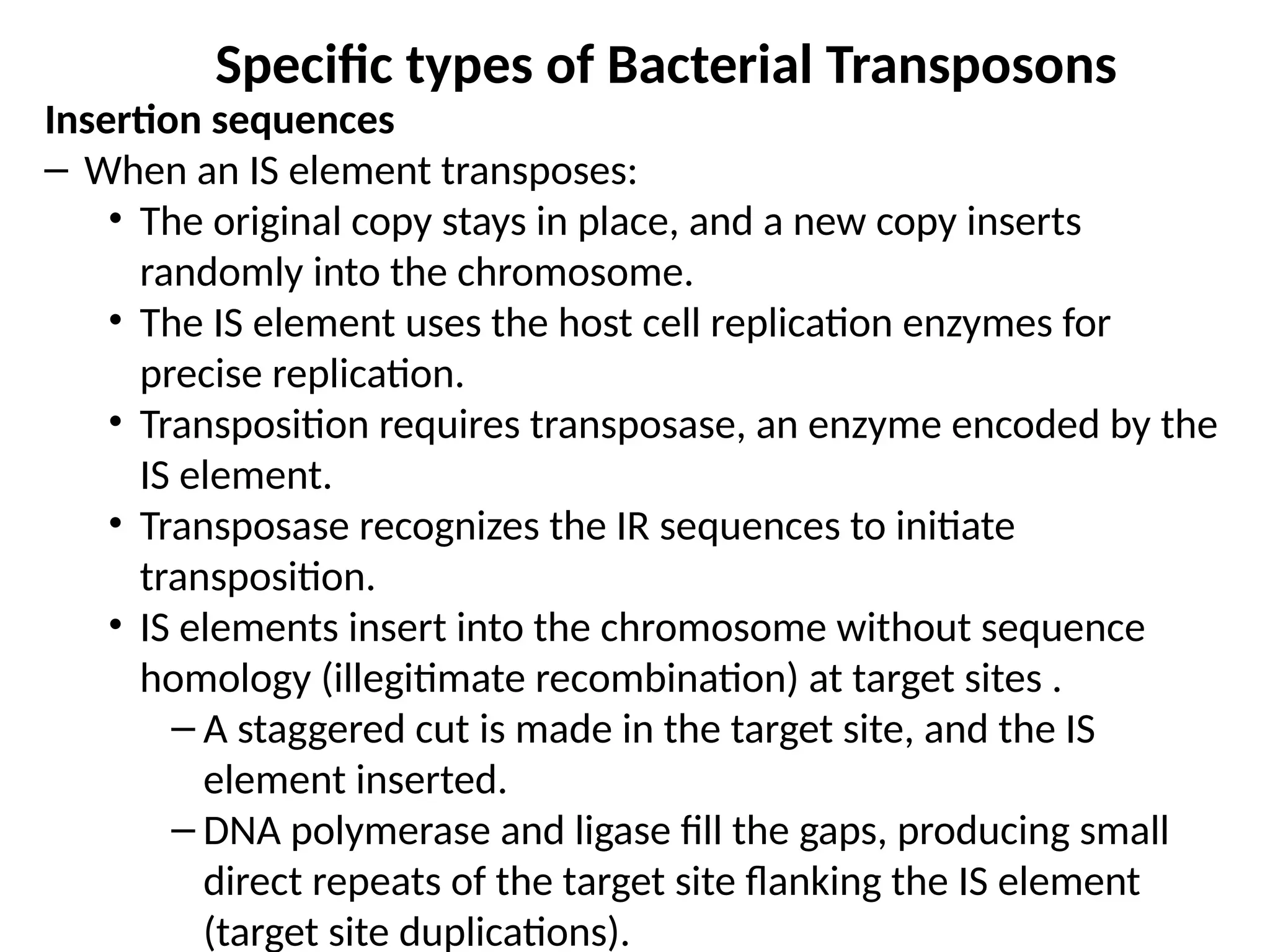
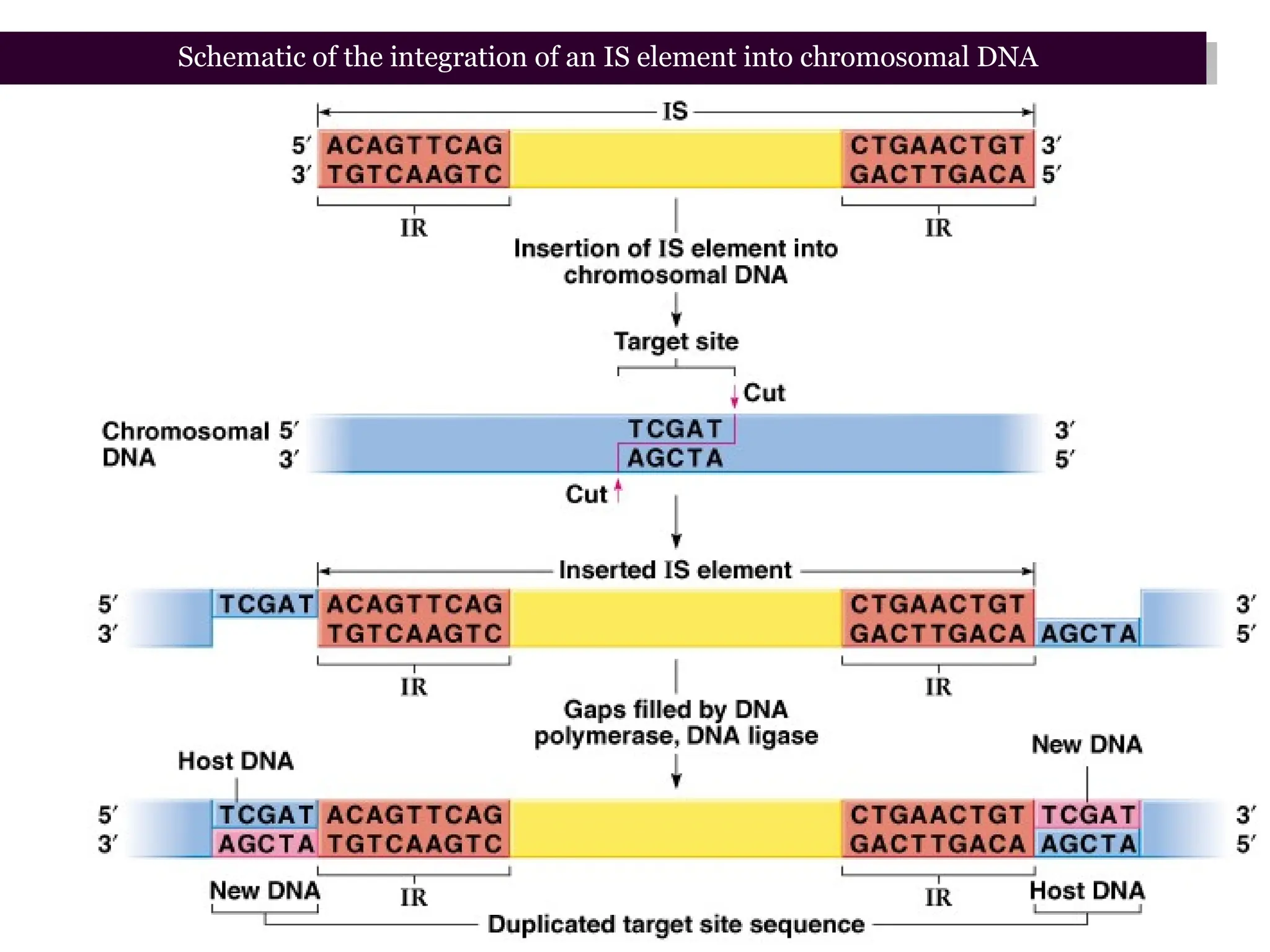
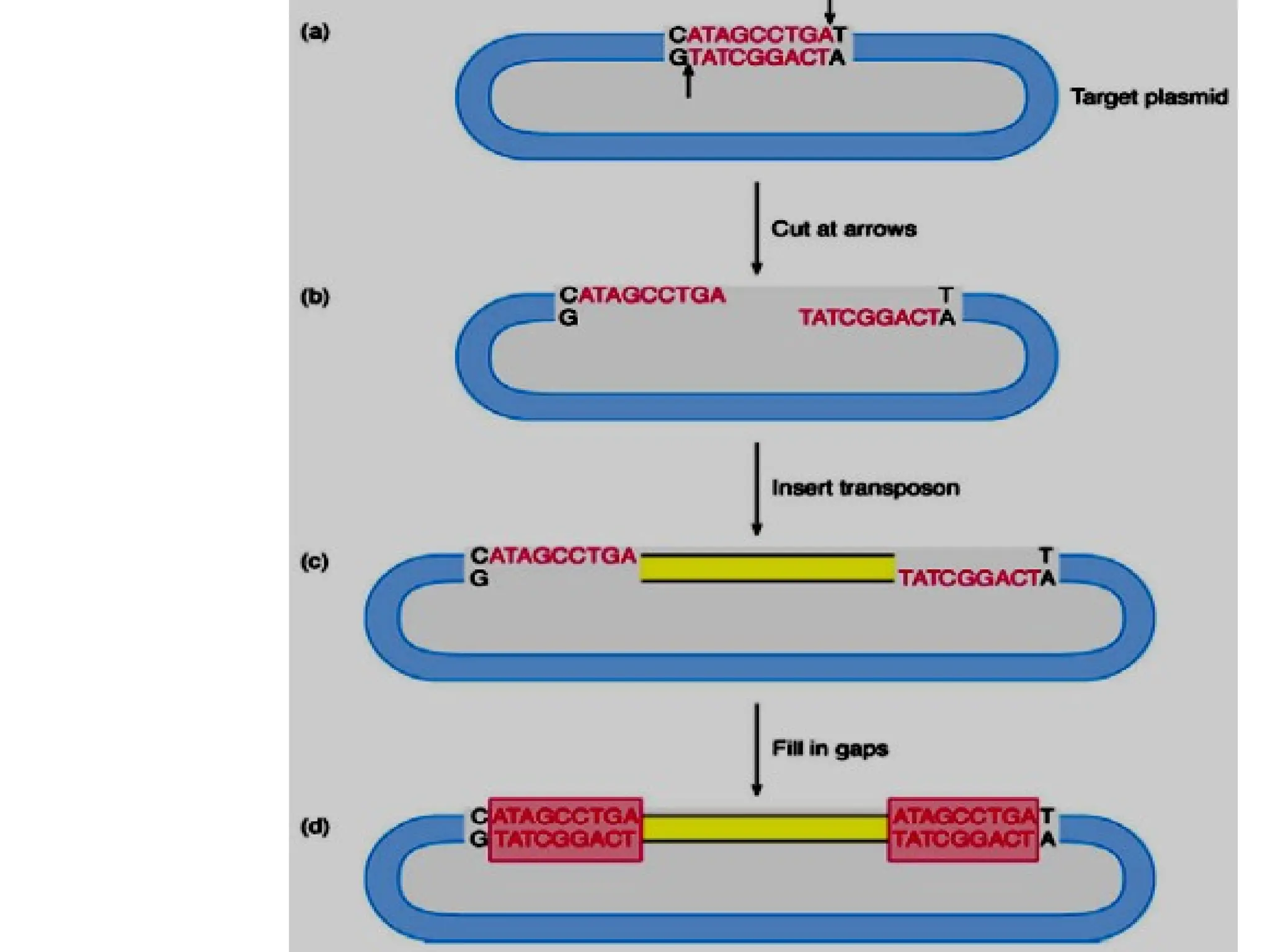
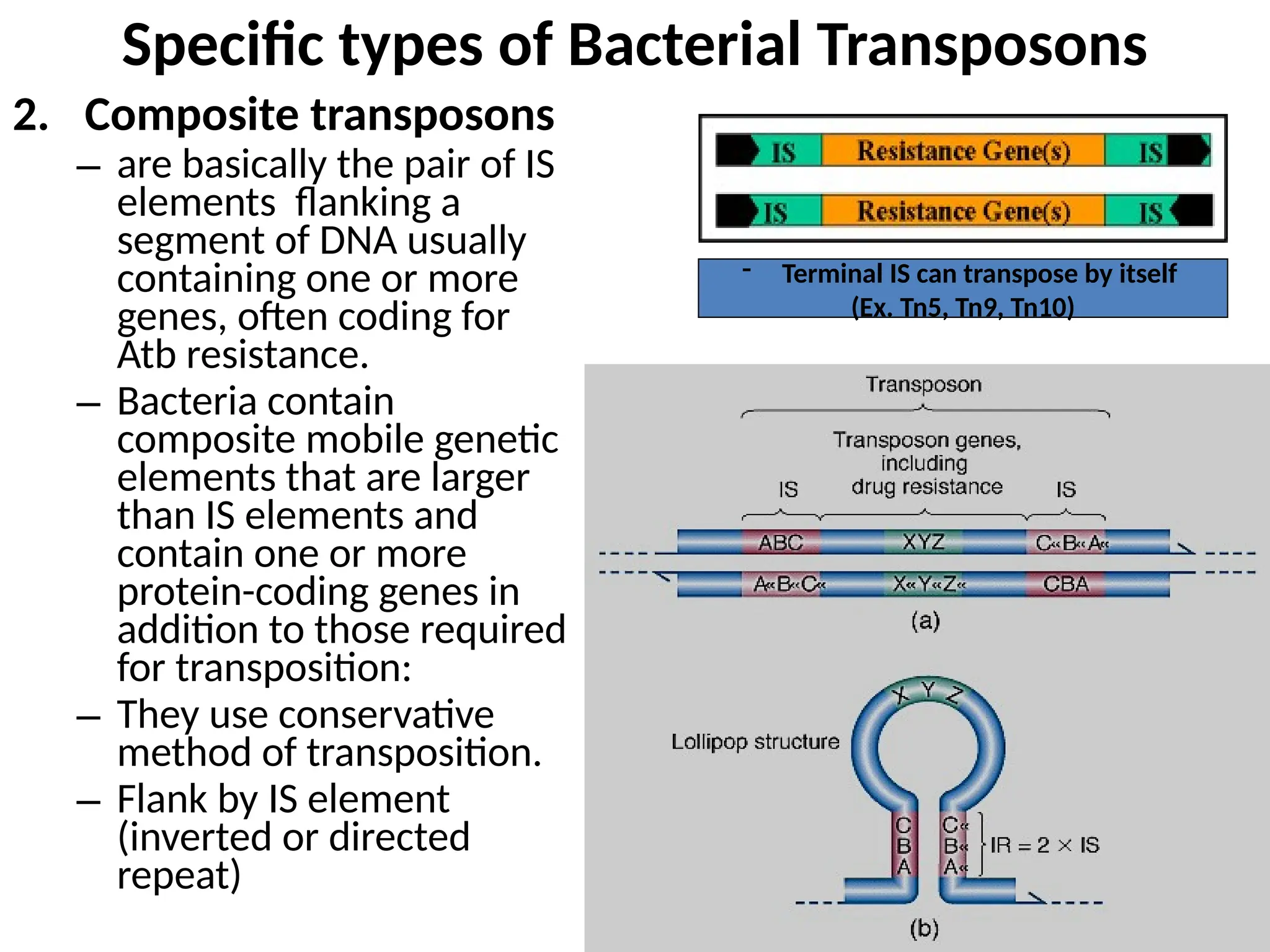
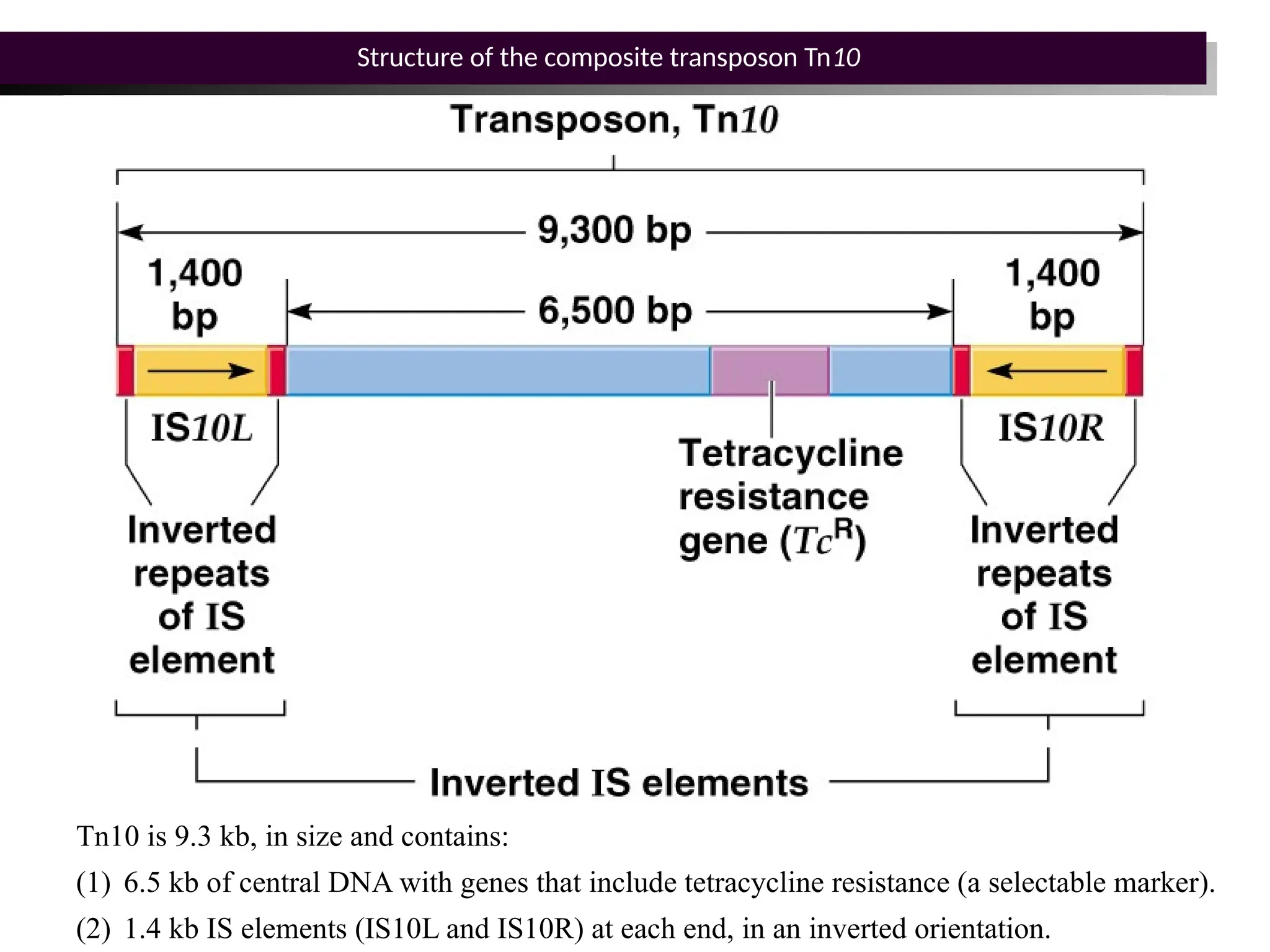
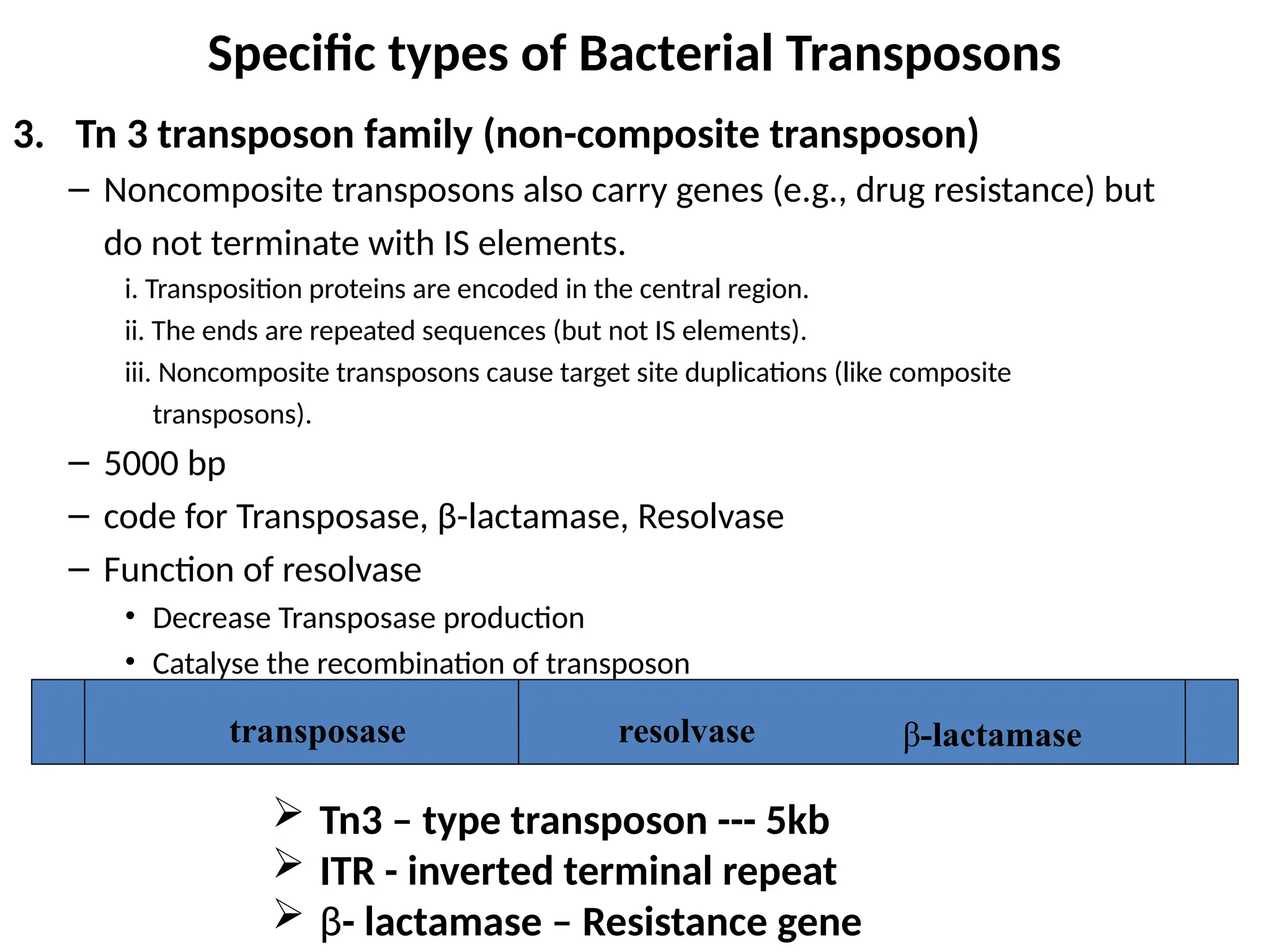
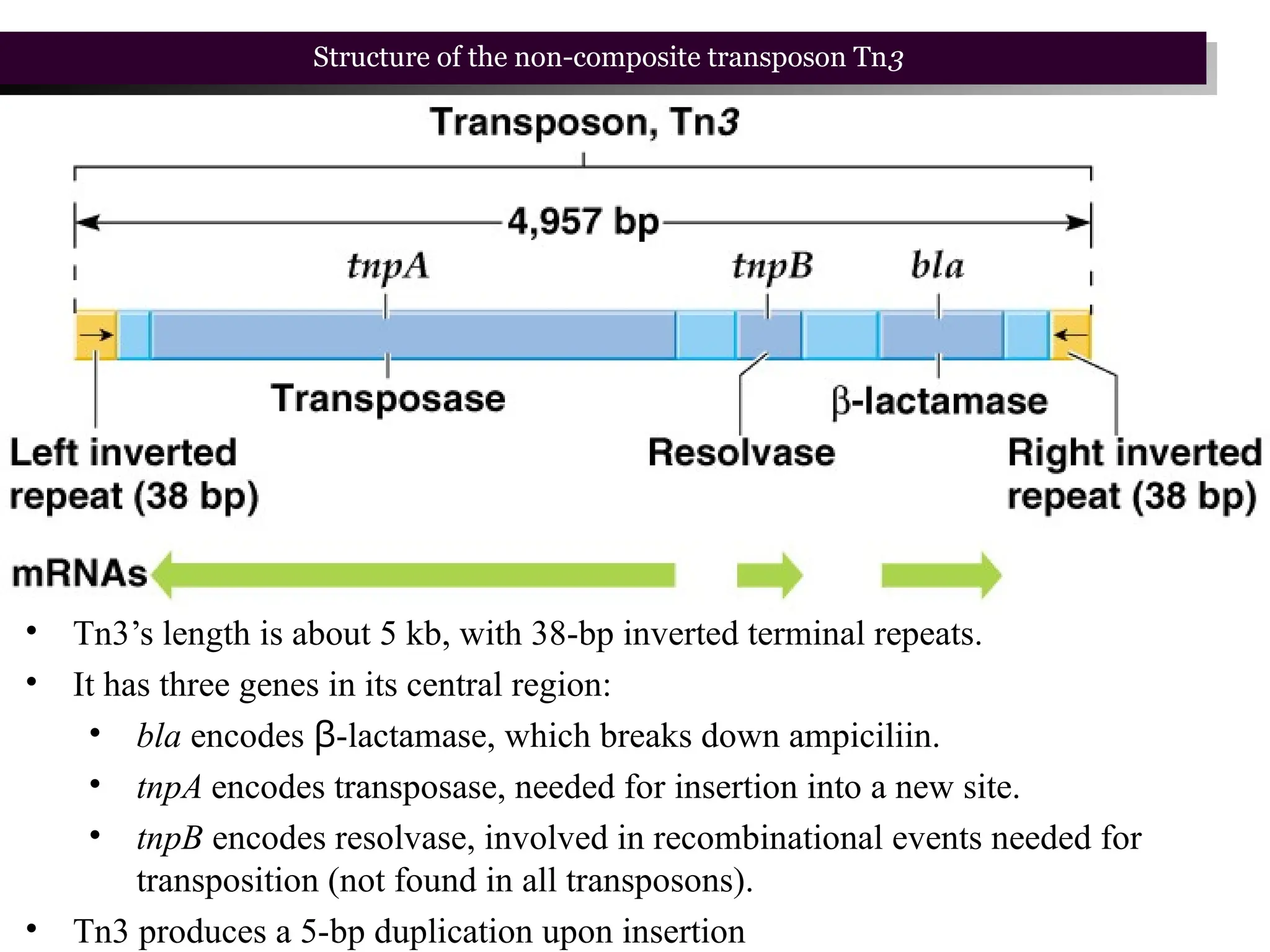
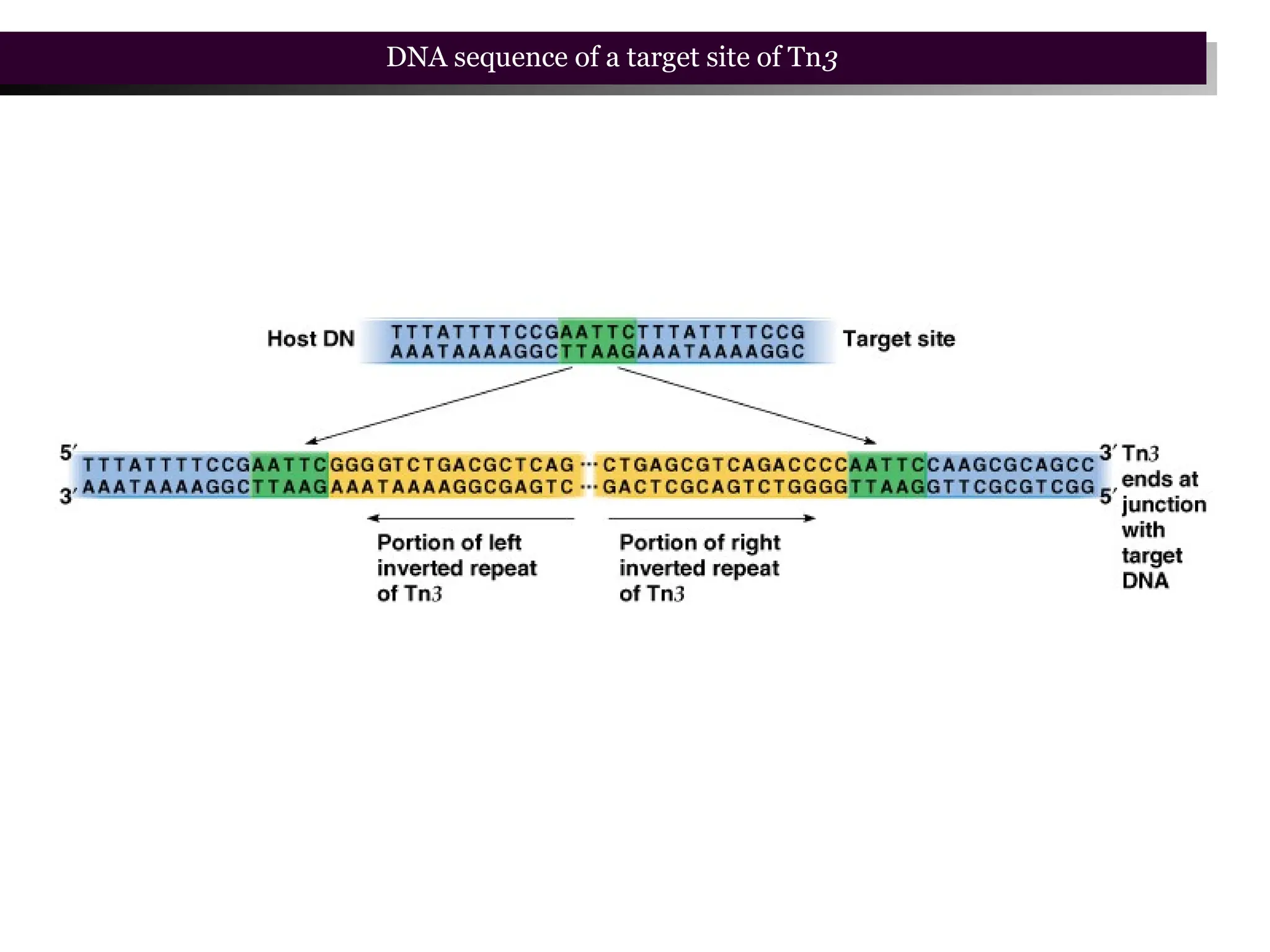
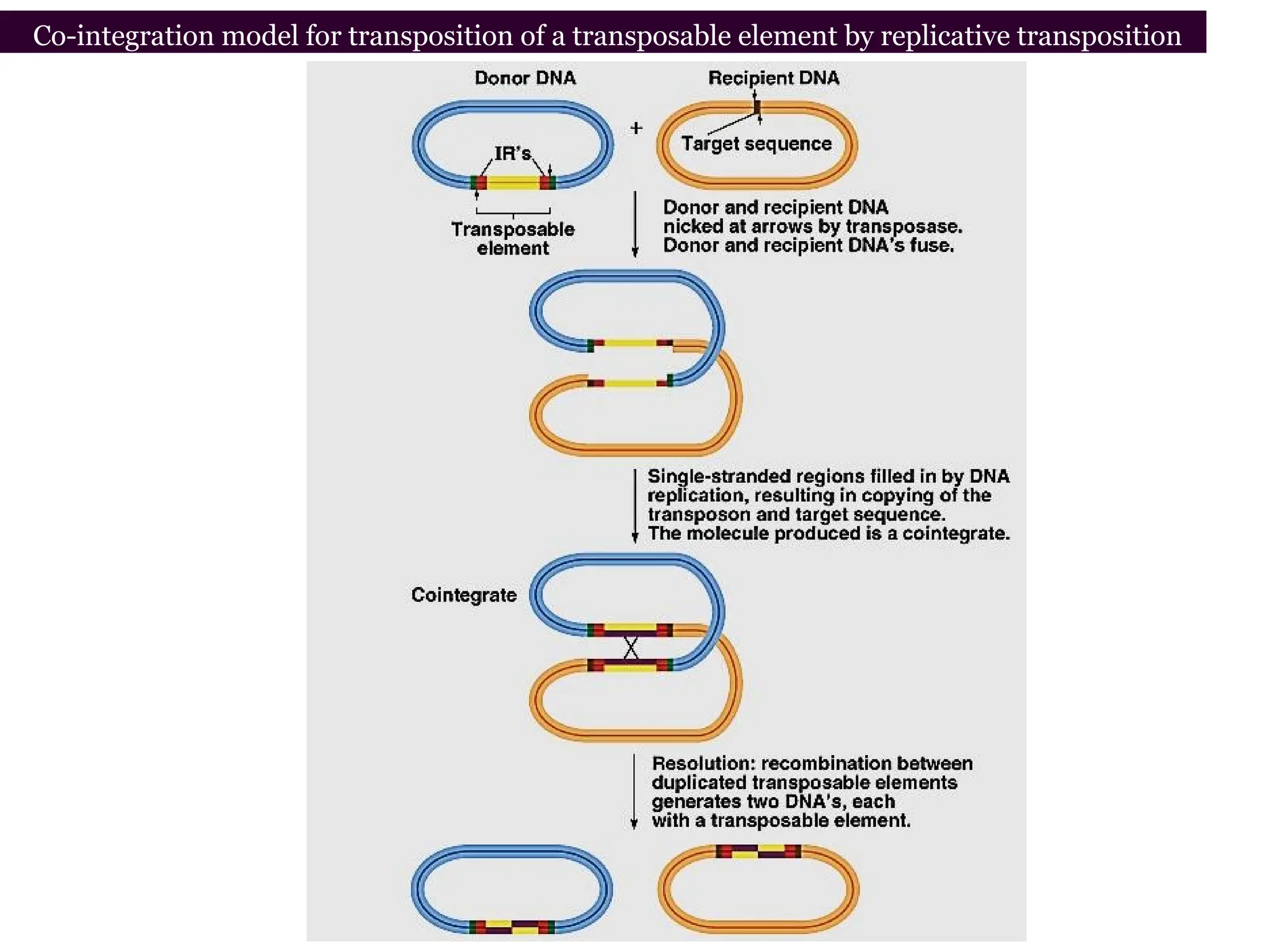
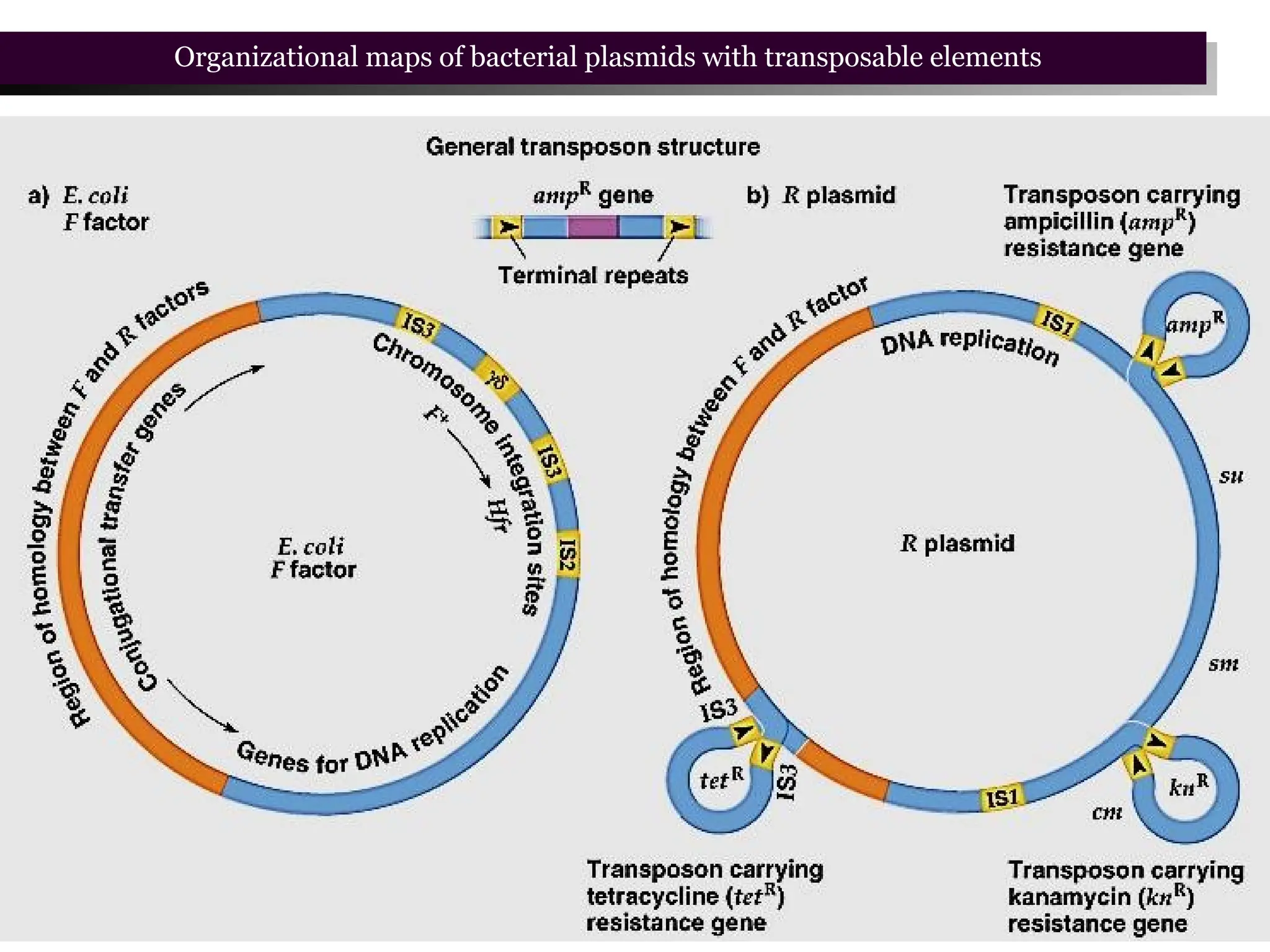
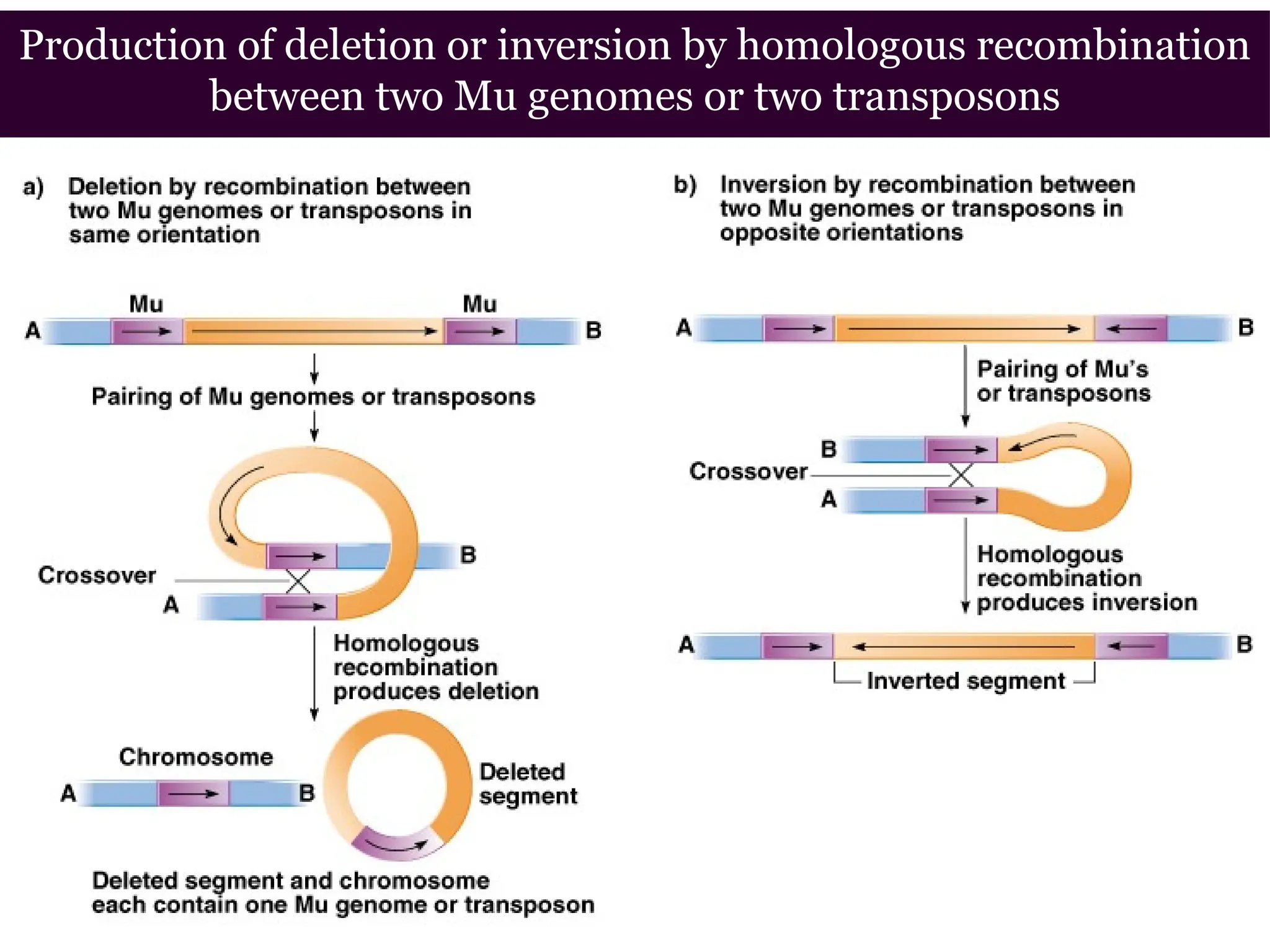
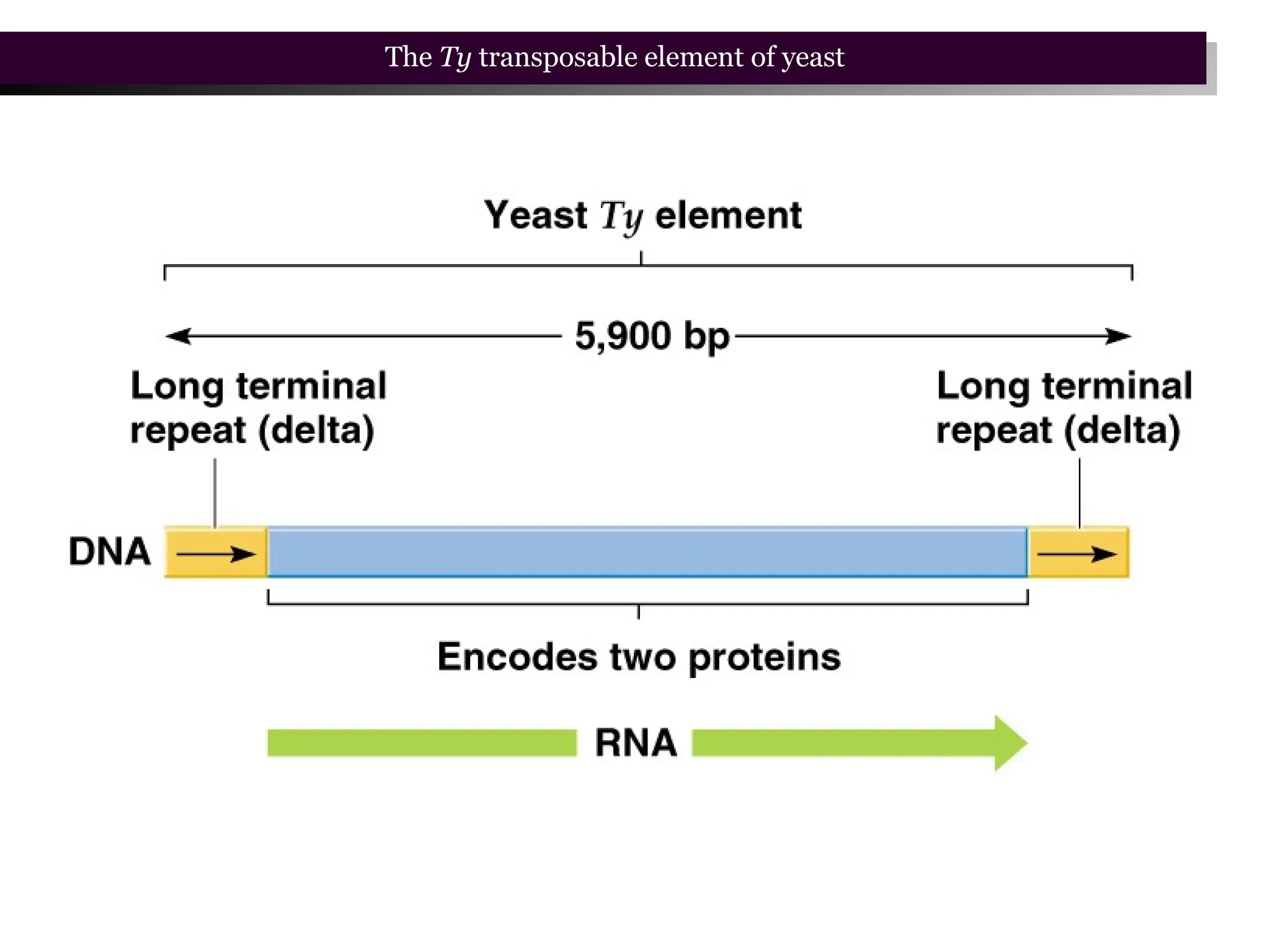
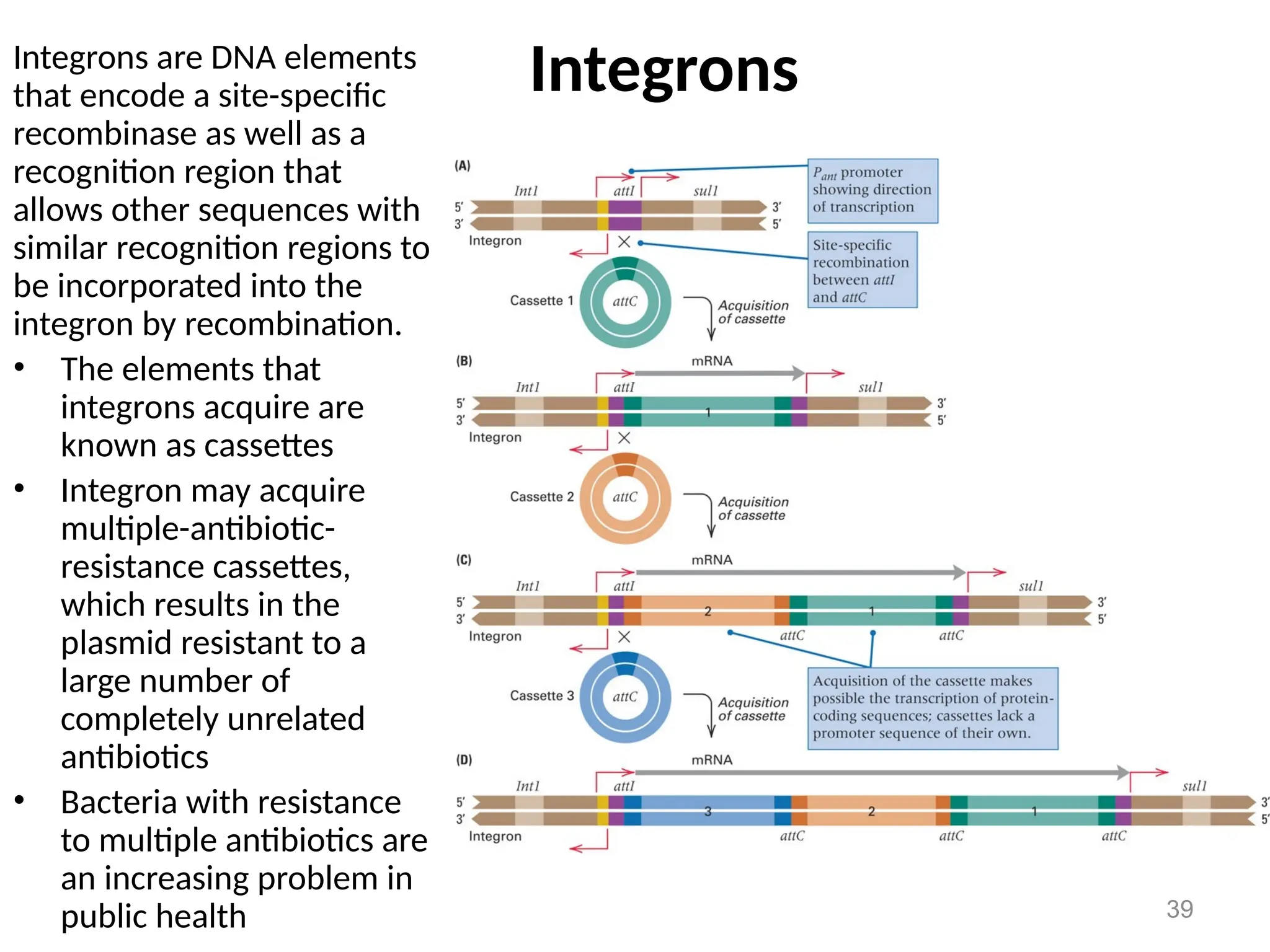
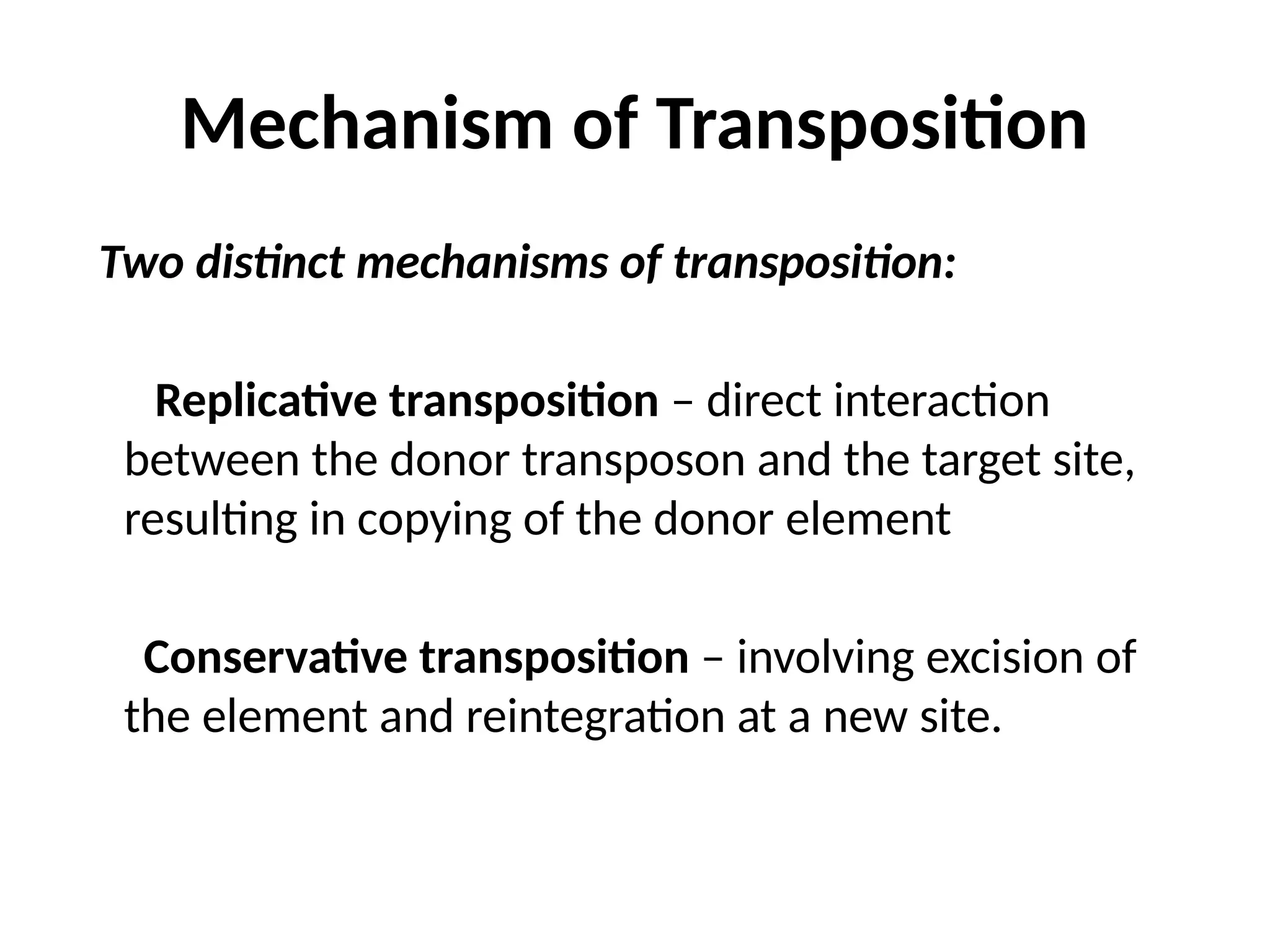
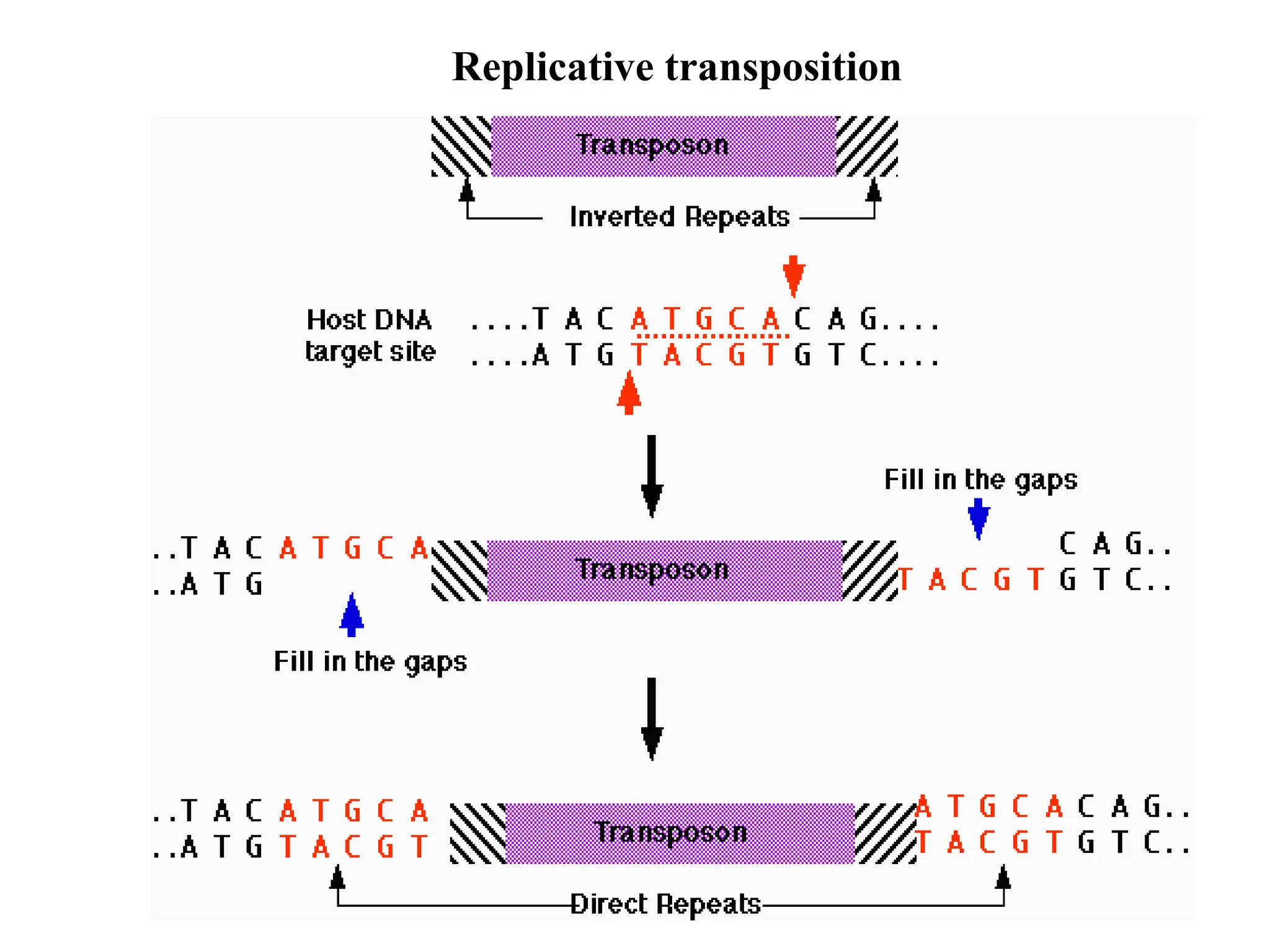
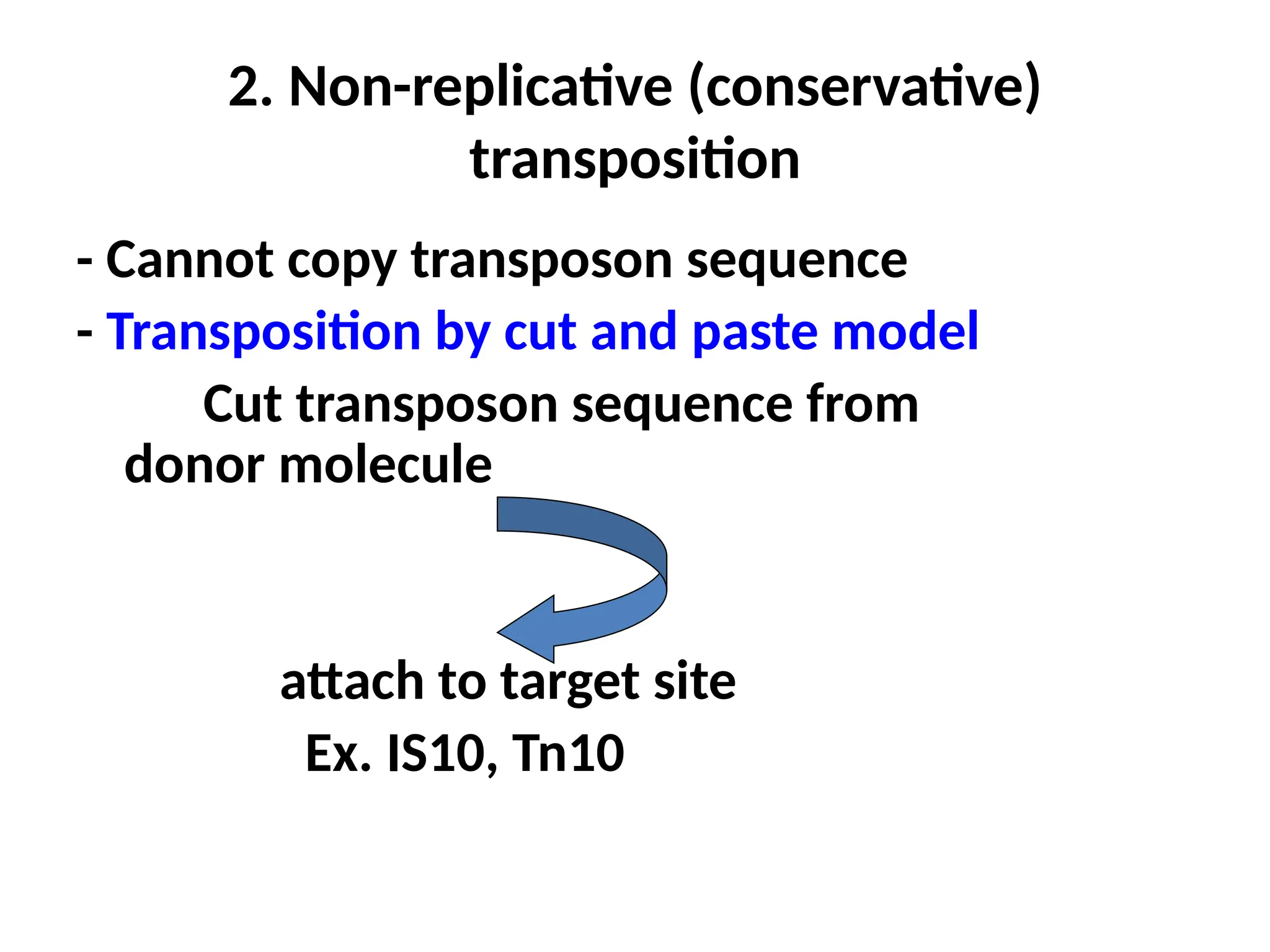
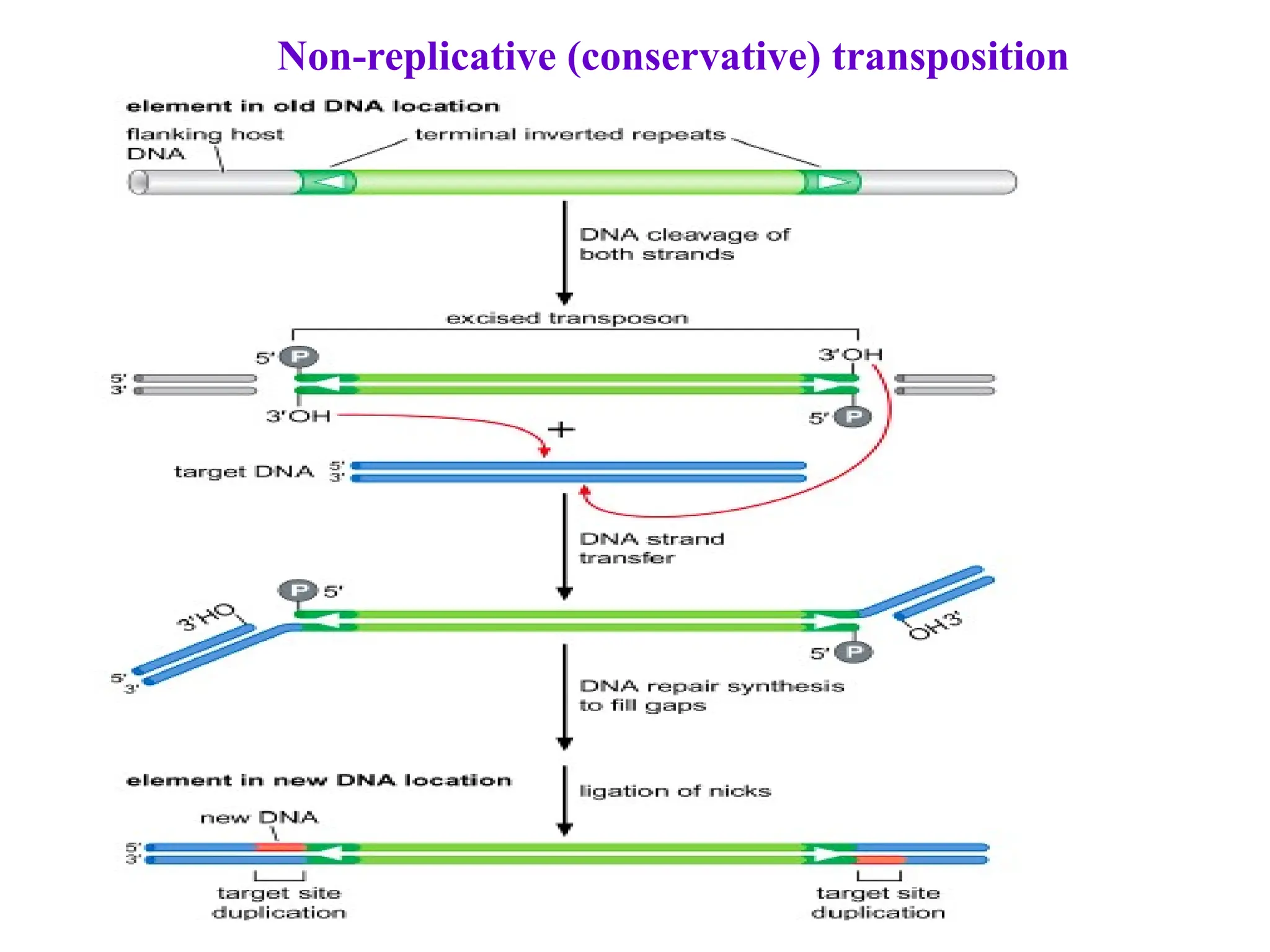
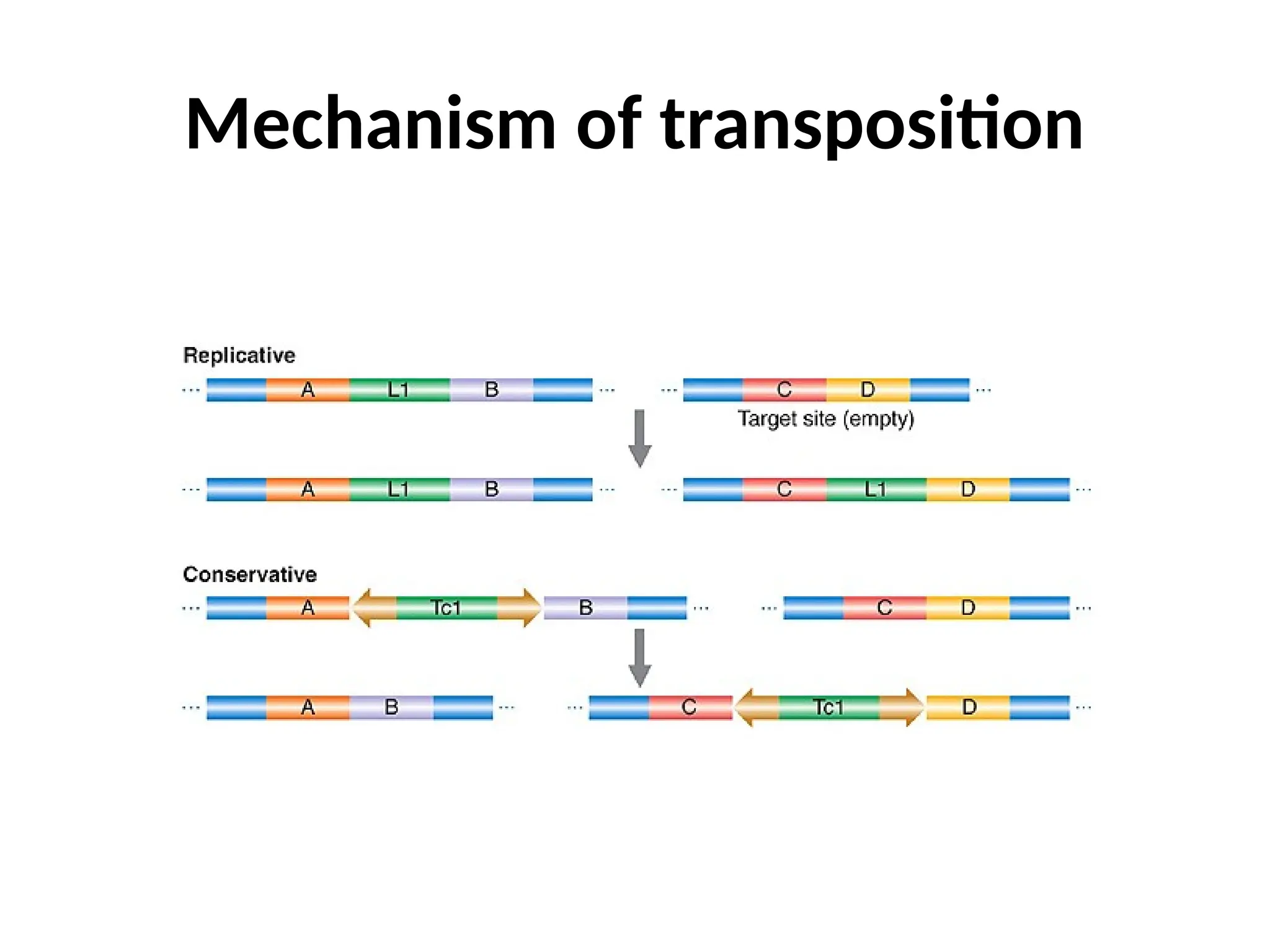
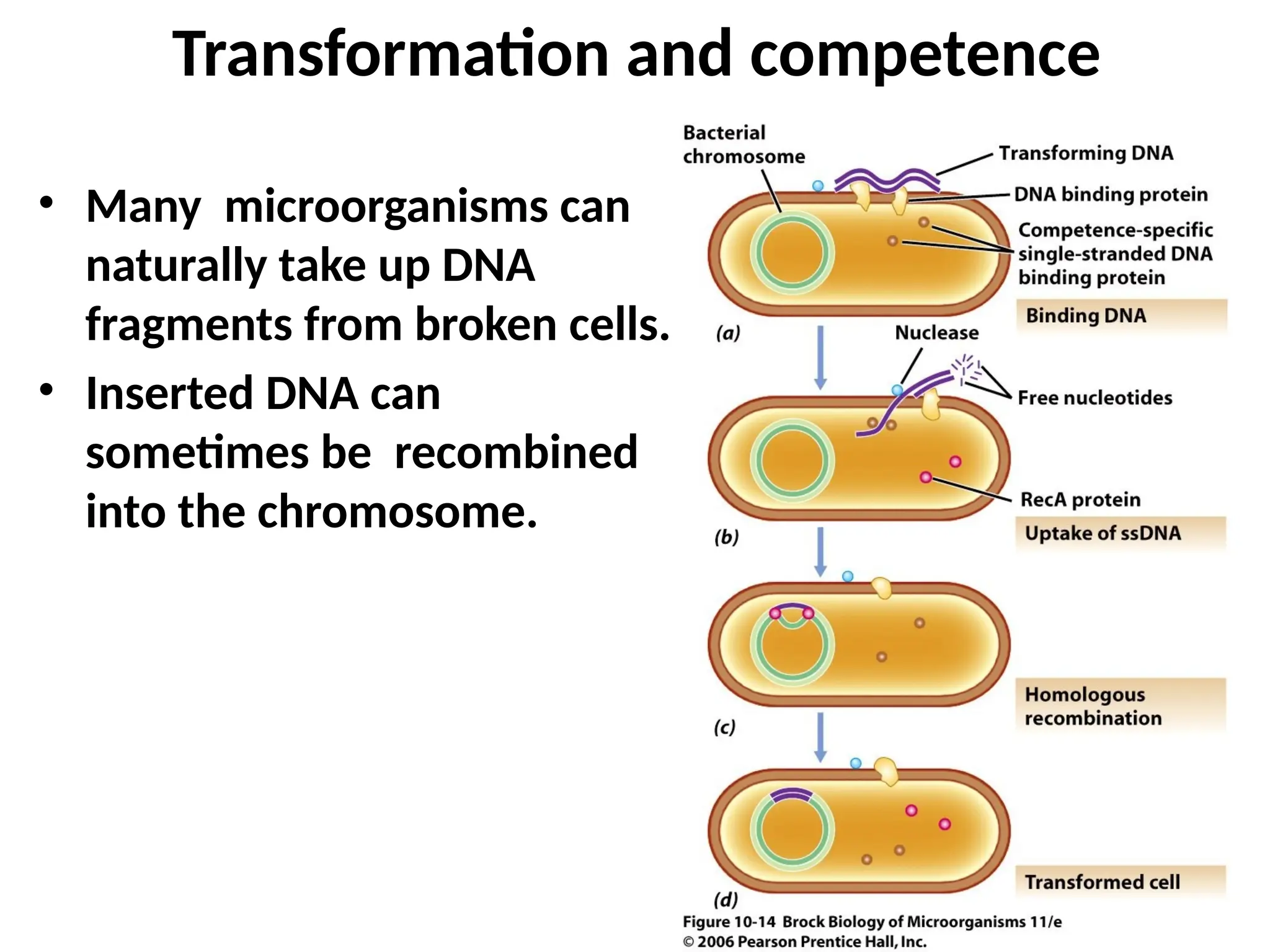
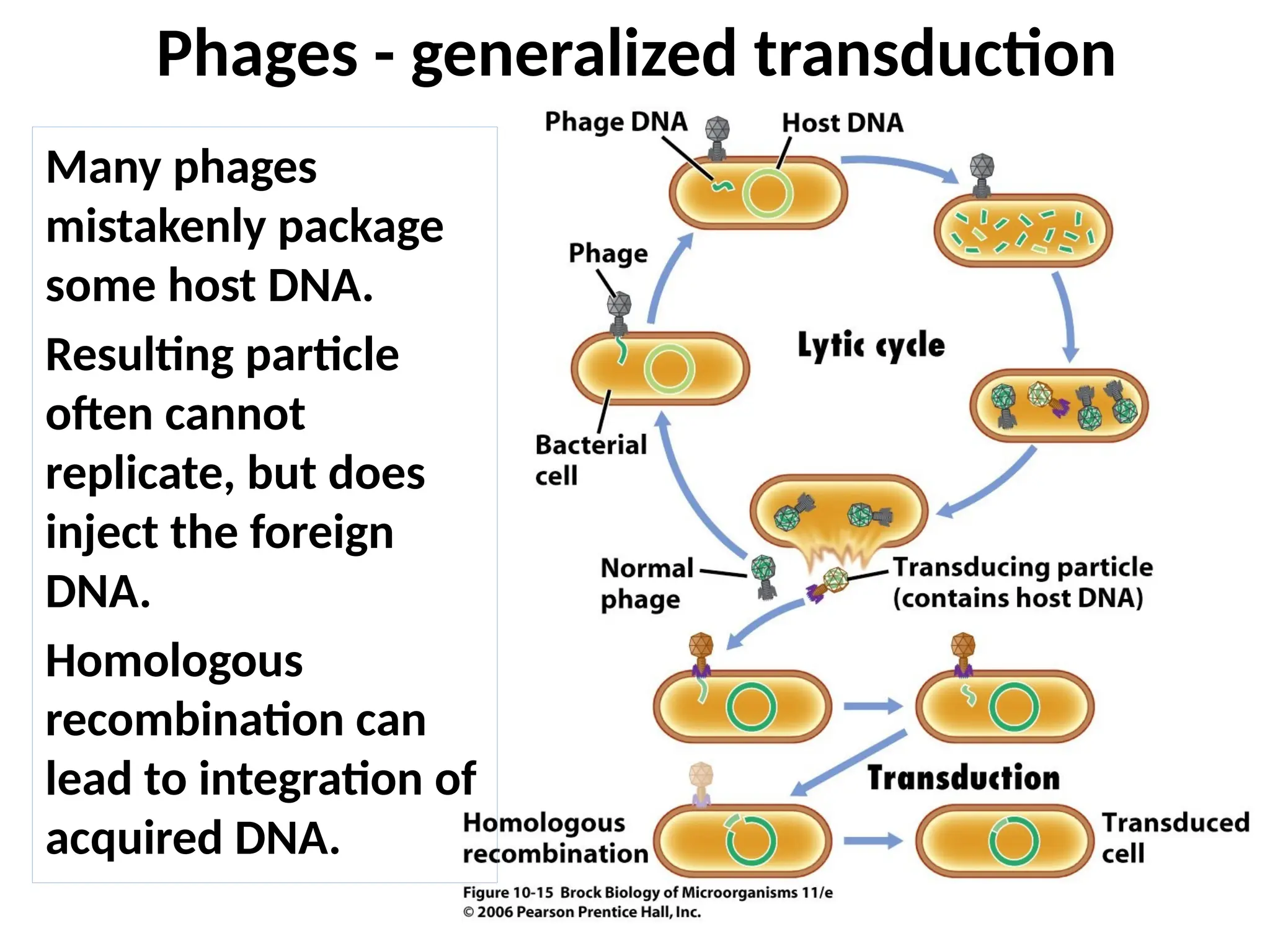
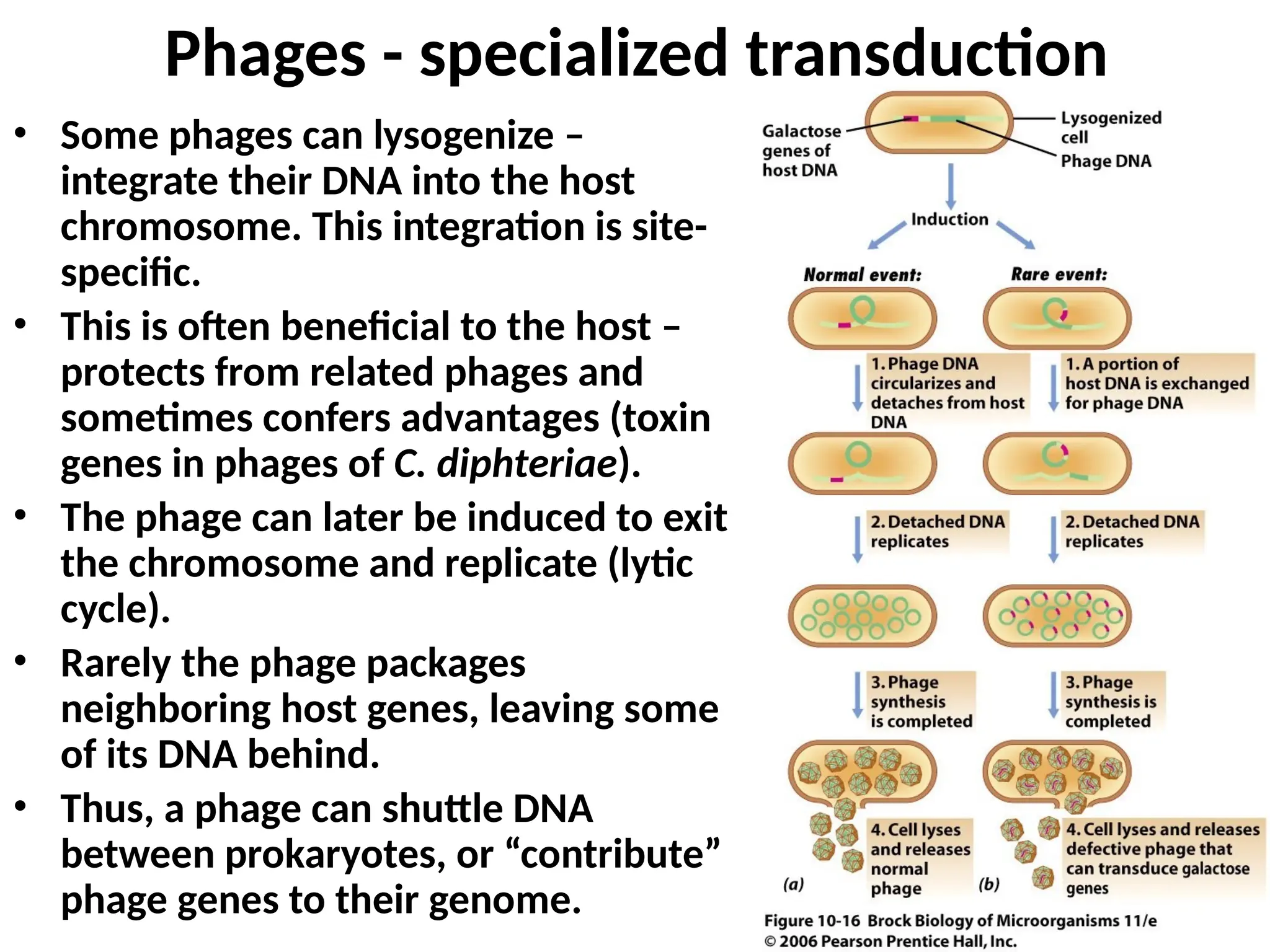
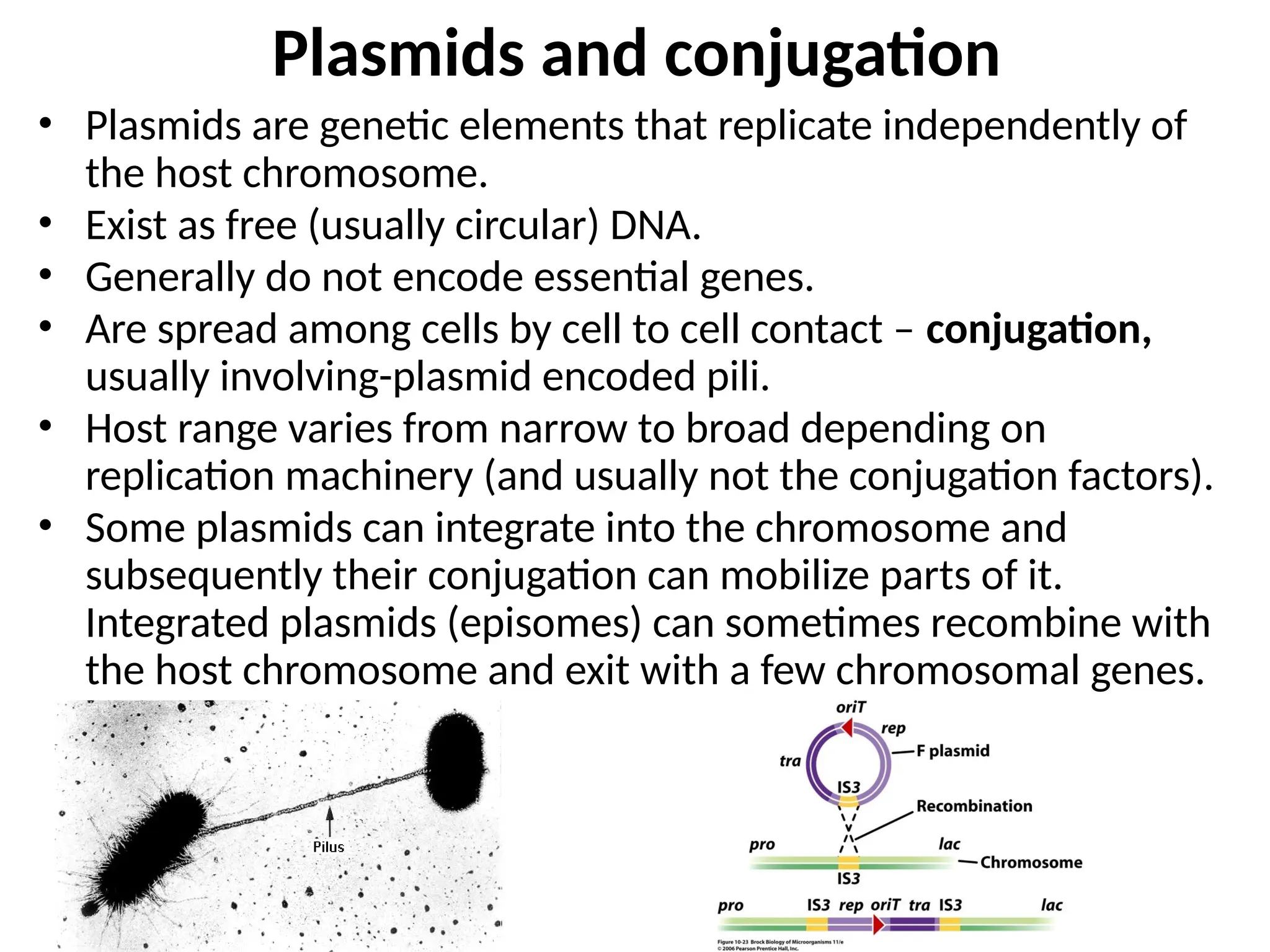
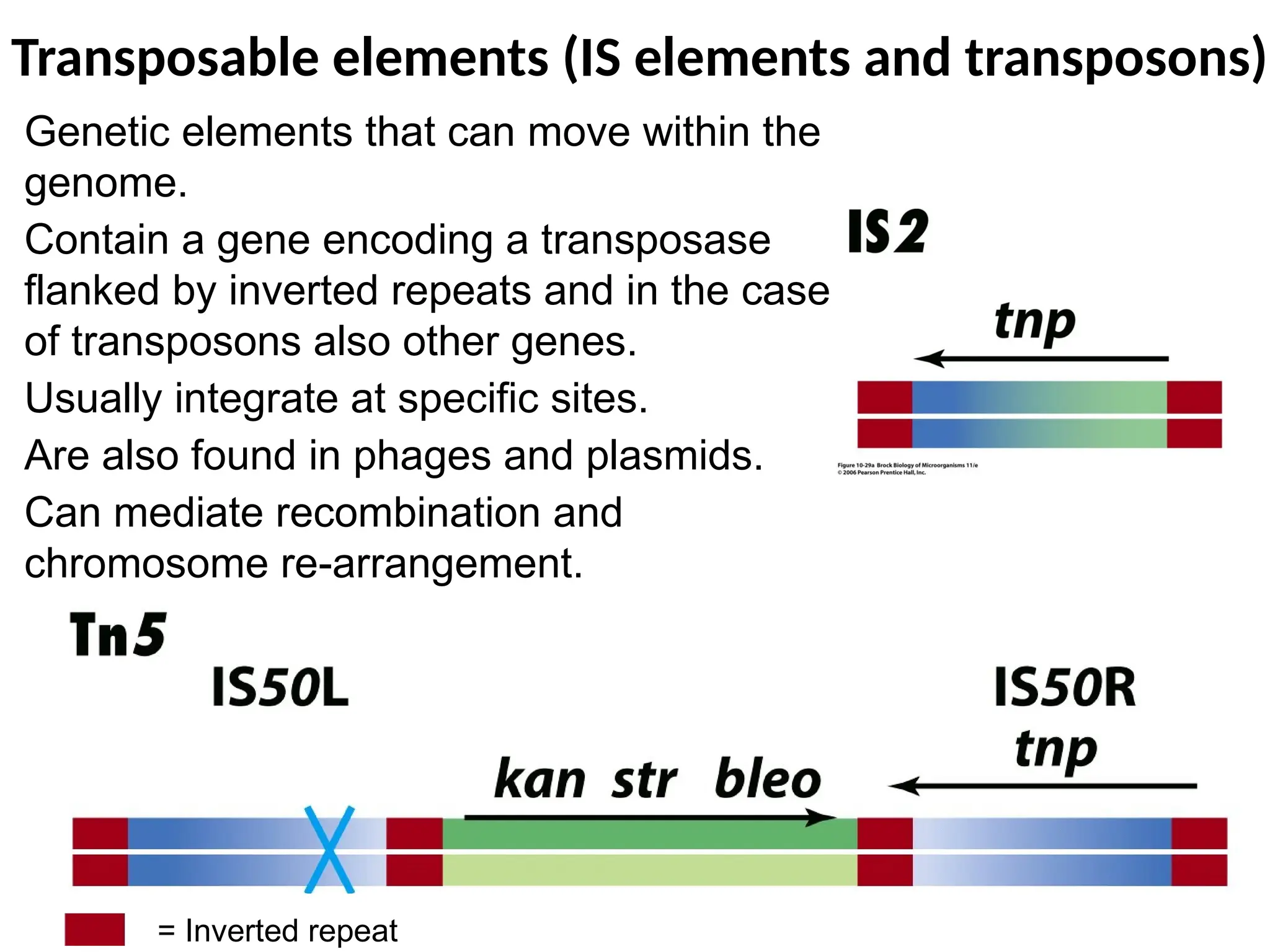
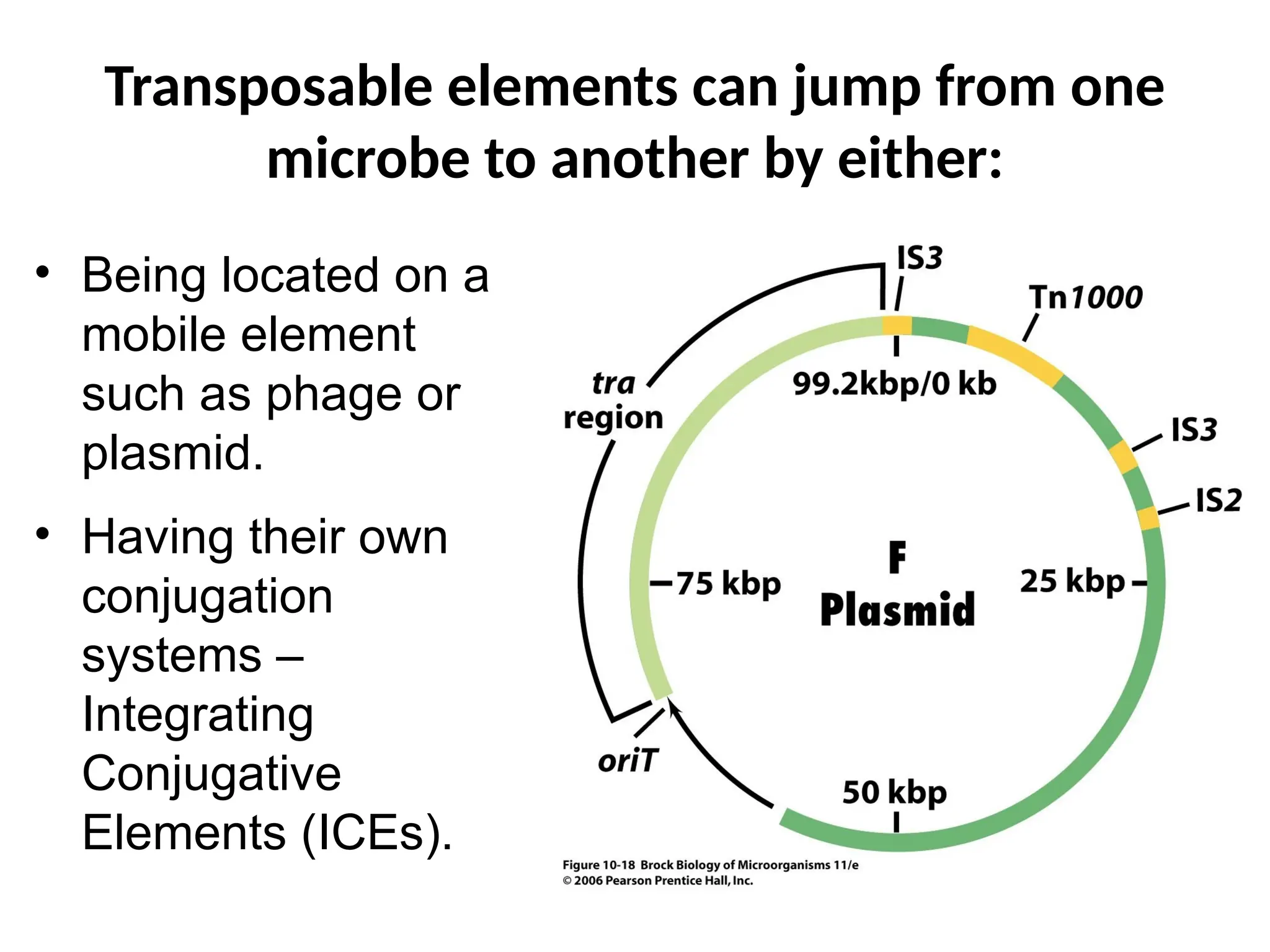
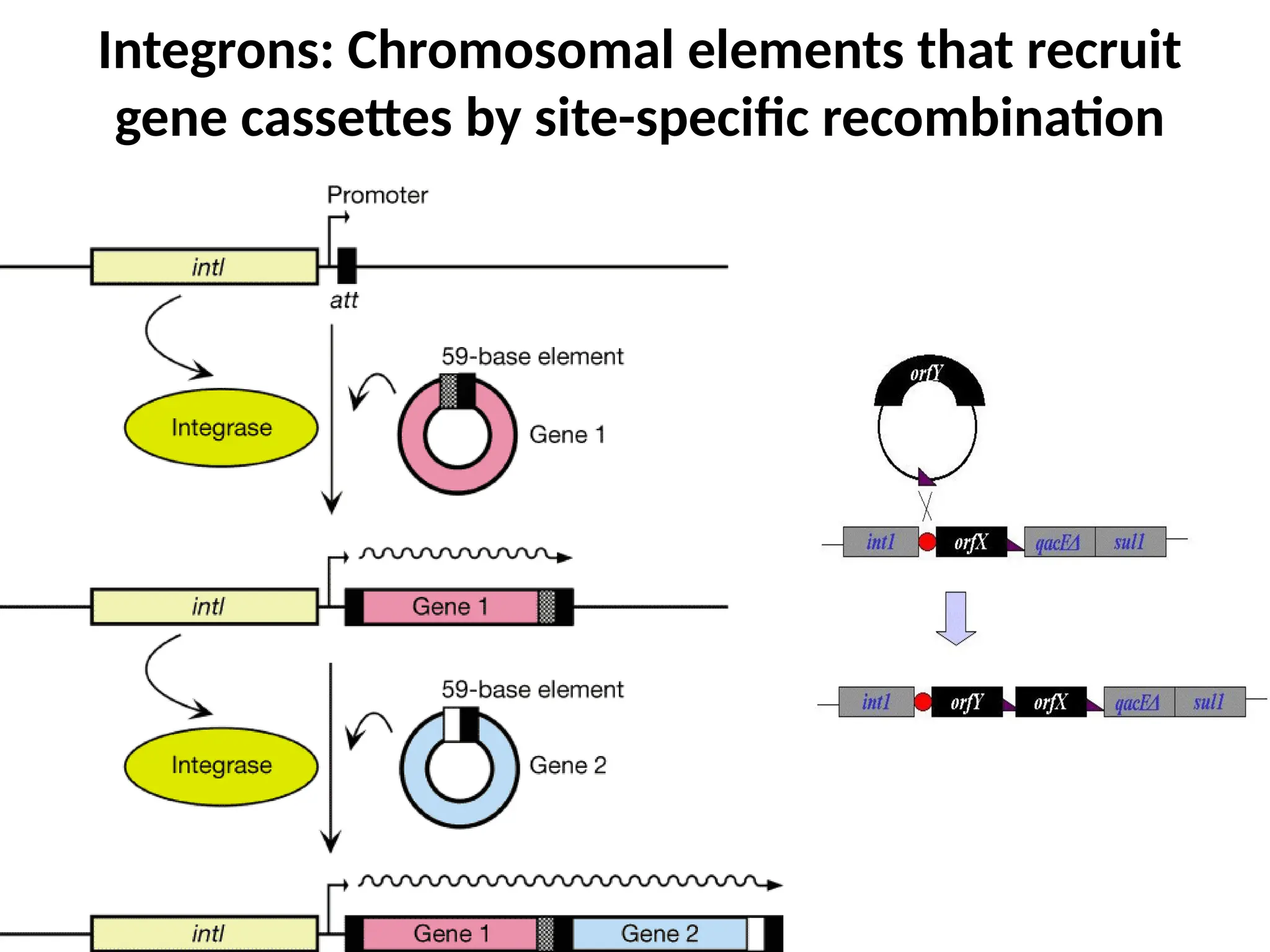
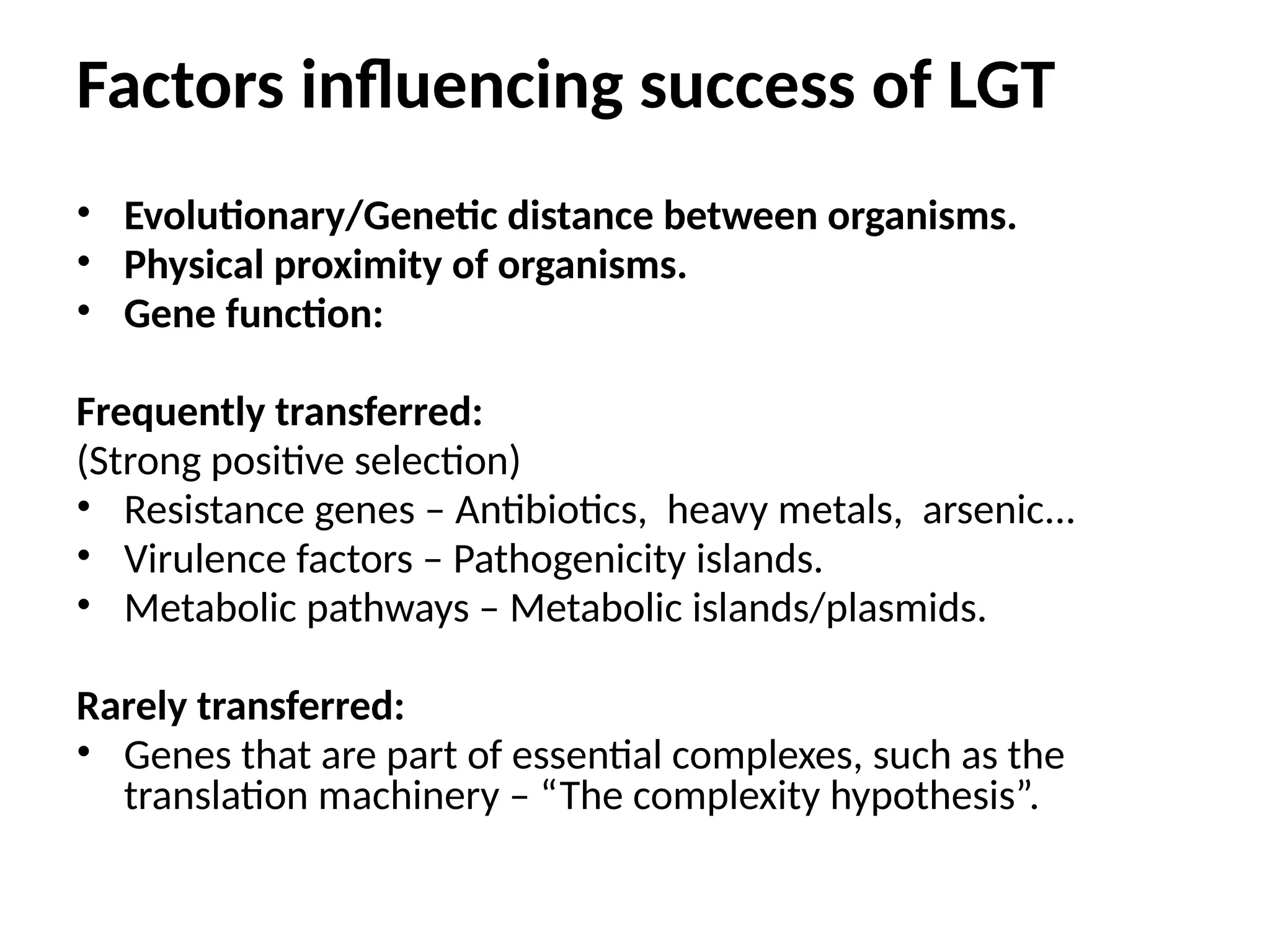
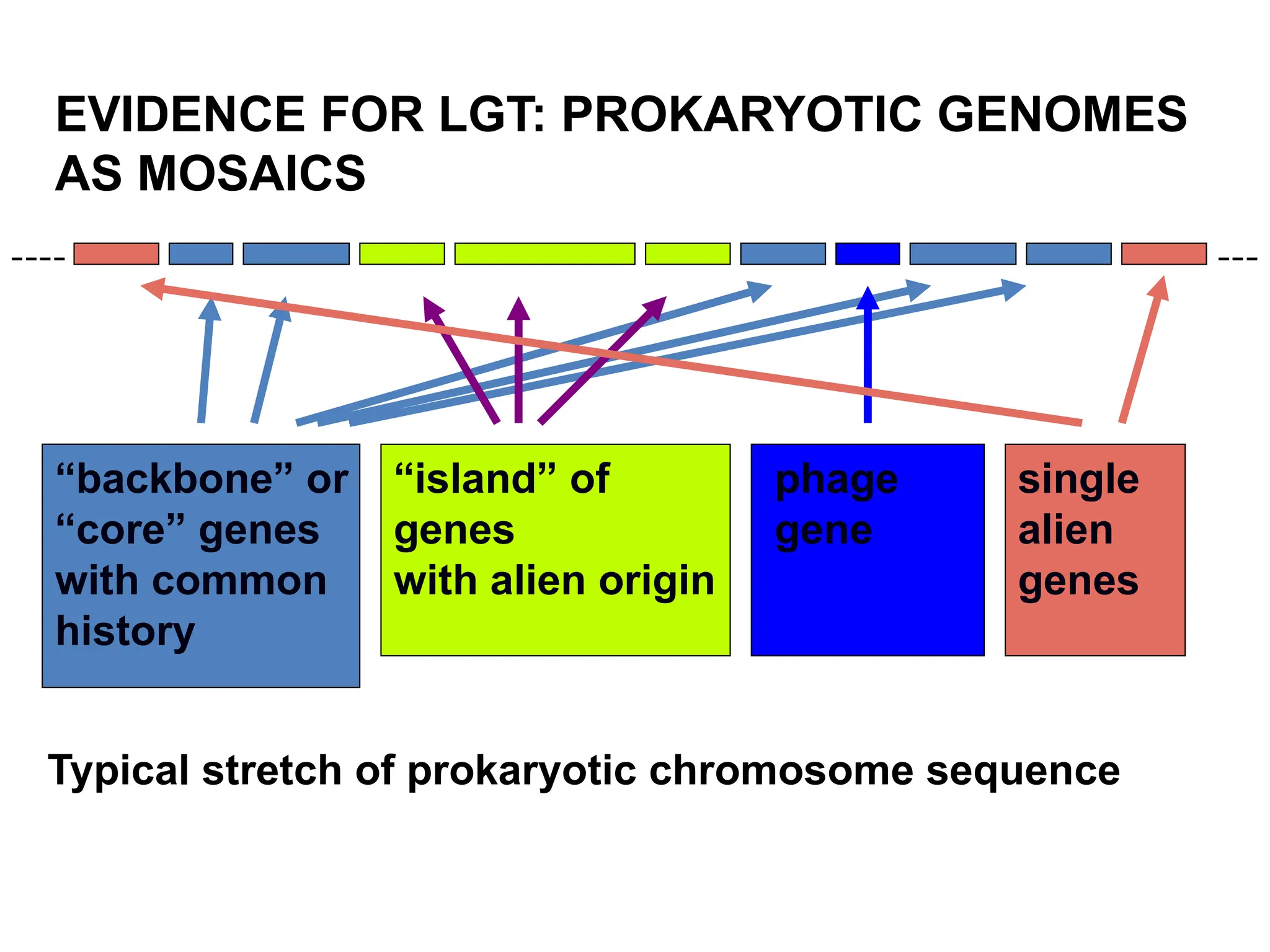
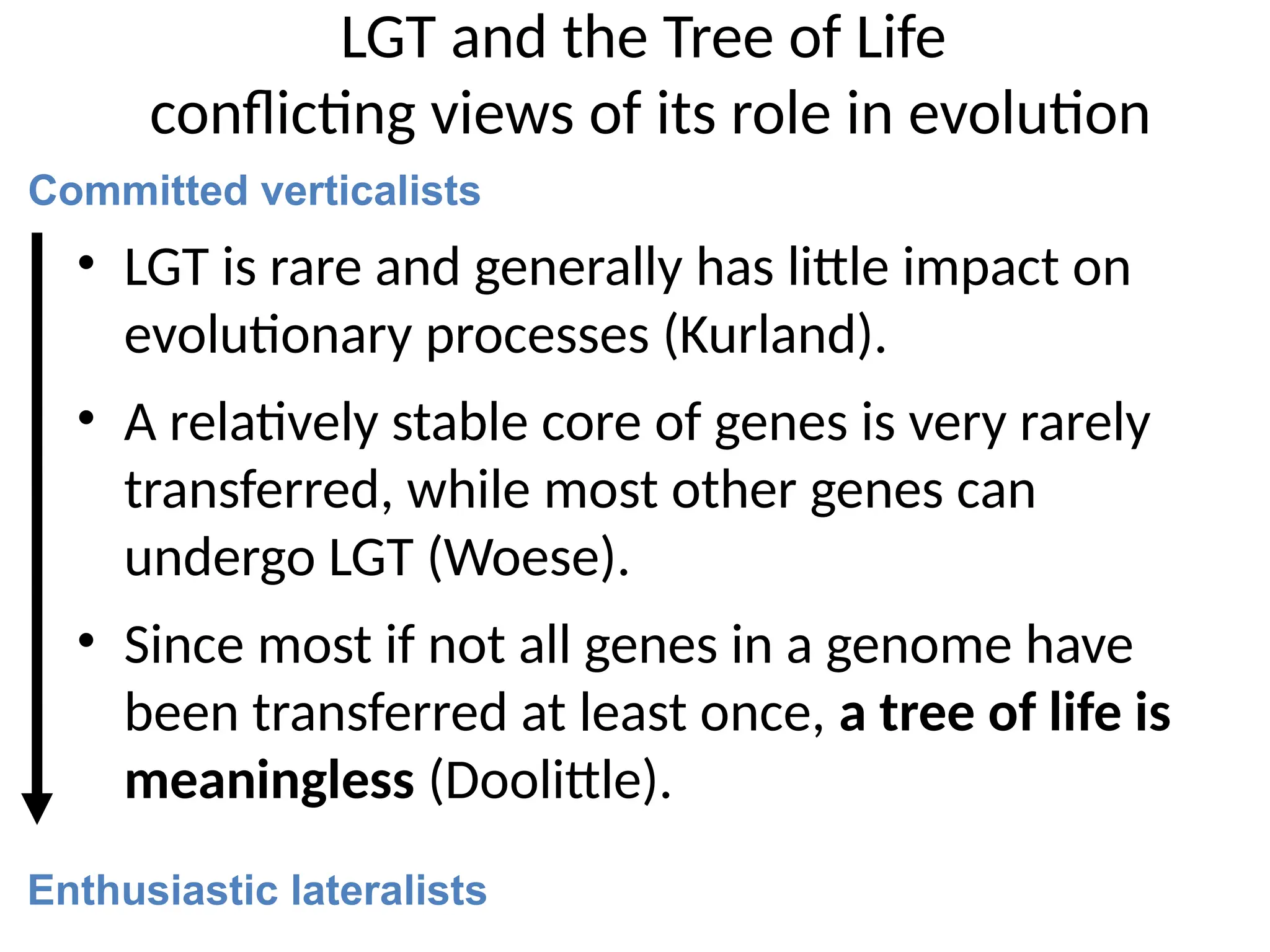
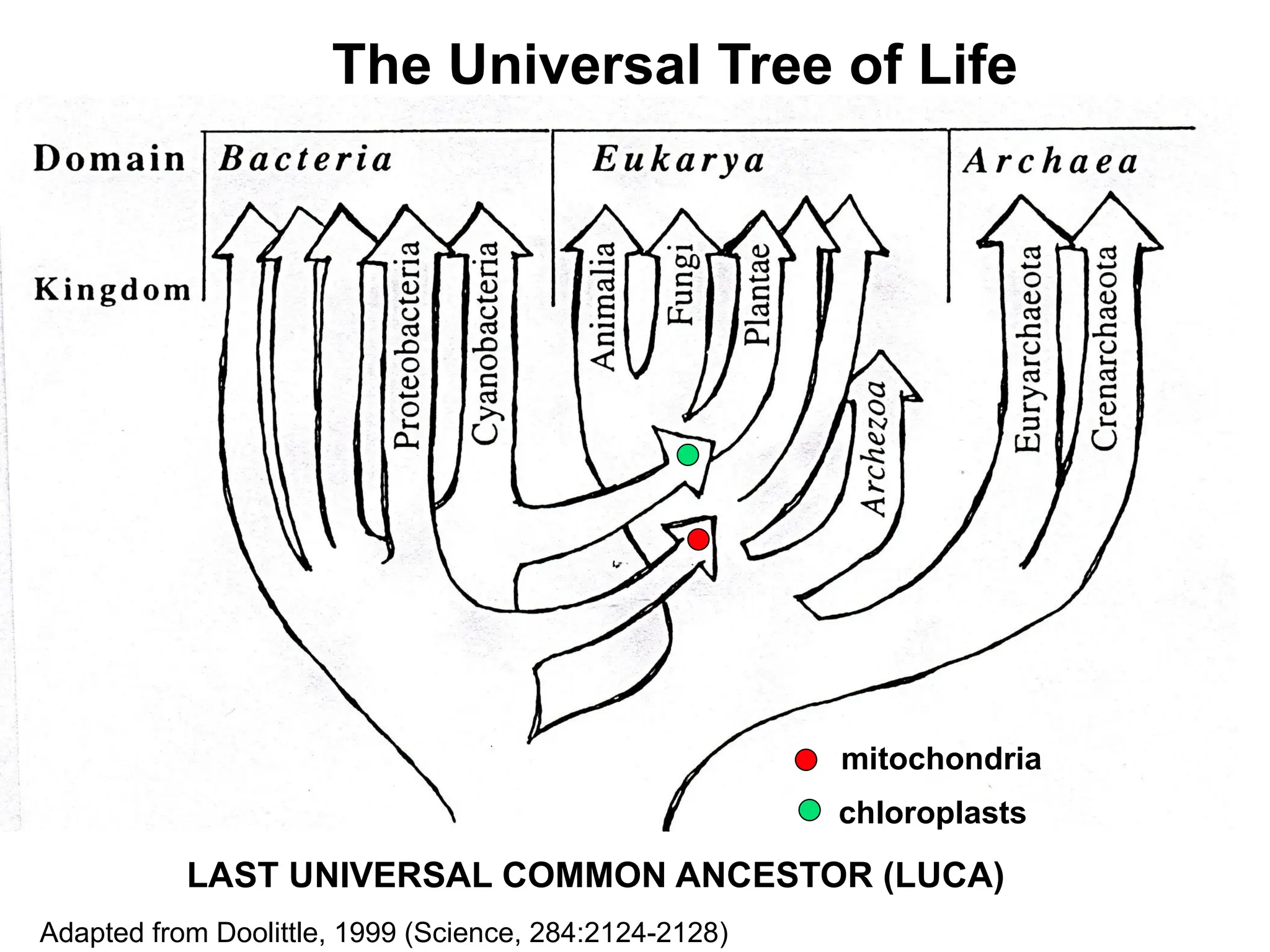
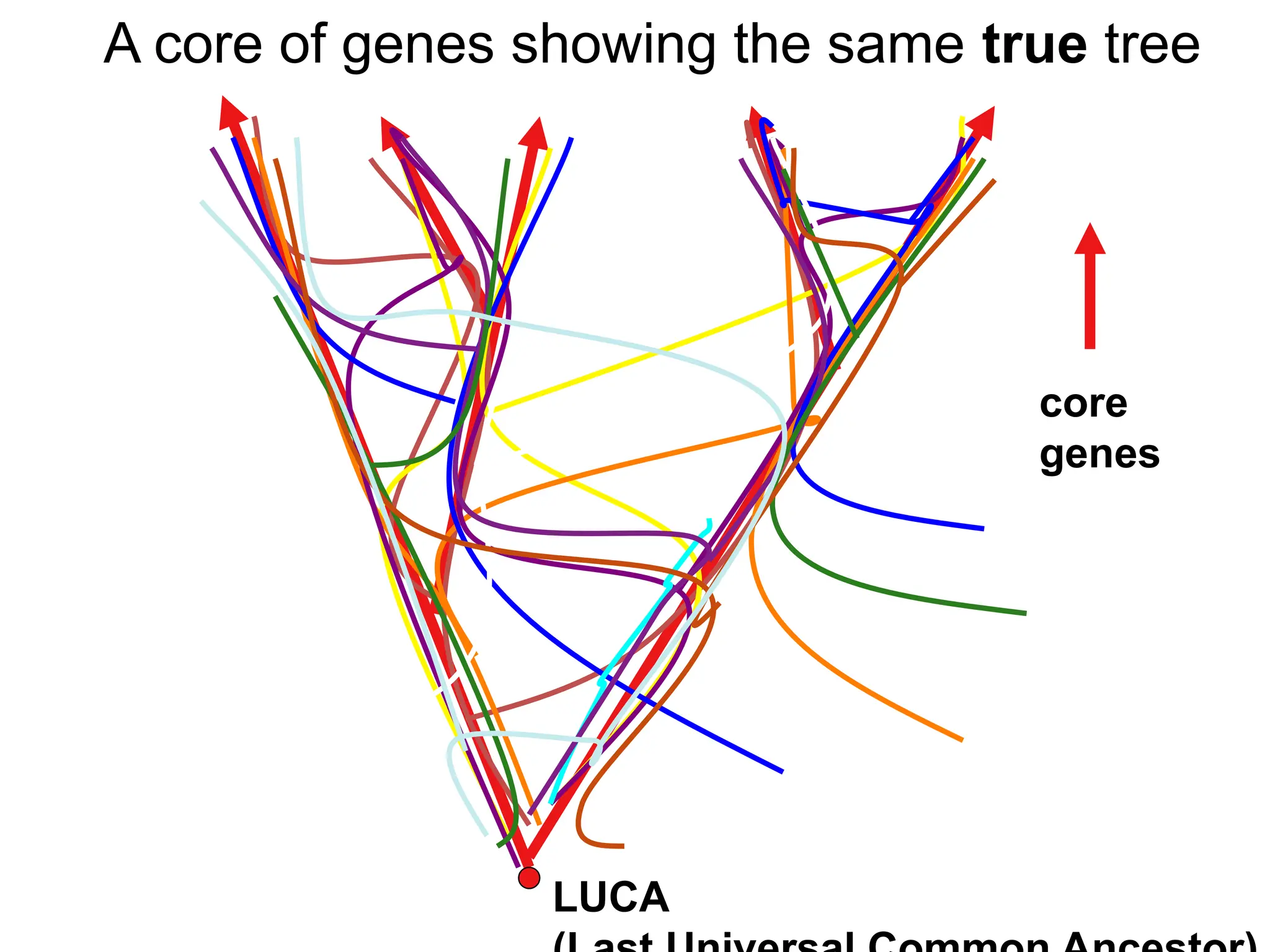
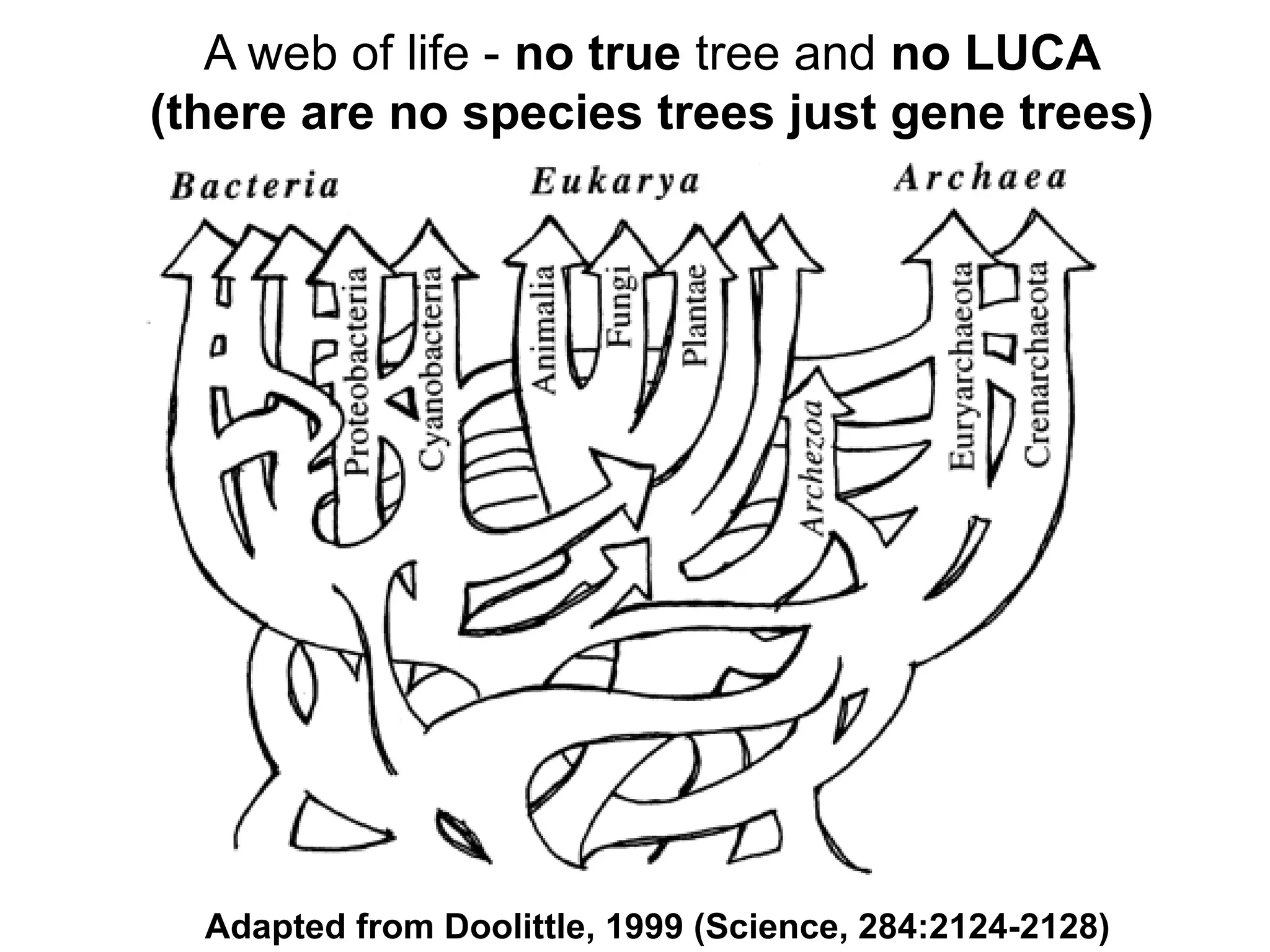
Transposons, also known as jumping genes, are DNA sequences that can move within a genome, causing mutations and rearrangements that drive evolution. They include insertion sequences and two main classes: DNA transposons and retrotransposons, the latter using RNA intermediates for transposition. Transposons have significant implications in gene regulation, genetic diversity, and can contribute to diseases and antibiotic resistance.