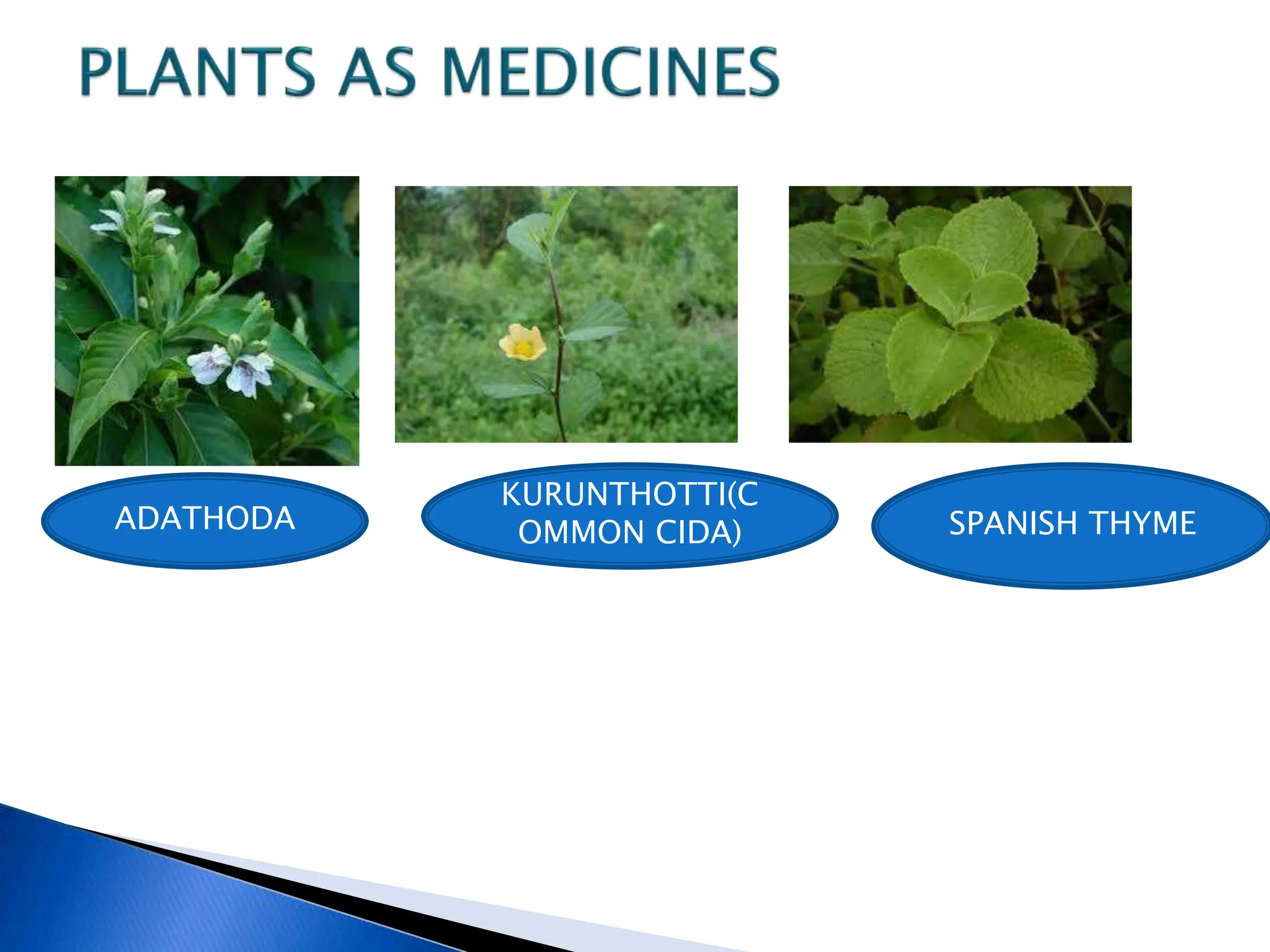
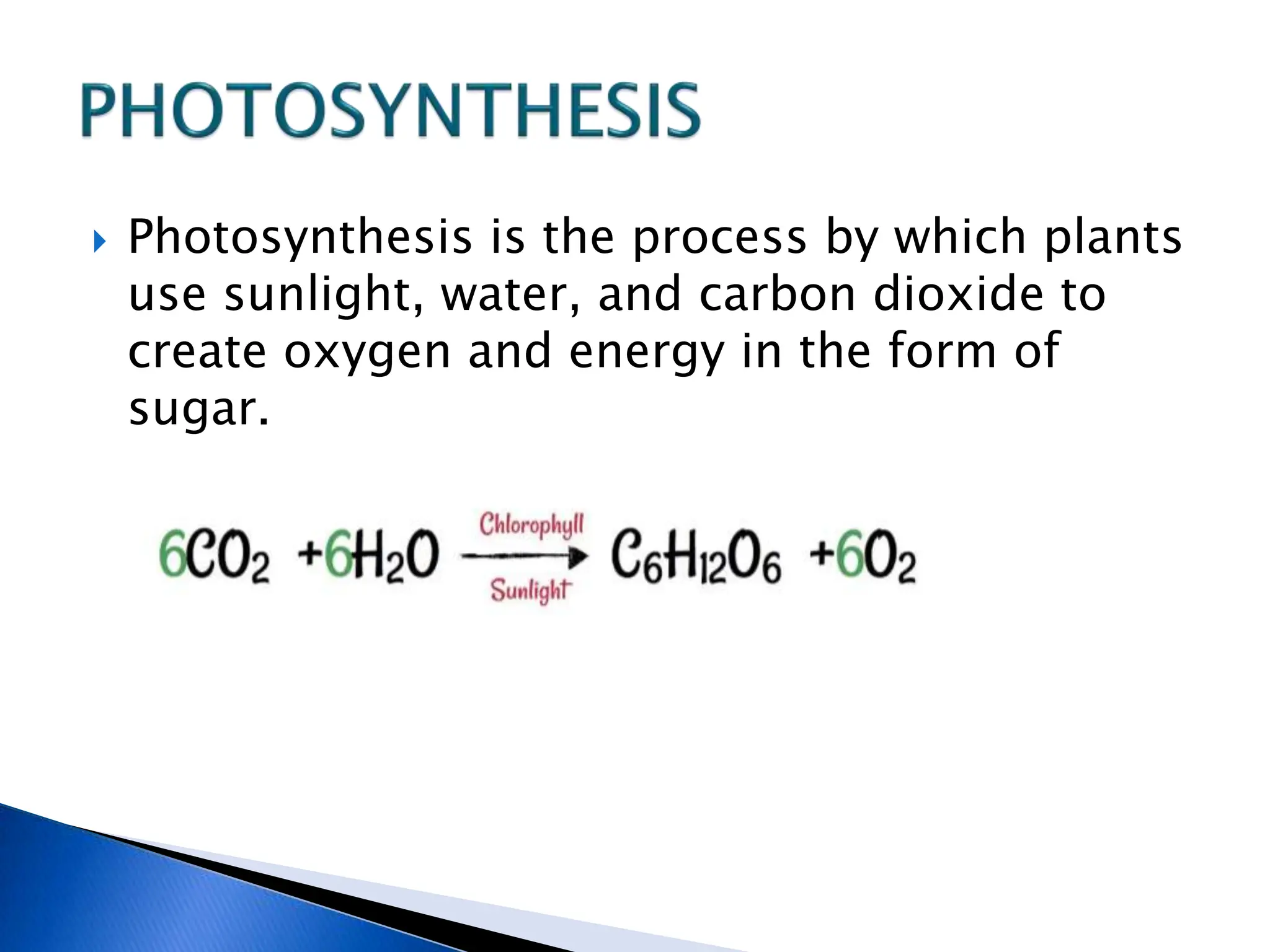
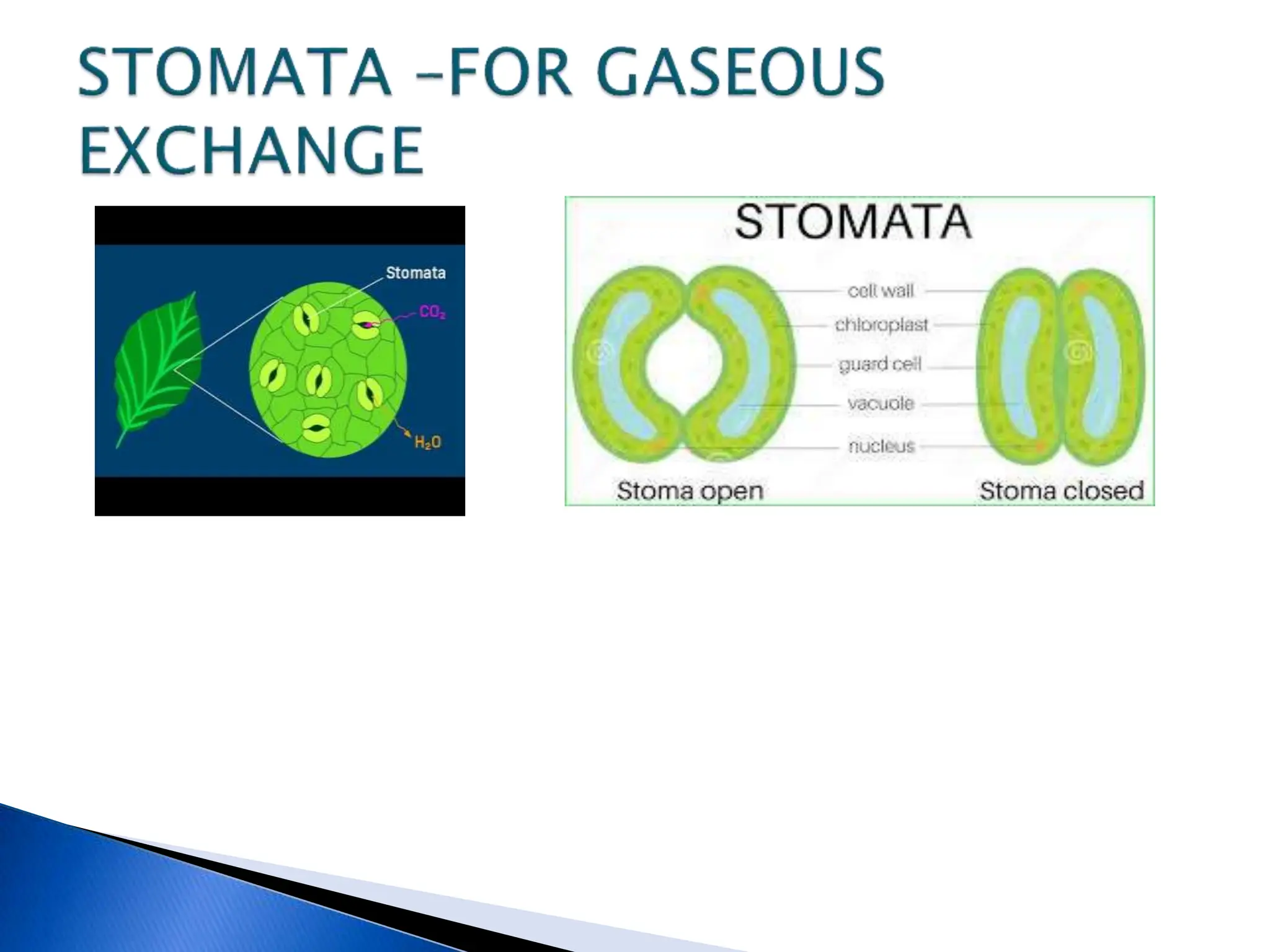
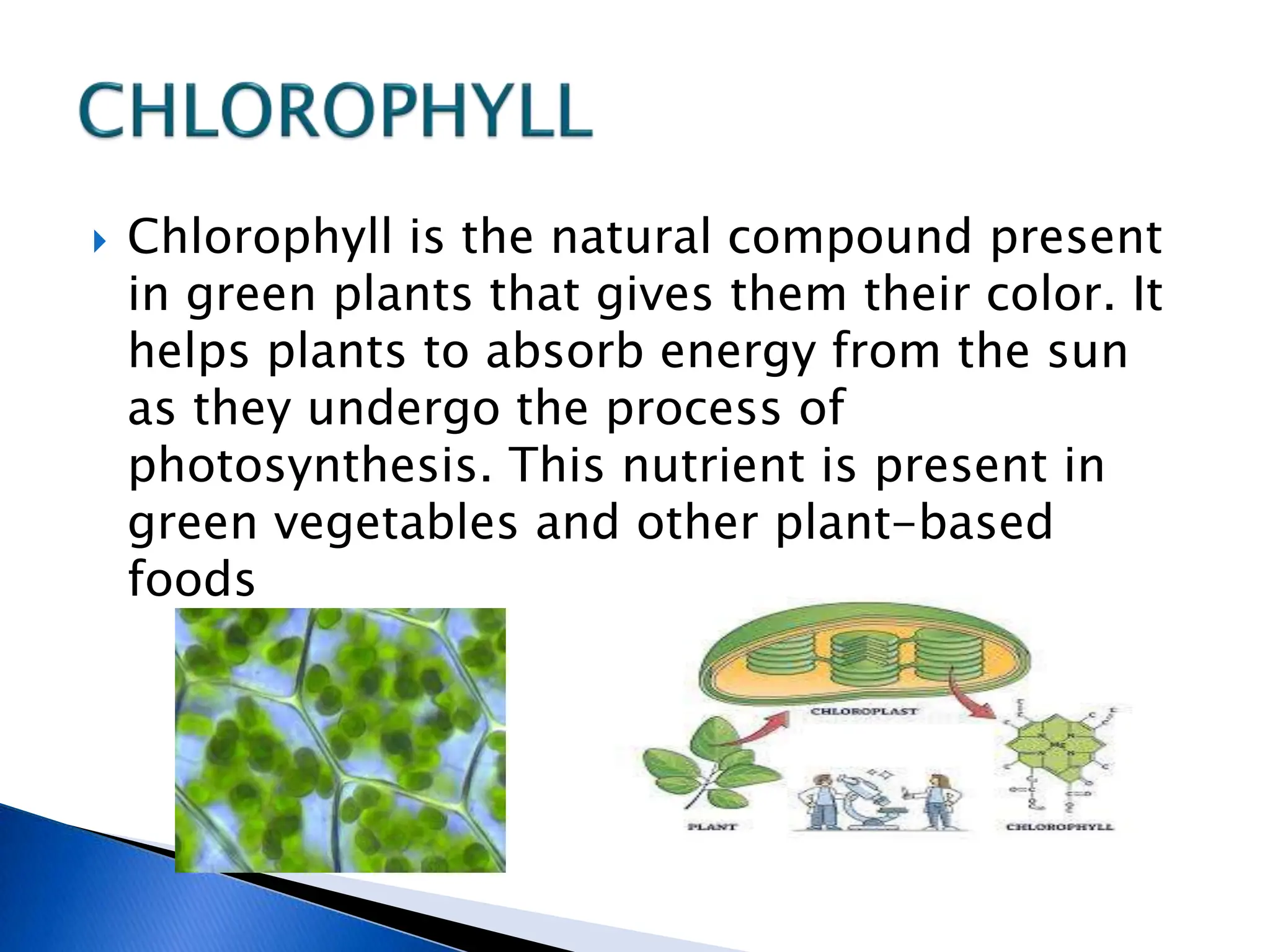
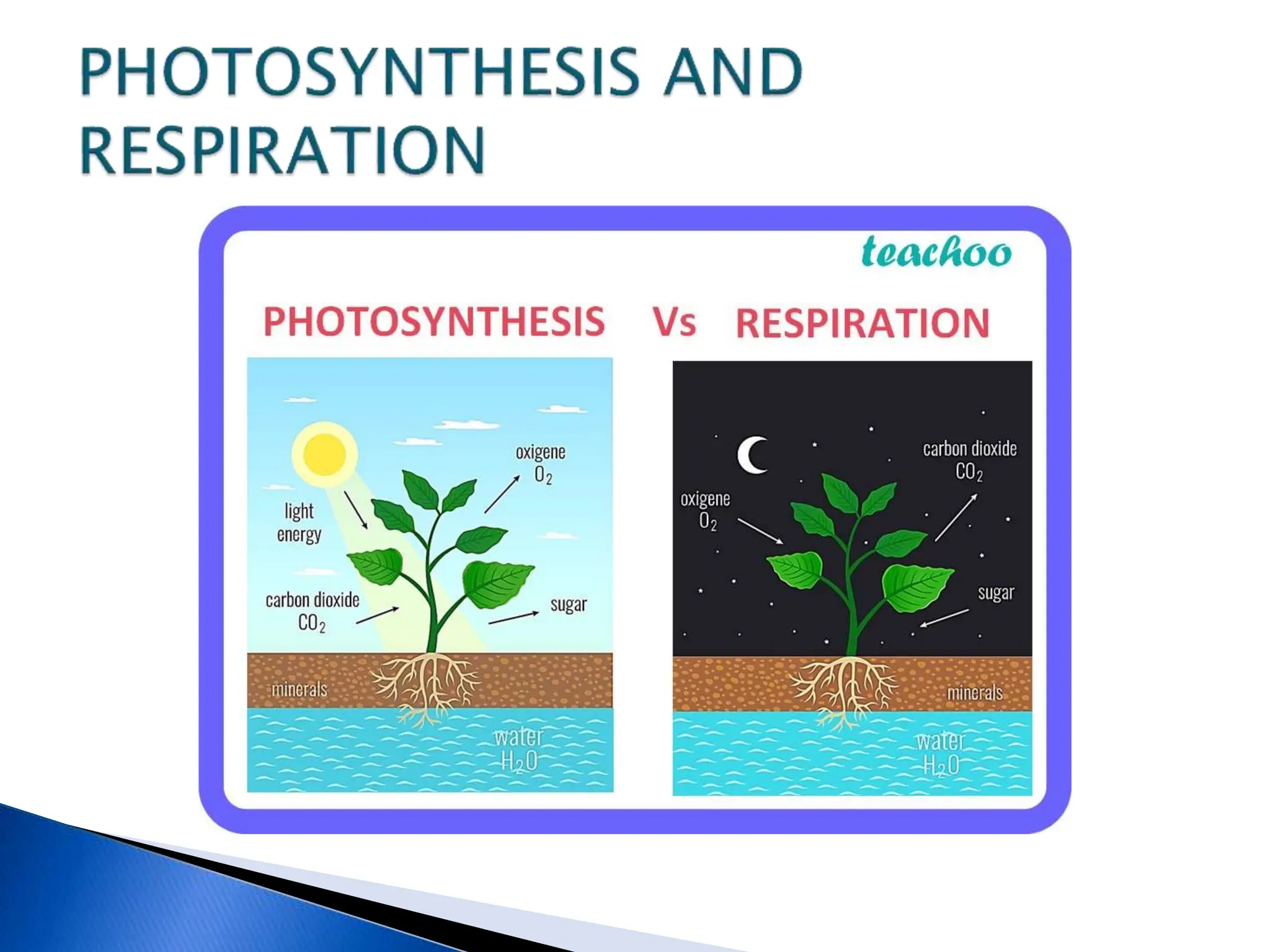
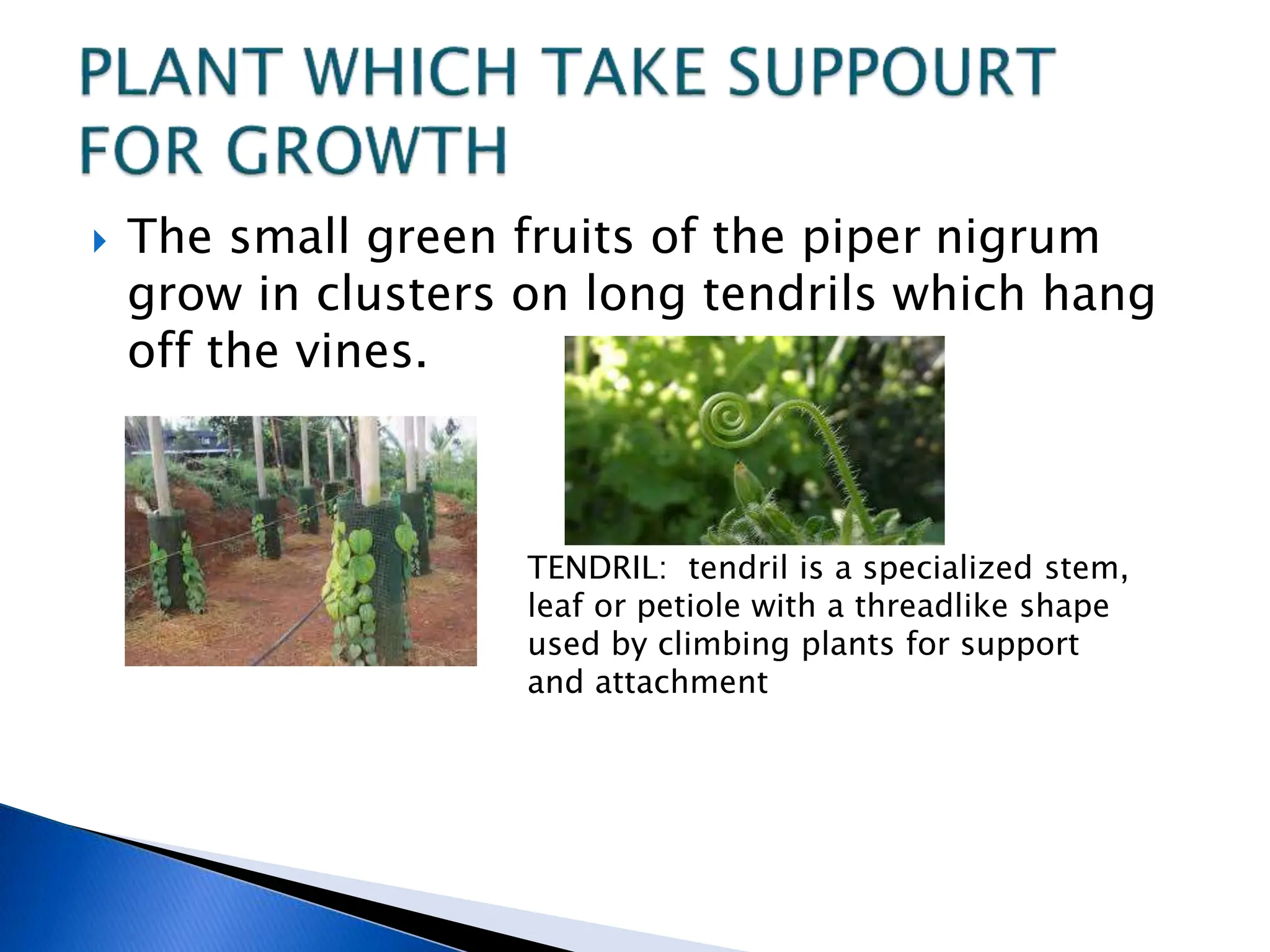
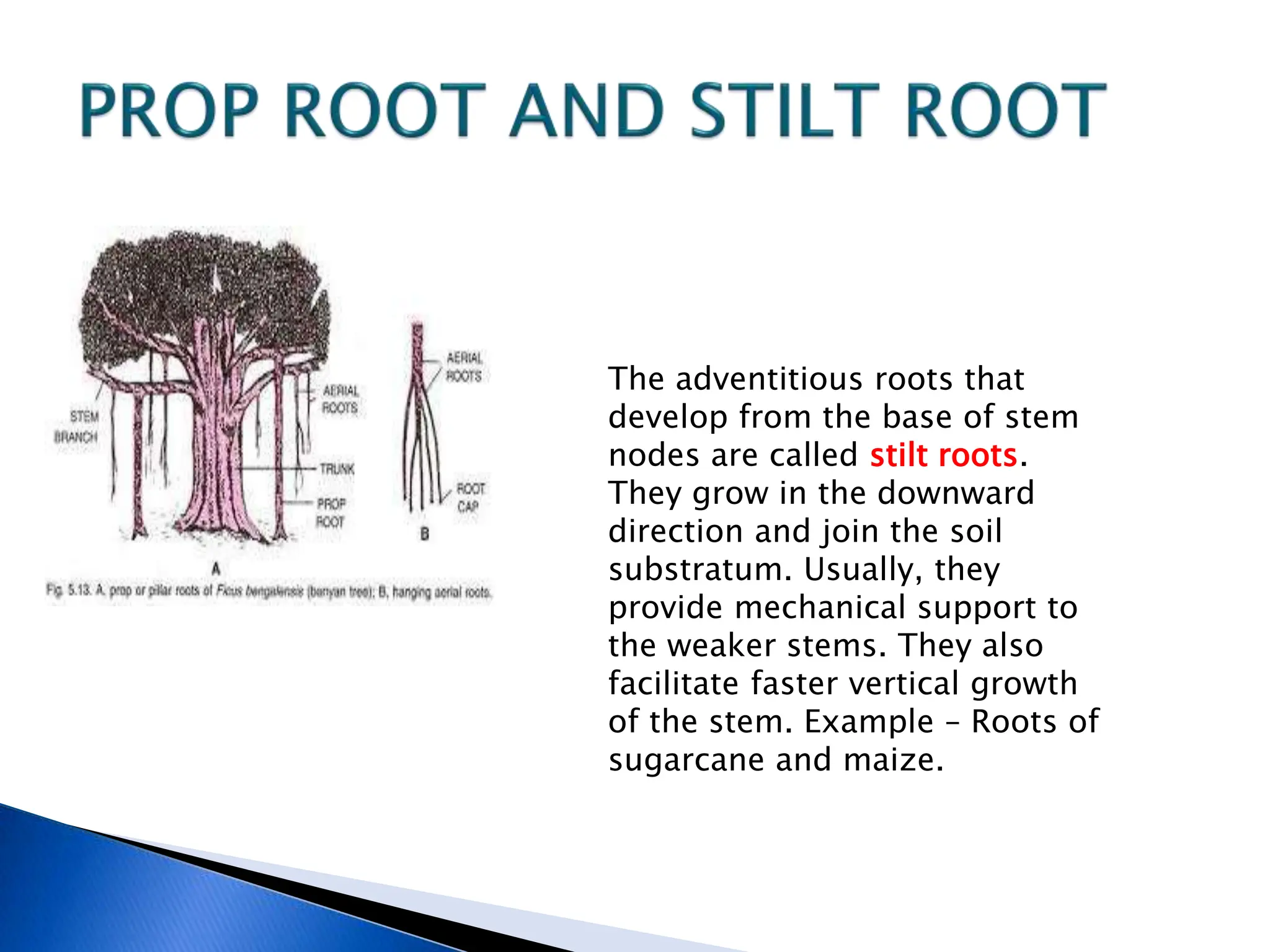
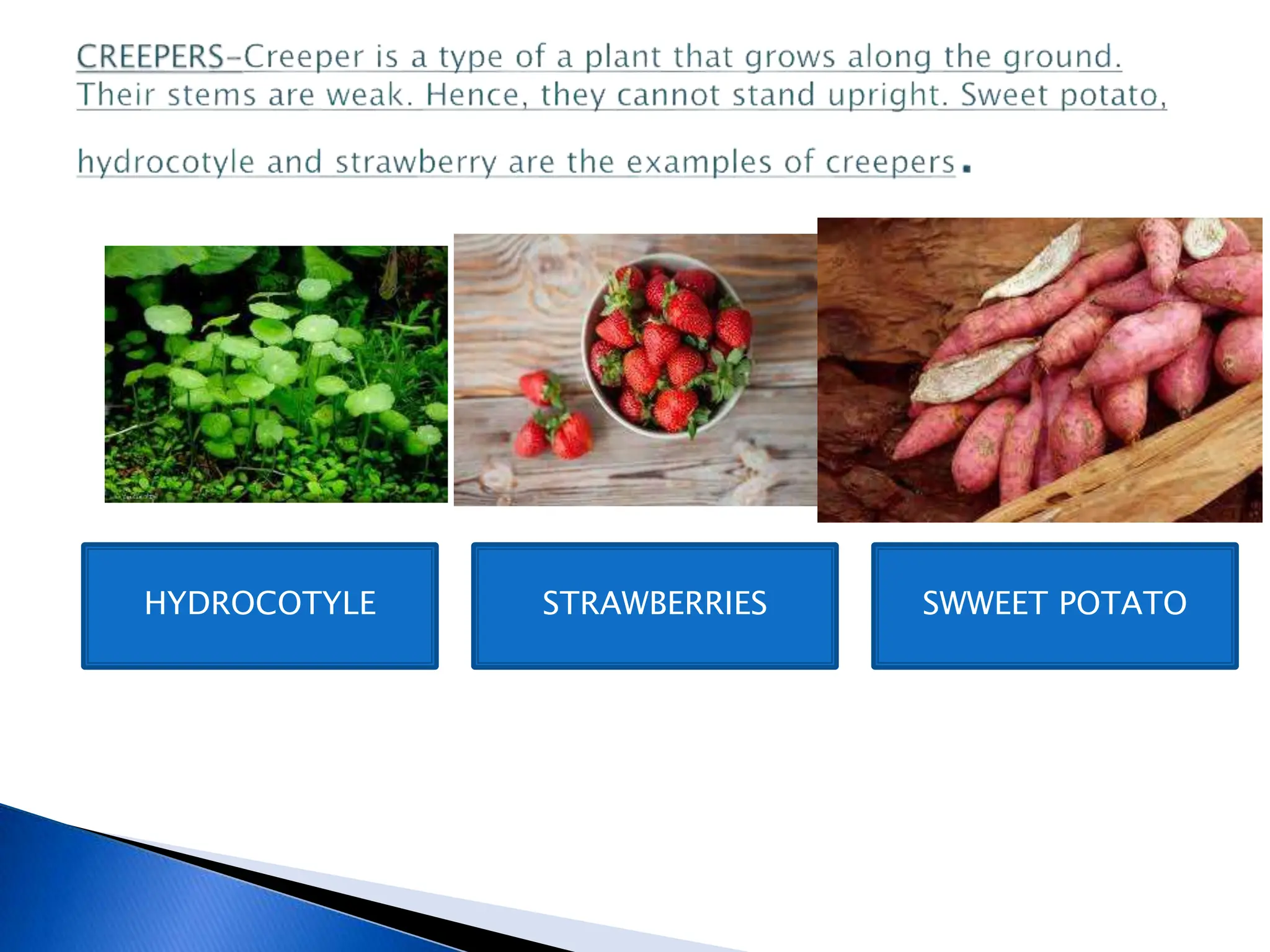
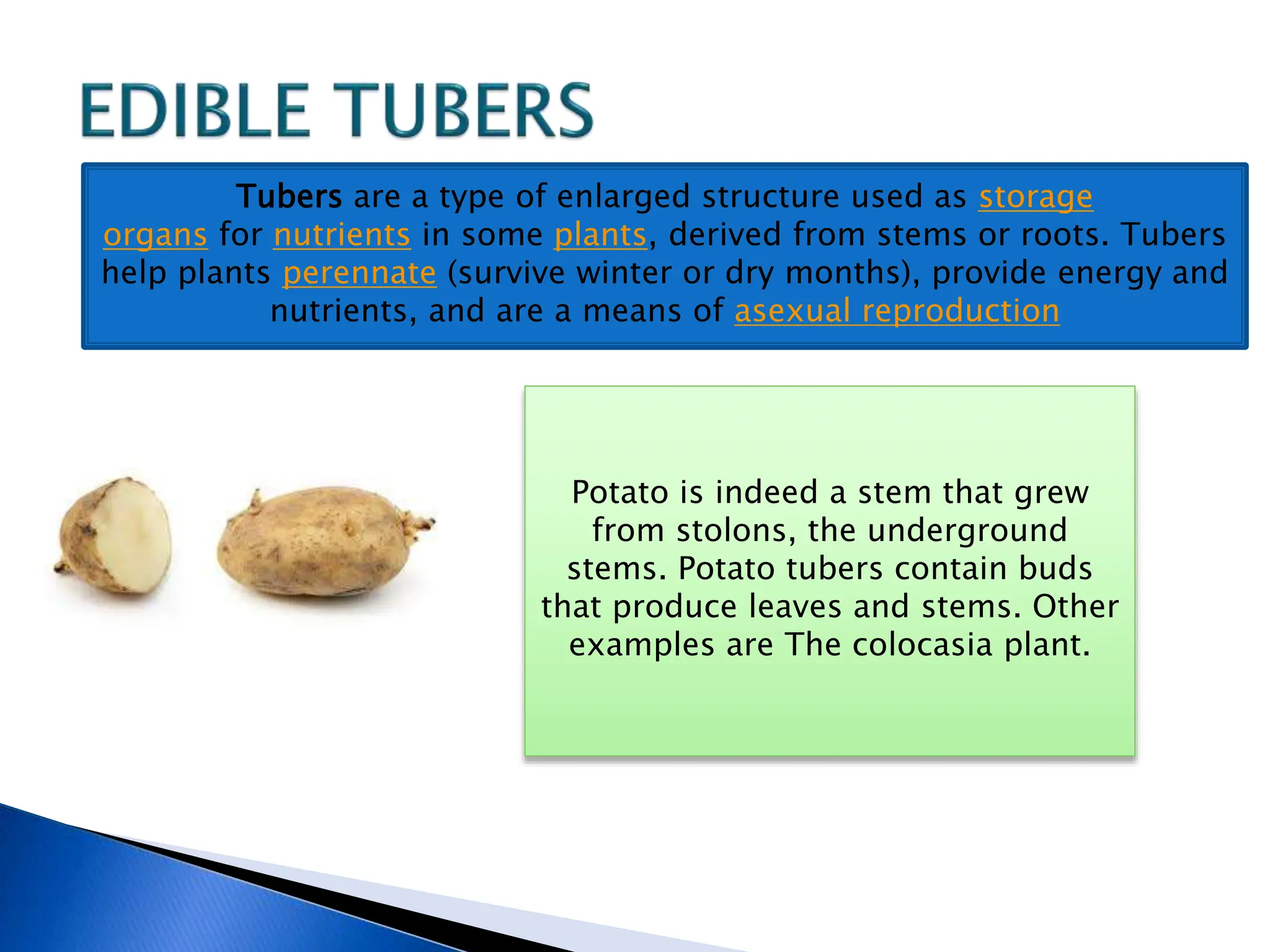
The document discusses the importance of a balanced diet and the roles of various nutrients derived from plants and foods, emphasizing the interconnectedness of plant biology, including photosynthesis and cellular respiration. It explains different plant structures and types, such as epiphytes, climbers, and parasitic plants, highlighting their adaptations and functions. Additionally, the document notes the significance of trees and forests in providing habitats and resources in ecosystems.