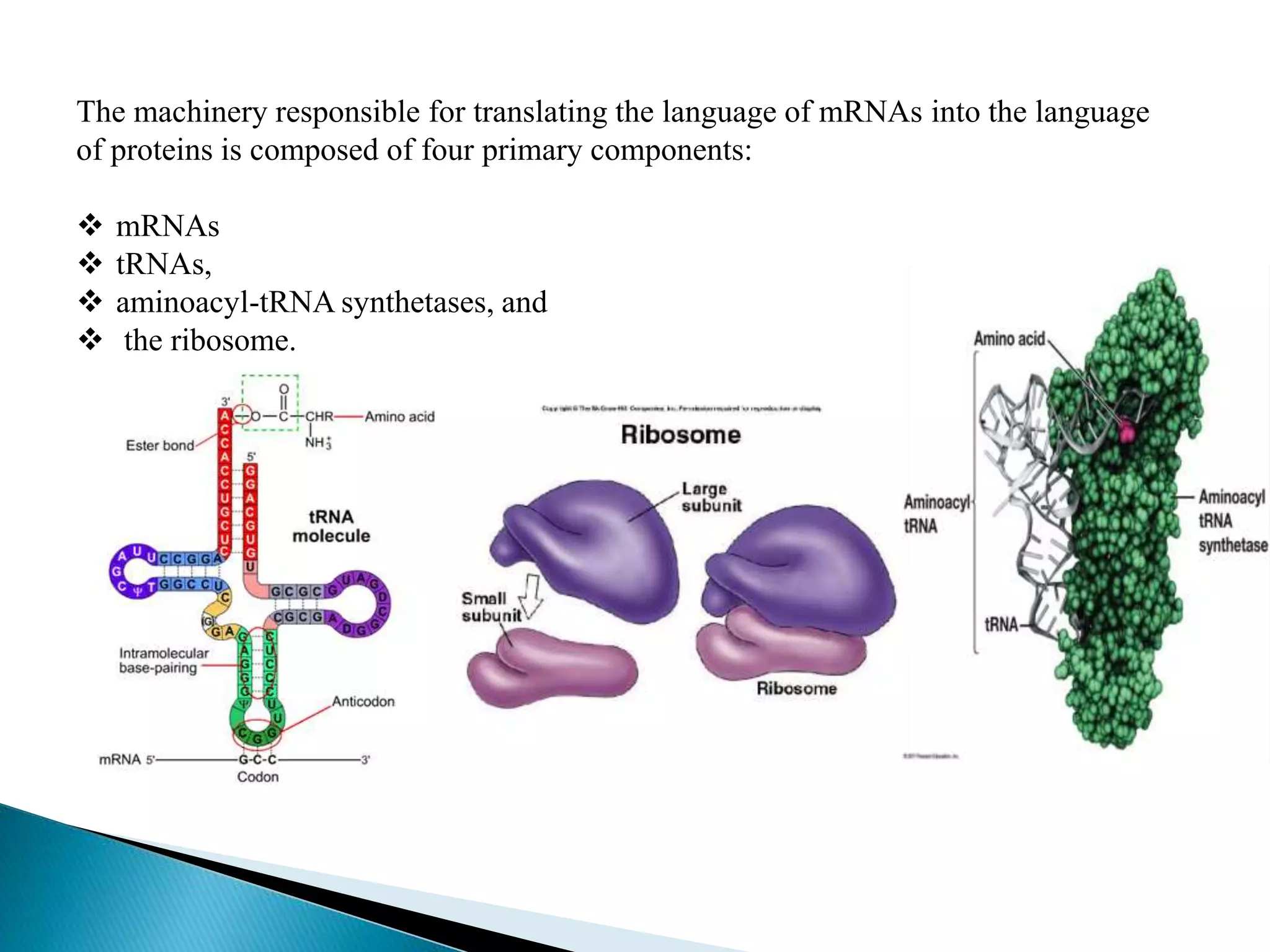
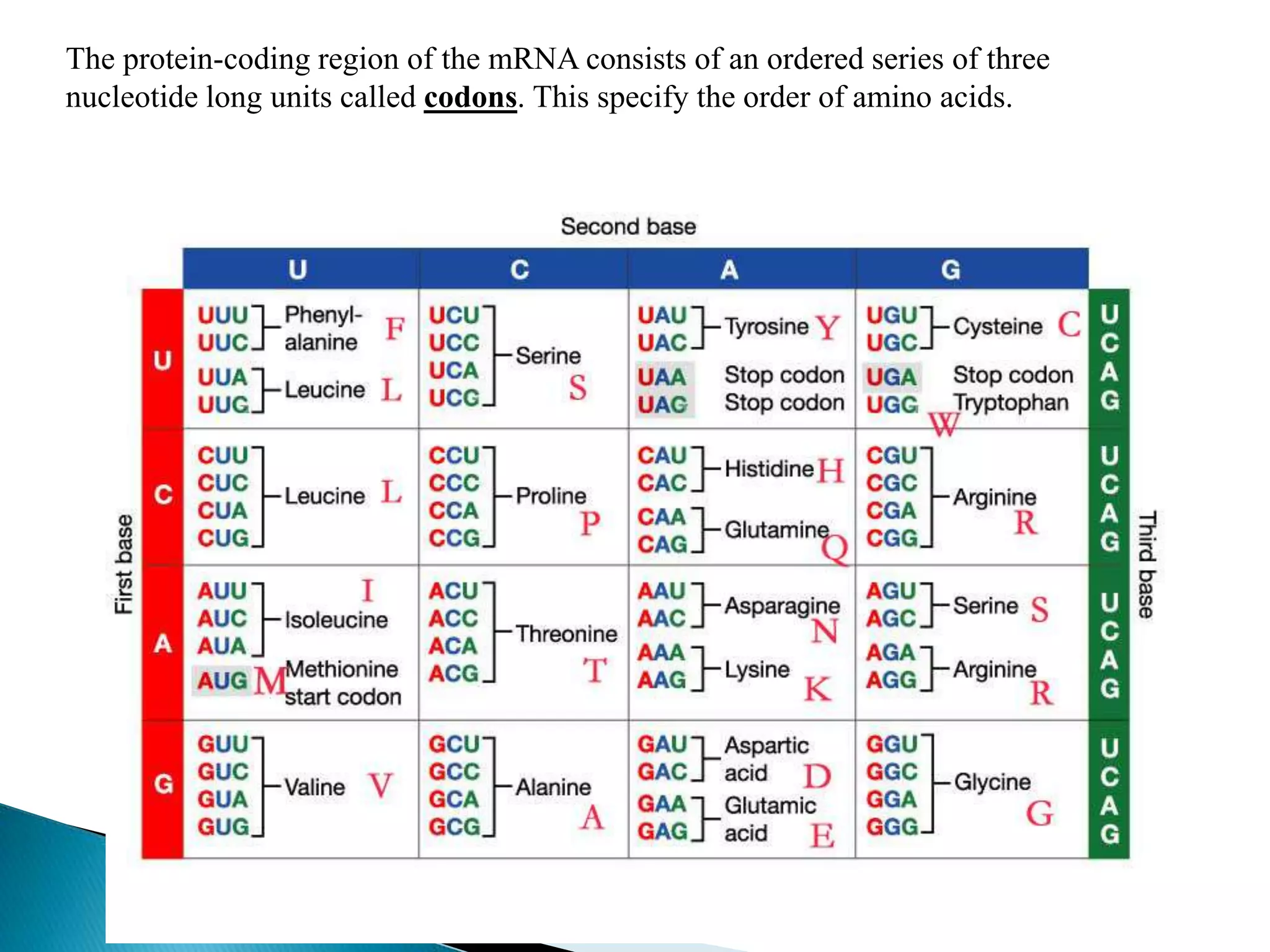
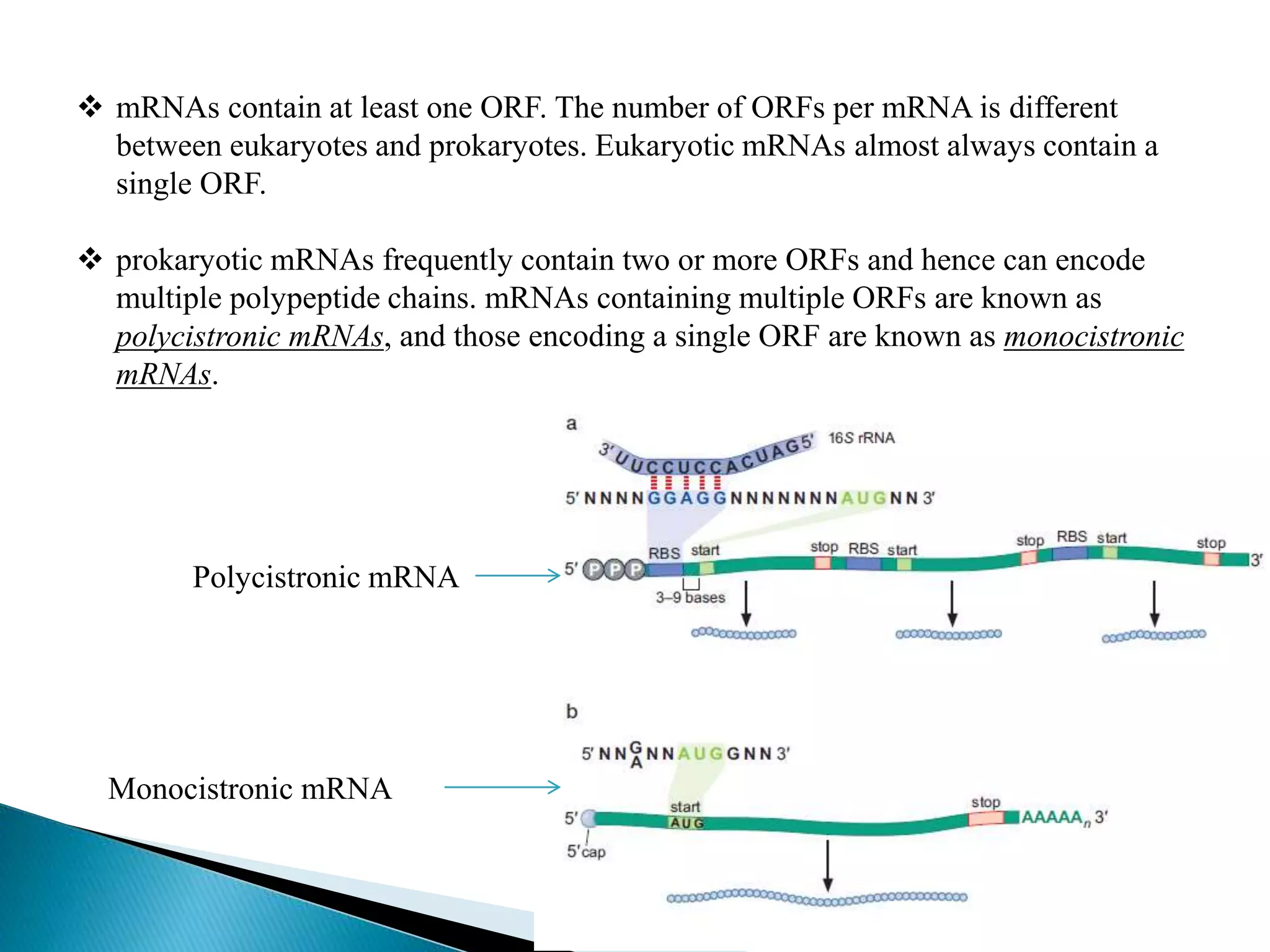
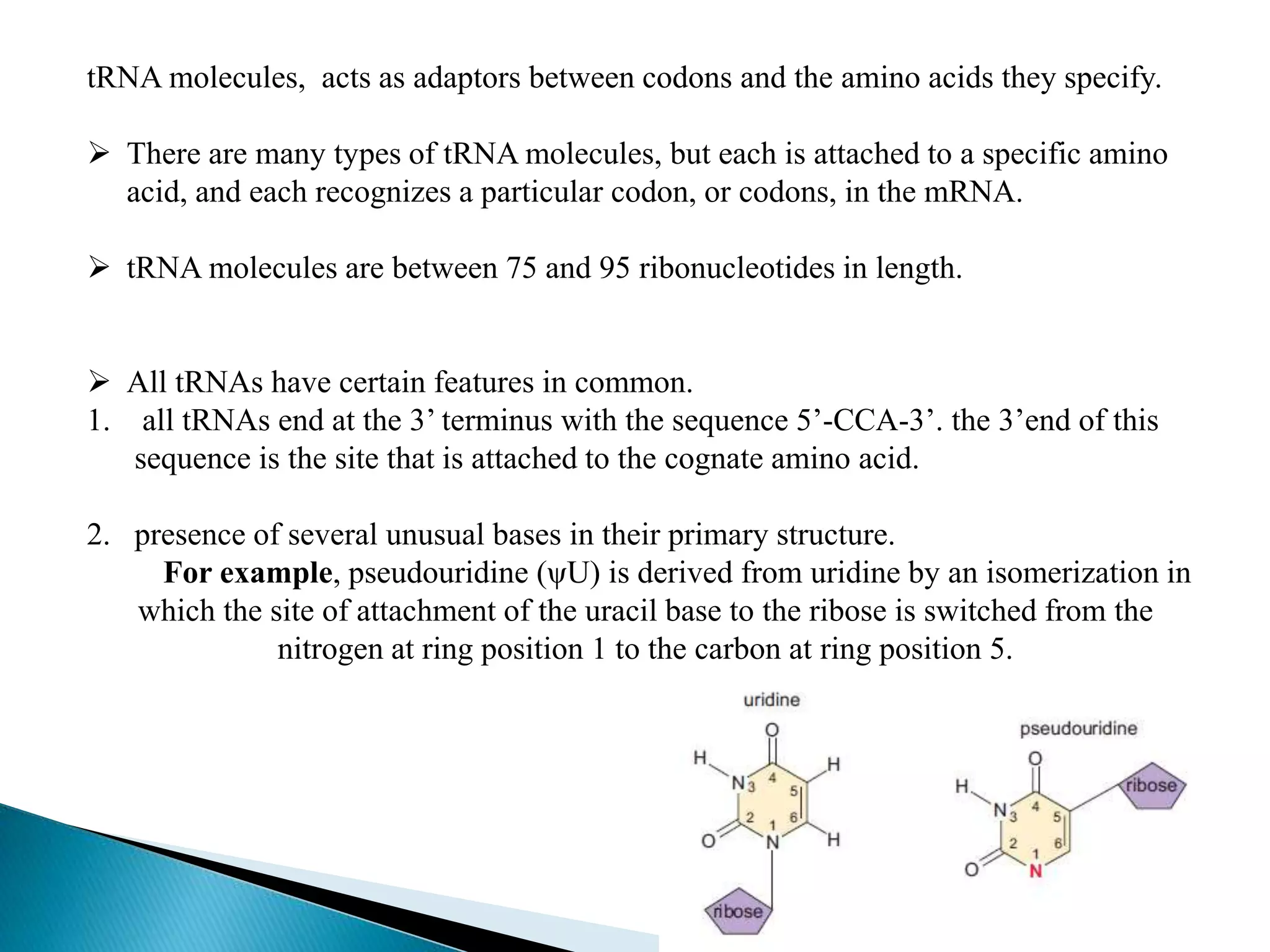
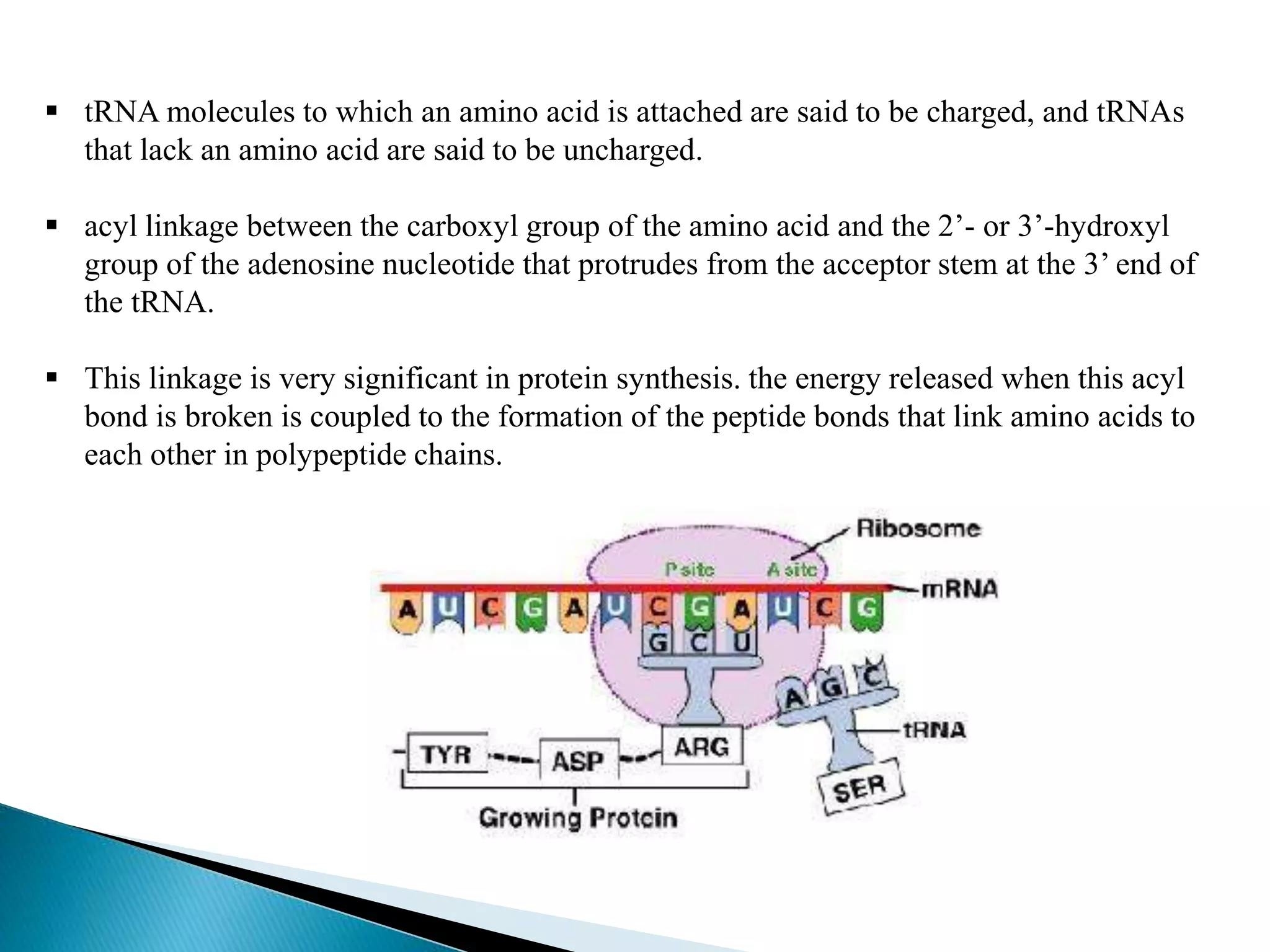
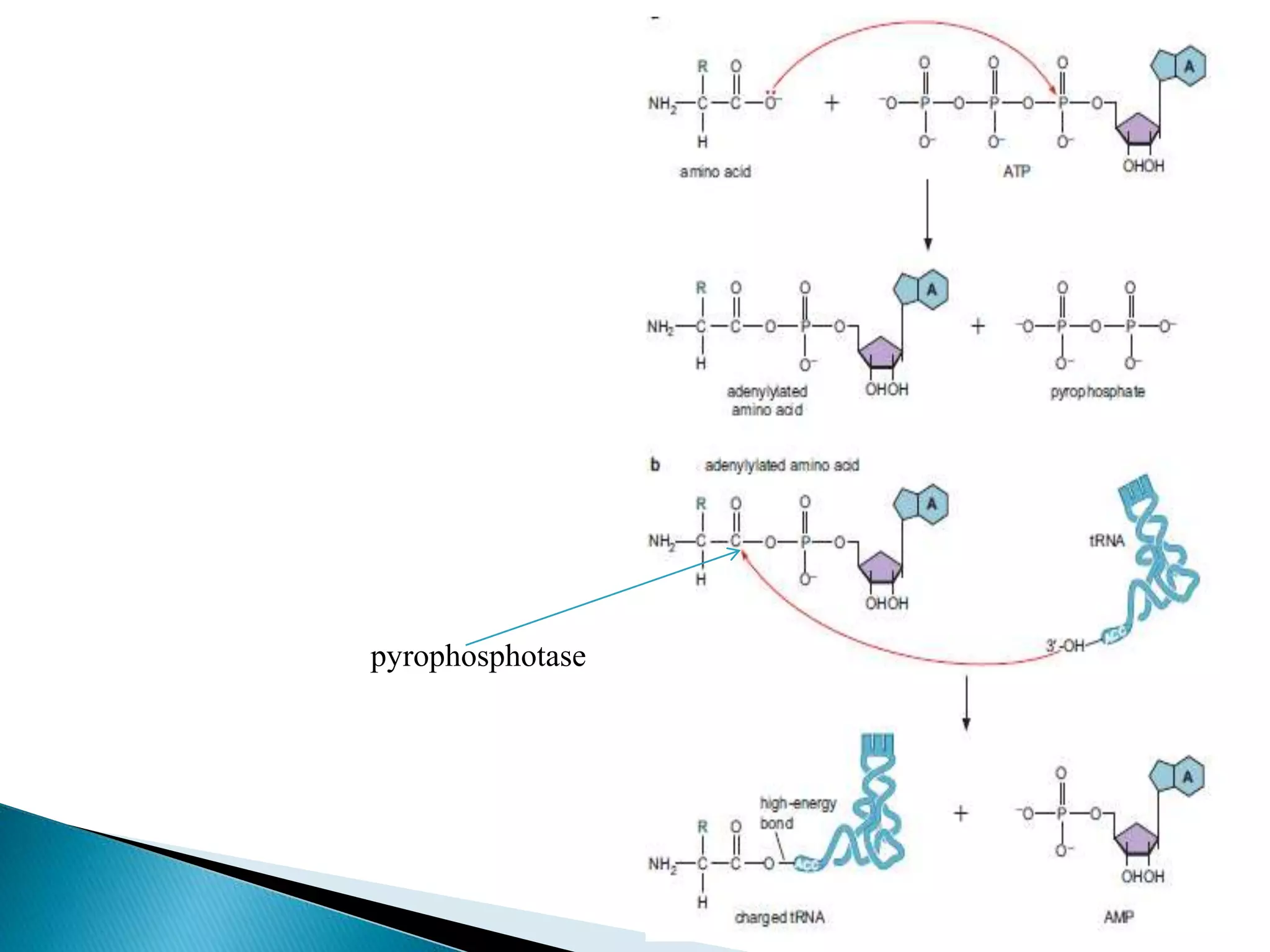
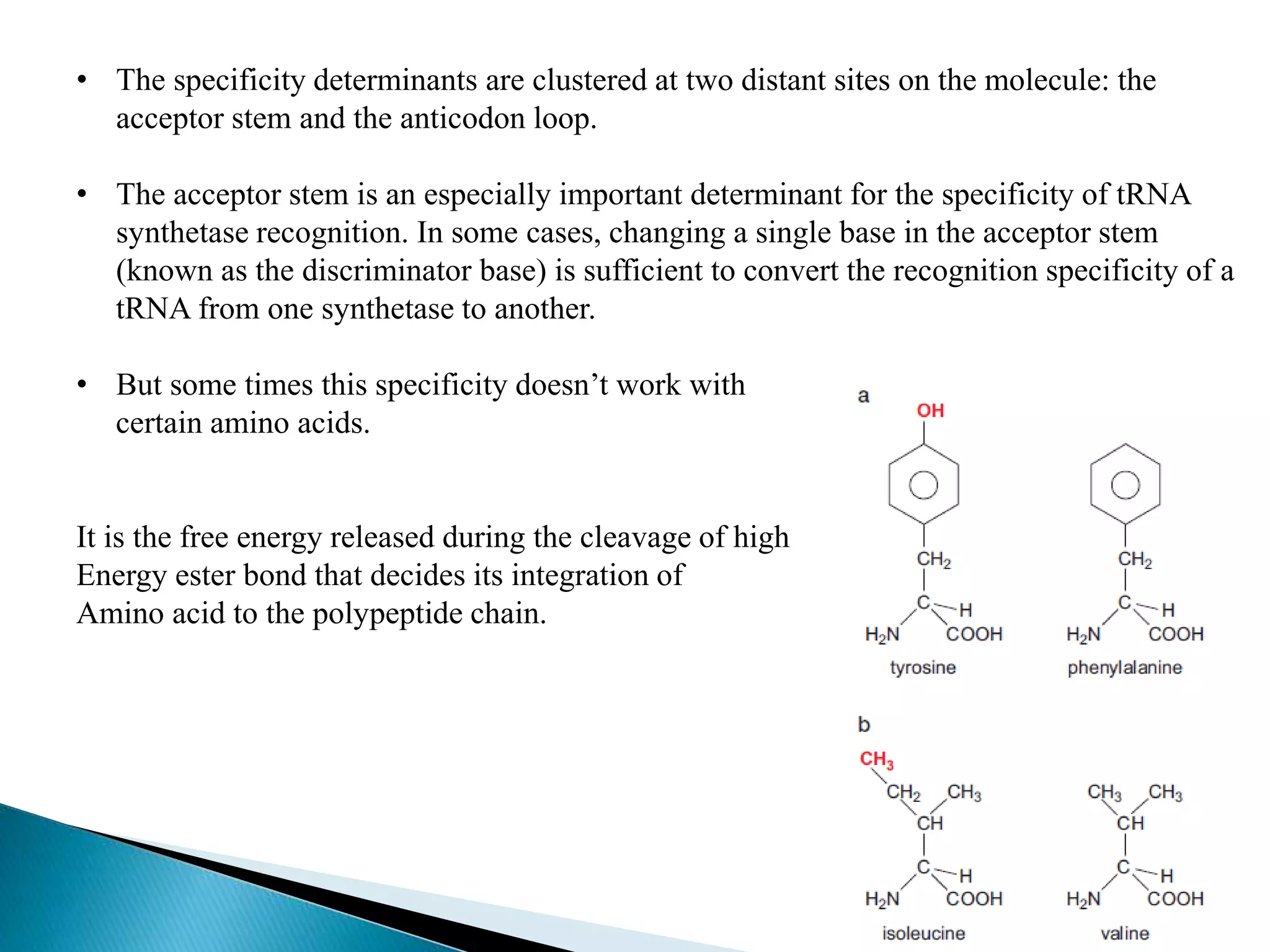
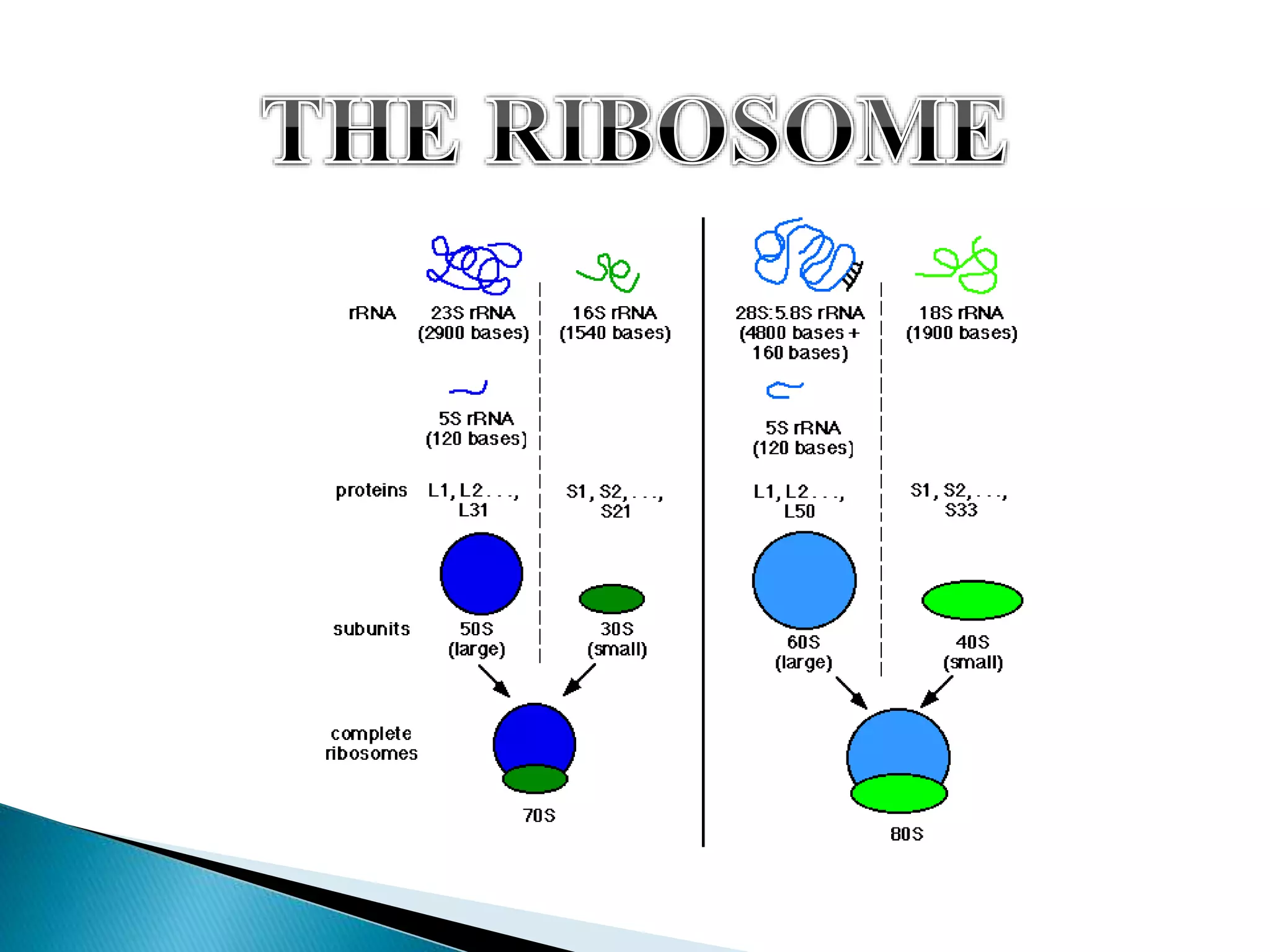
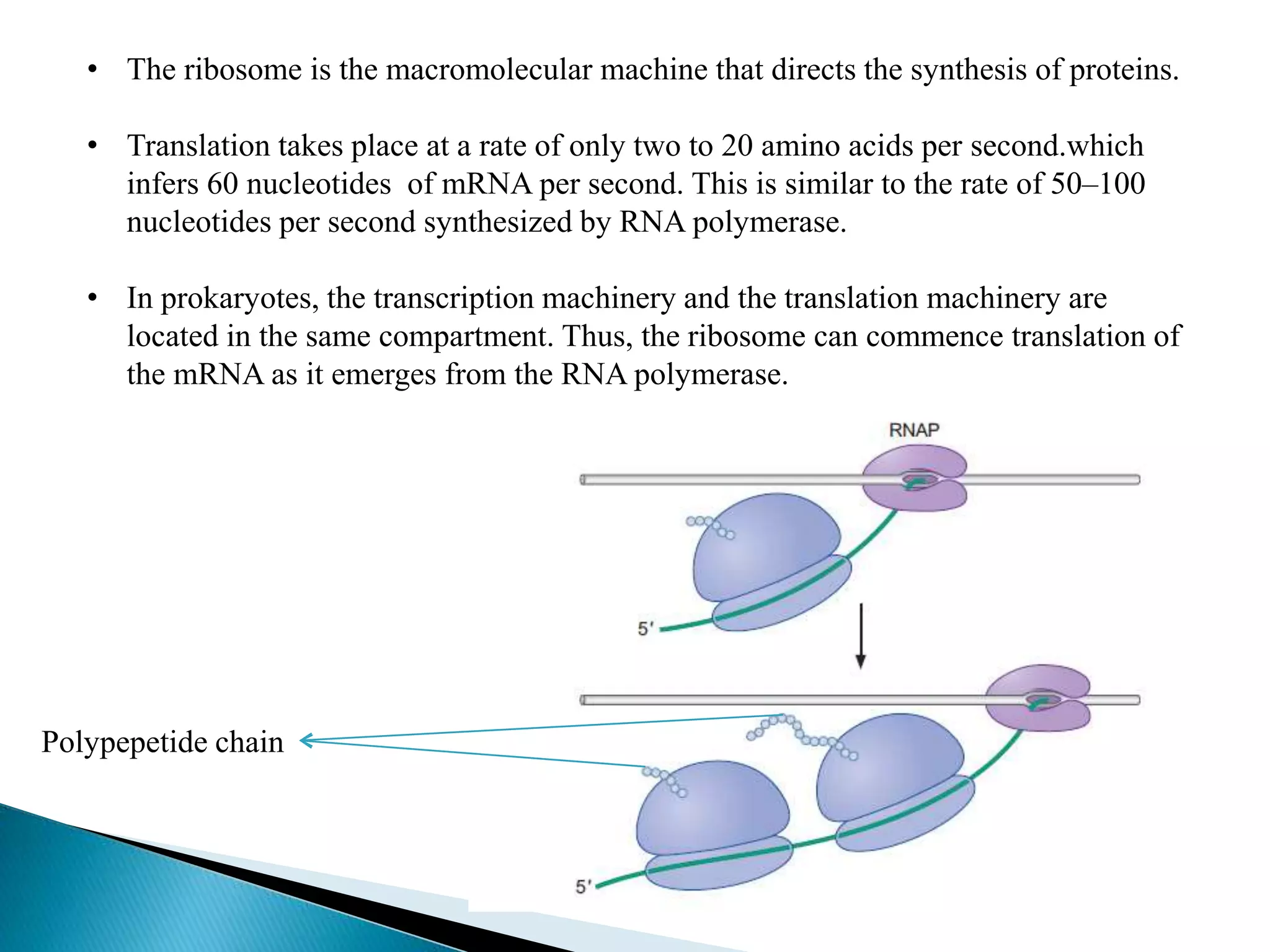
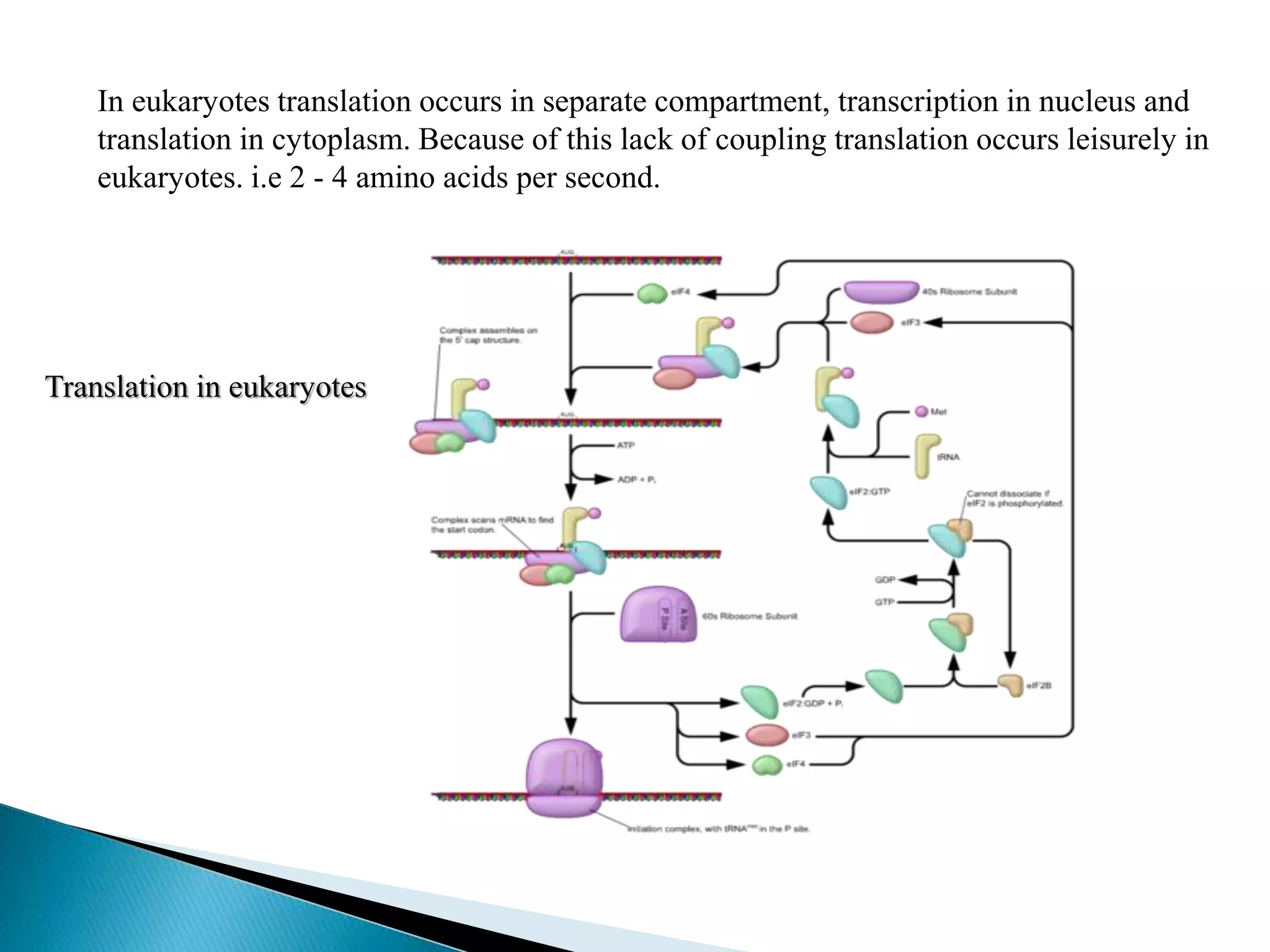
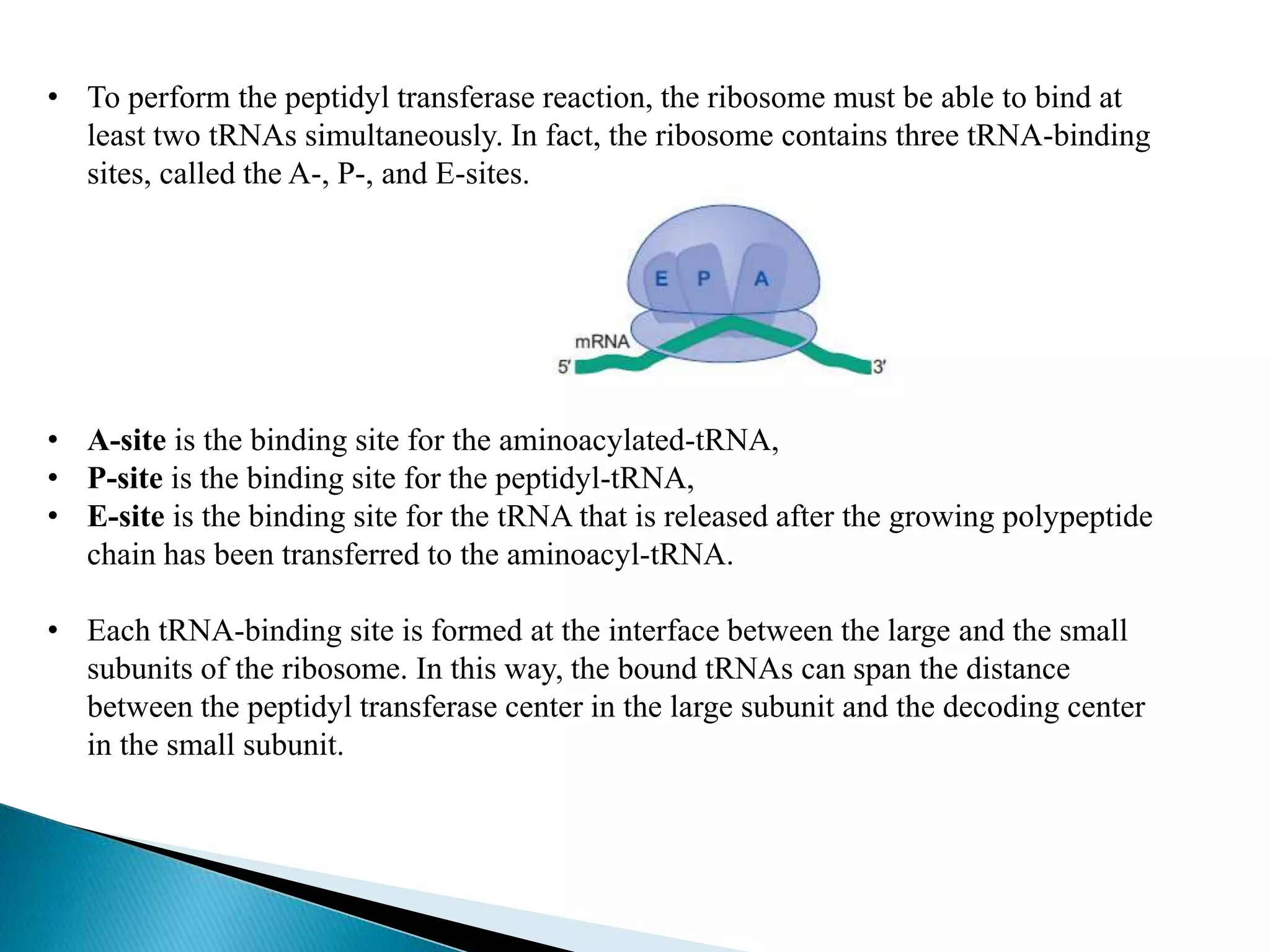
This document discusses the process of translation in cells. It defines translation as the process by which the genetic information in messenger RNA (mRNA) is used to direct the synthesis of proteins. The key components involved in translation are mRNA, transfer RNA (tRNA), aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, and ribosomes. Translation involves tRNAs carrying amino acids to the ribosome, where they are linked together into a polypeptide chain according to the codons in the mRNA.