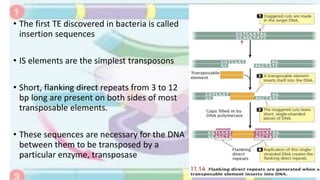
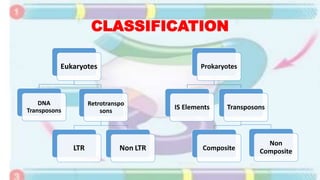
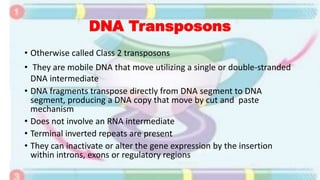
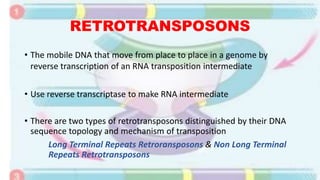
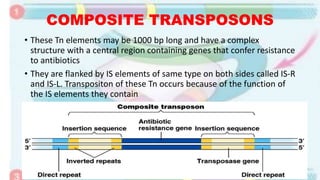
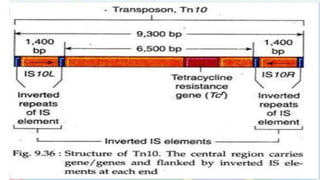
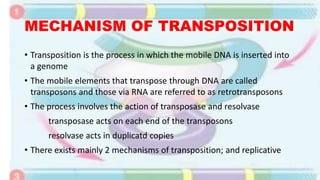
Transposable elements are mobile DNA sequences found in all organisms that were first discovered by Barbara McClintock in corn in the 1940s. They make up at least 50% of human DNA and move via "cut and paste" or reverse transcription mechanisms. There are several classes of transposable elements including DNA transposons, LTR retrotransposons, non-LTR retrotransposons, and insertion sequences found in bacteria. Transposable elements move within genomes through the action of the transposase enzyme and can cause mutations when they insert into genes.