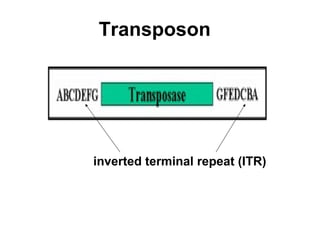
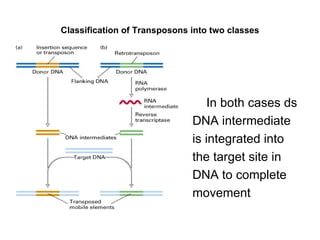
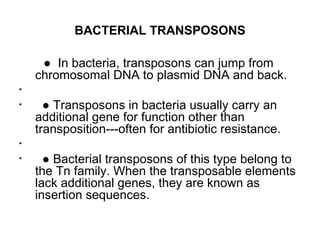
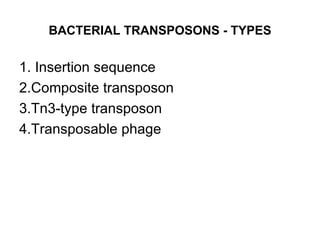
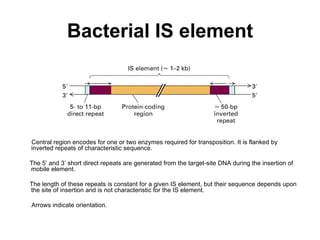
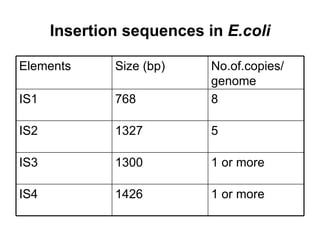
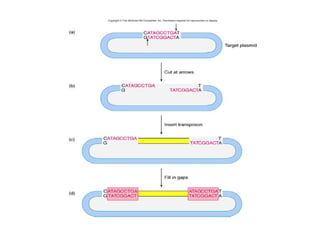
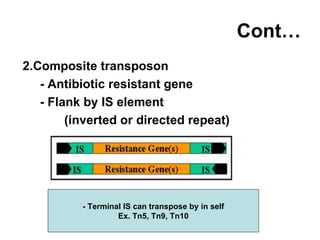
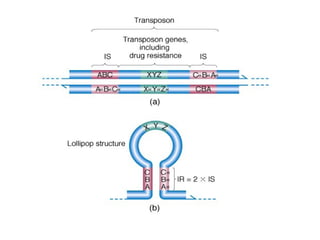
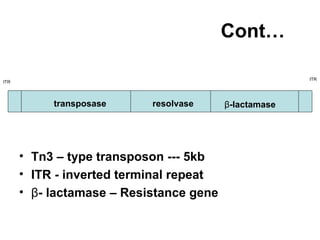
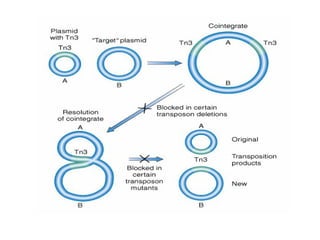
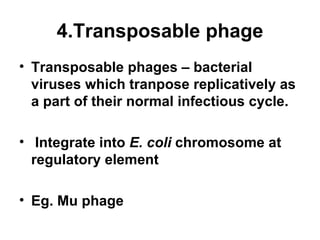
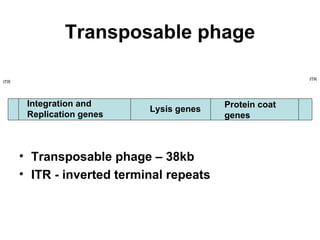
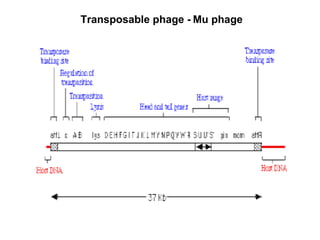
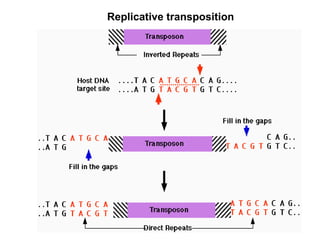
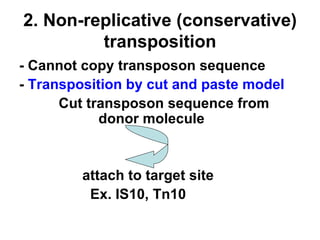
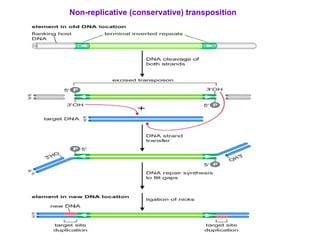
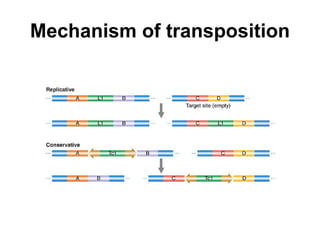
Bacterial transposons are mobile segments of DNA that can move within bacterial genomes. There are two main types: insertion sequences, which consist only of the DNA required for transposition; and composite transposons, which contain additional genes like antibiotic resistance genes flanked by insertion sequences. Transposons can move within genomes through replicative or conservative transposition and have played an important role in bacterial evolution and antibiotic resistance.