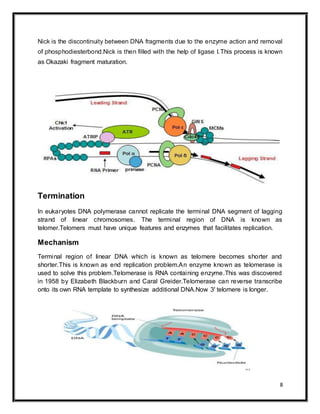
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. It occurs in three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation begins at origins of replication and involves unwinding of the DNA double helix by helicases. During elongation, DNA polymerases add nucleotides to build new strands based on the existing DNA templates. Termination occurs when the replication forks meet at the end of the DNA molecule. DNA replication is semi-conservative, meaning each new DNA molecule contains one original and one new strand of DNA.