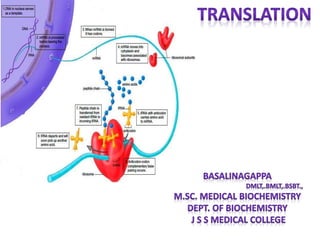
Translation is the process by which messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded to build polypeptides through a sequence of steps—initiation, elongation, and termination—utilizing transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomes. Each tRNA carries a specific amino acid and matches its anticodon to the codons on the mRNA during polypeptide synthesis, forming peptide bonds that lengthen the amino acid chain until a stop codon signals termination. Post-translational modifications then occur to the newly formed polypeptide to attain its functional state in cellular processes.