The document discusses traditional and Modigliani-Miller (MM) approaches to capital structure.
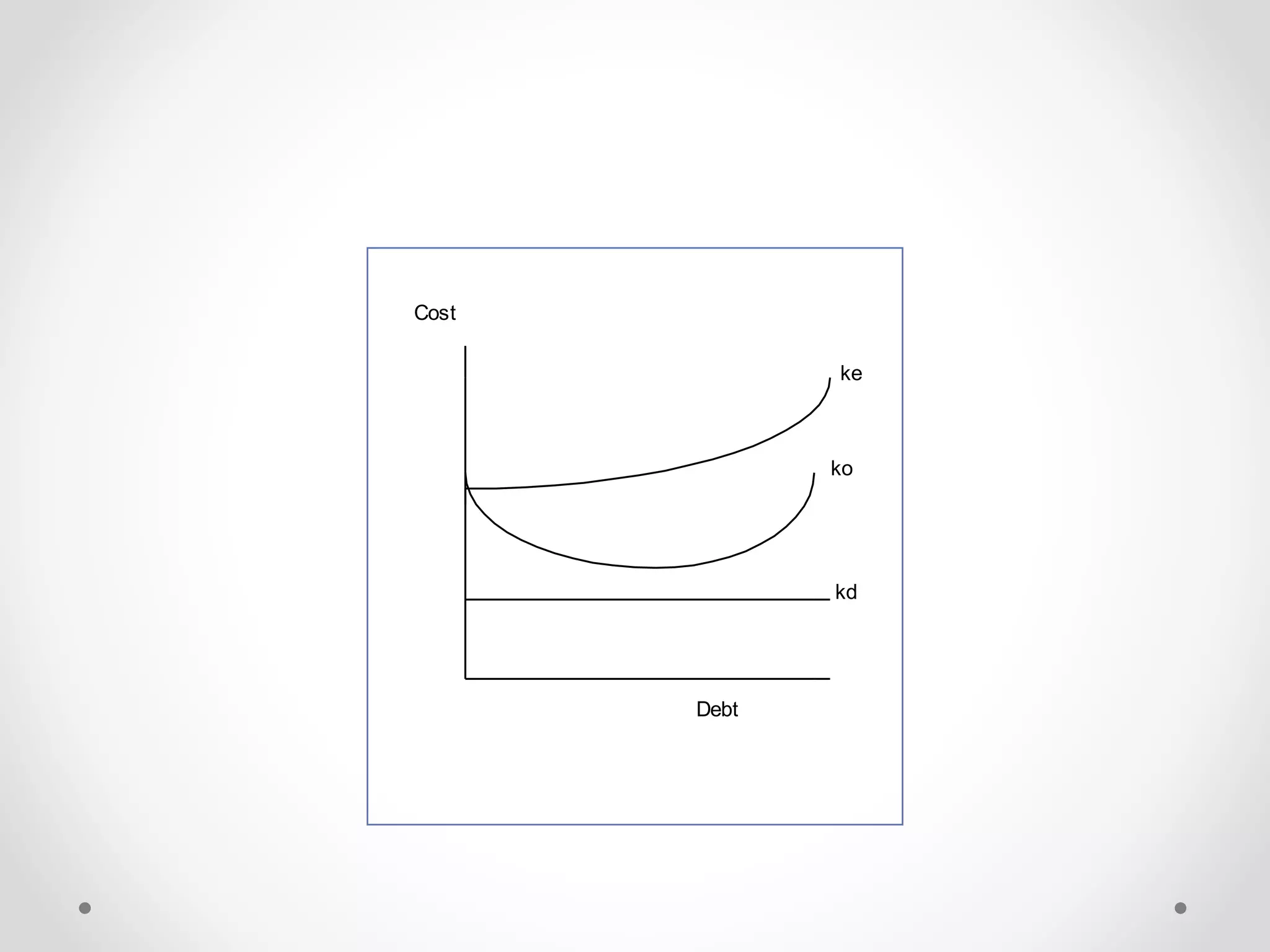
The traditional approach argues that a company's value and cost of capital can be optimized through a judicious mix of debt and equity, up to a certain level of debt. Beyond this, increased financial risk from more debt outweighs the benefits of cheaper debt.
The MM approach argues that a company's value depends only on its operating income and risk, not its capital structure. It proposes that markets will equalize any differences in value or cost of capital through arbitrage. The cost of equity rises in line with debt, keeping the weighted average cost of capital constant.
While influential, the MM approach makes