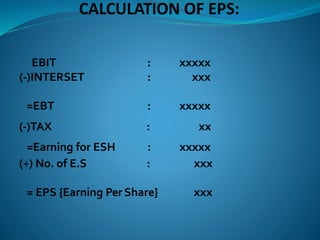
The document discusses various approaches to determine an appropriate capital structure, focusing on the EBIT-EPS approach which aims to maximize earnings per share (EPS) against different levels of debt and equity. It highlights the importance of analyzing capital structures, potential trade-offs, and the implications of leverage on earnings. Additionally, it notes the drawbacks of the EBIT-EPS approach, particularly its tendency to overlook risk premiums associated with increased debt.