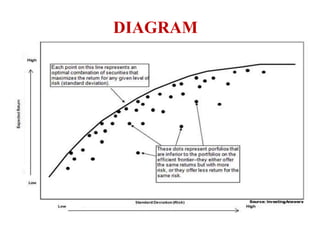
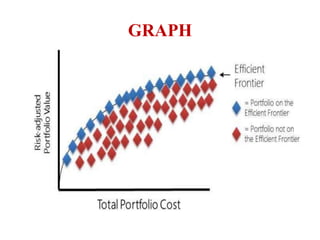
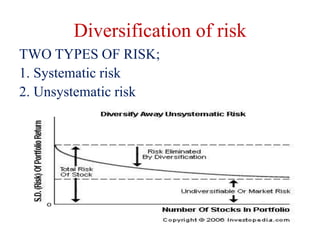
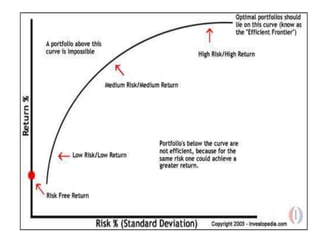
Portfolio management involves selecting a collection of financial or physical assets to maximize returns while minimizing risk through diversification. The Markowitz model, introduced by Harry Markowitz, provides a framework for selecting the optimal portfolio based on risk-return tradeoffs, highlighting the importance of expected returns and variance. Effective portfolio construction aims to create a diversified mix of investments to achieve the highest possible returns for a given level of risk, while considering systematic and unsystematic risks.