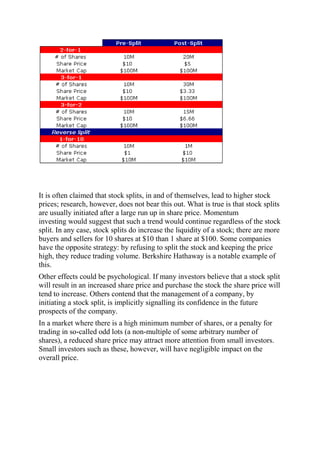
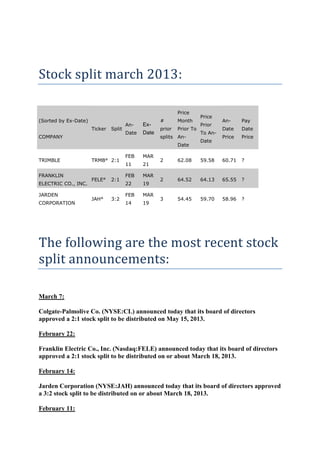
A stock split increases the number of a company's outstanding shares by issuing more shares to existing shareholders while reducing the market price per share, keeping the company's total market capitalization the same. Common split ratios are 2-for-1, 3-for-1, or 3-for-2. While stock splits themselves do not impact a company's value, they can increase liquidity by making shares more affordable to small investors and signaling management confidence, potentially leading to increased demand and short-term price rises after the split.