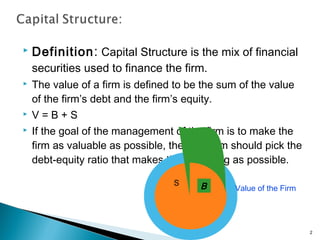
The document discusses capital structure, which is the mix of debt and equity used to finance a firm. The value of a firm is equal to the value of its debt plus the value of its equity. The optimal capital structure maximizes firm value by balancing the debt-equity ratio. Factors that influence the capital structure decision include business risk, taxes, financial flexibility, growth opportunities, and market conditions. Leverage increases risk for shareholders but also increases potential returns, as interest payments are tax deductible. Higher debt leads to greater financial risk.