This document discusses several theories of capital structure:
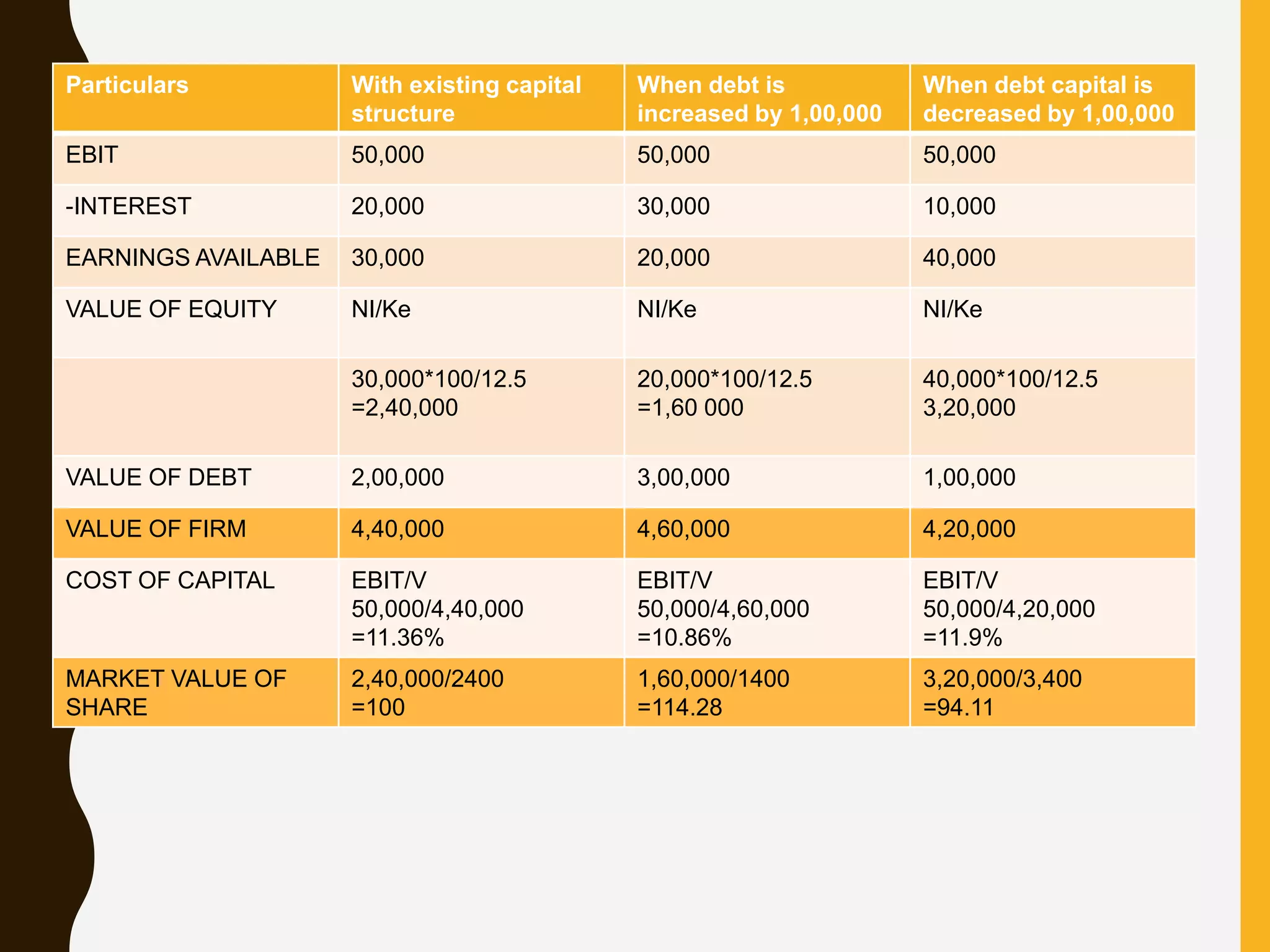
1. The net income approach developed by Durand states that a firm's value and cost of capital depend on its capital structure.
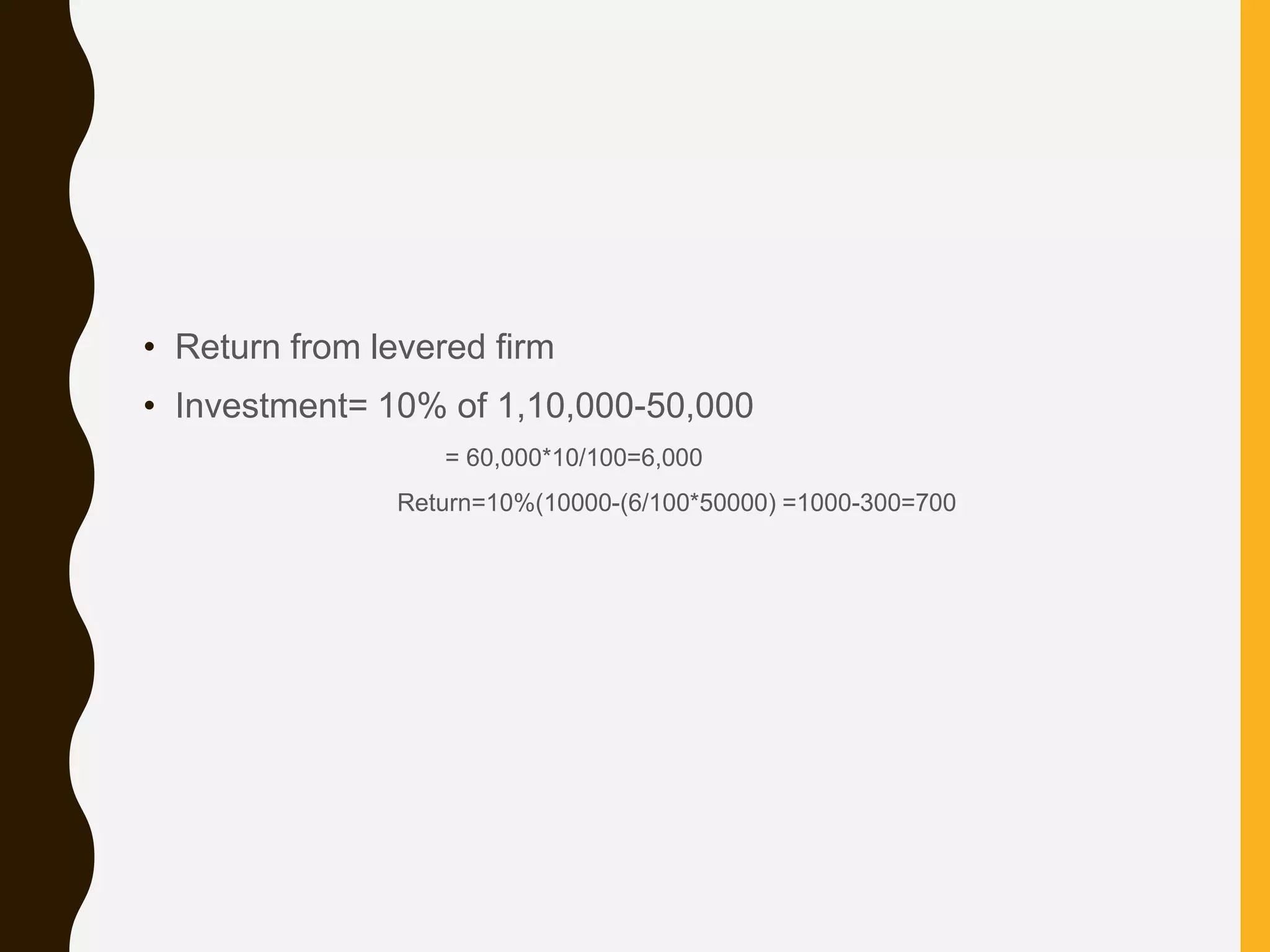
2. The net operating income approach and Modigliani-Miller approach state that a firm's total value and cost of capital are independent of its capital structure.
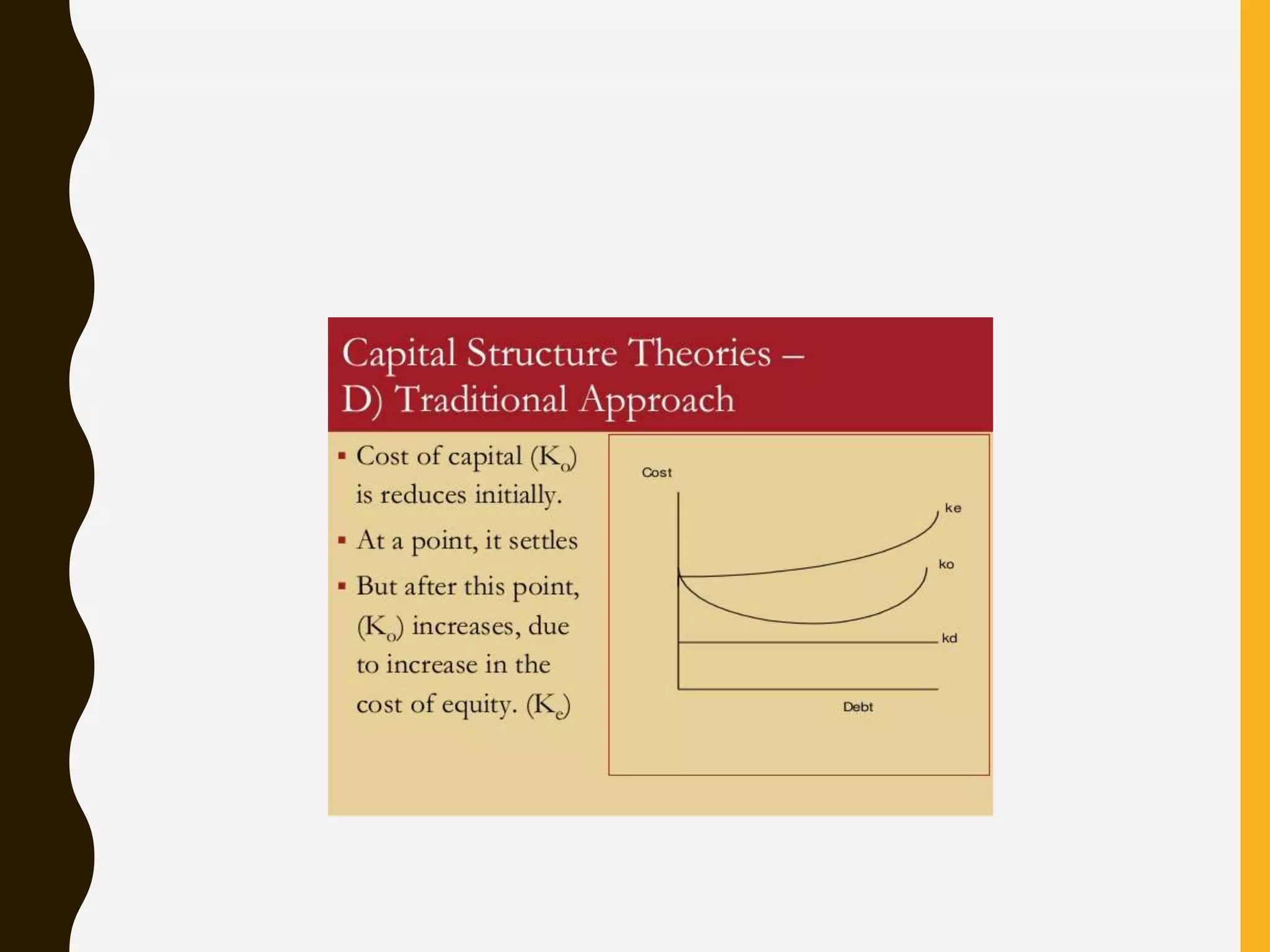
3. The traditional approach proposes that a firm's cost of capital first decreases then remains stable and eventually increases with higher leverage, implying an optimal capital structure.