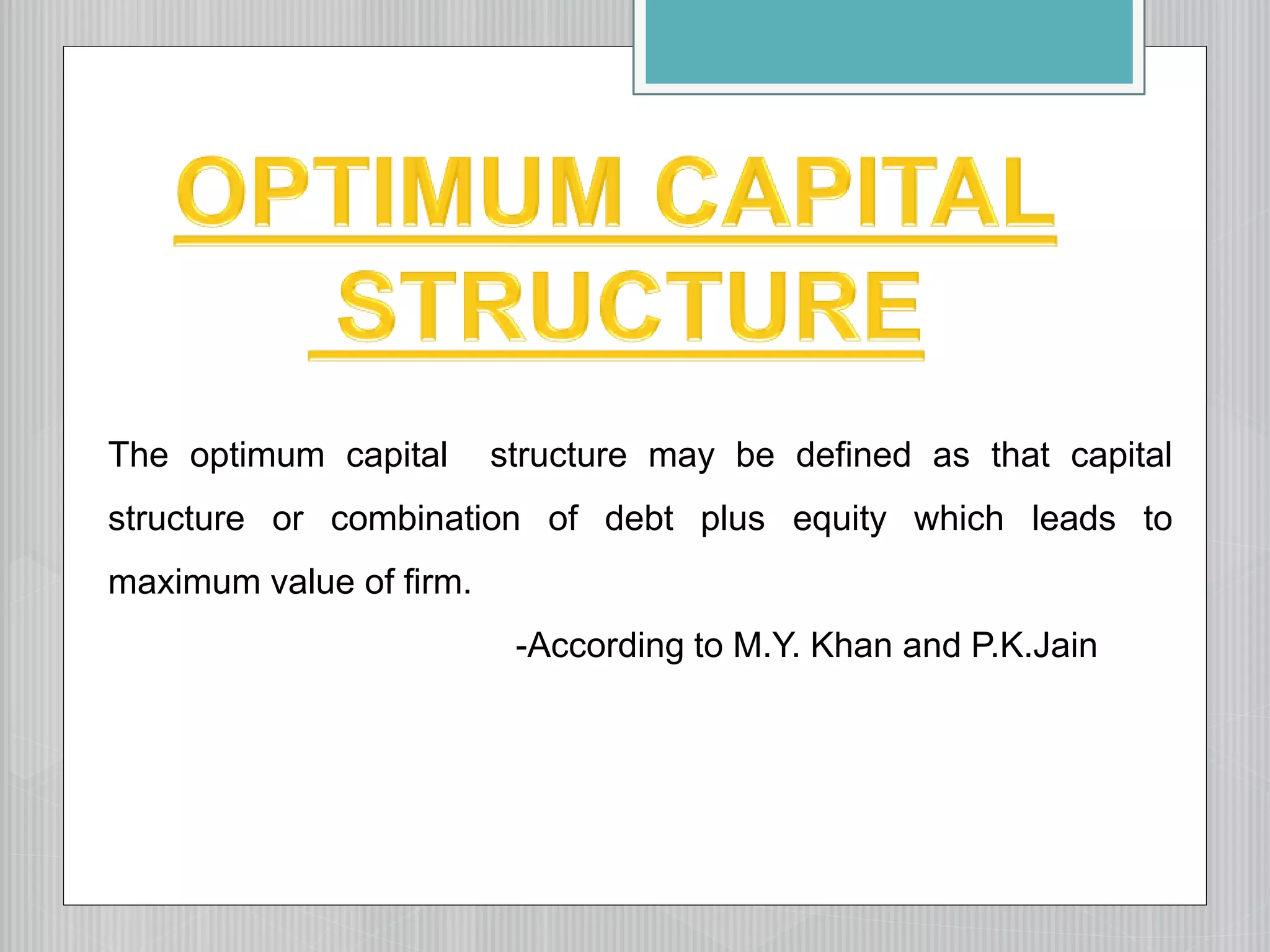
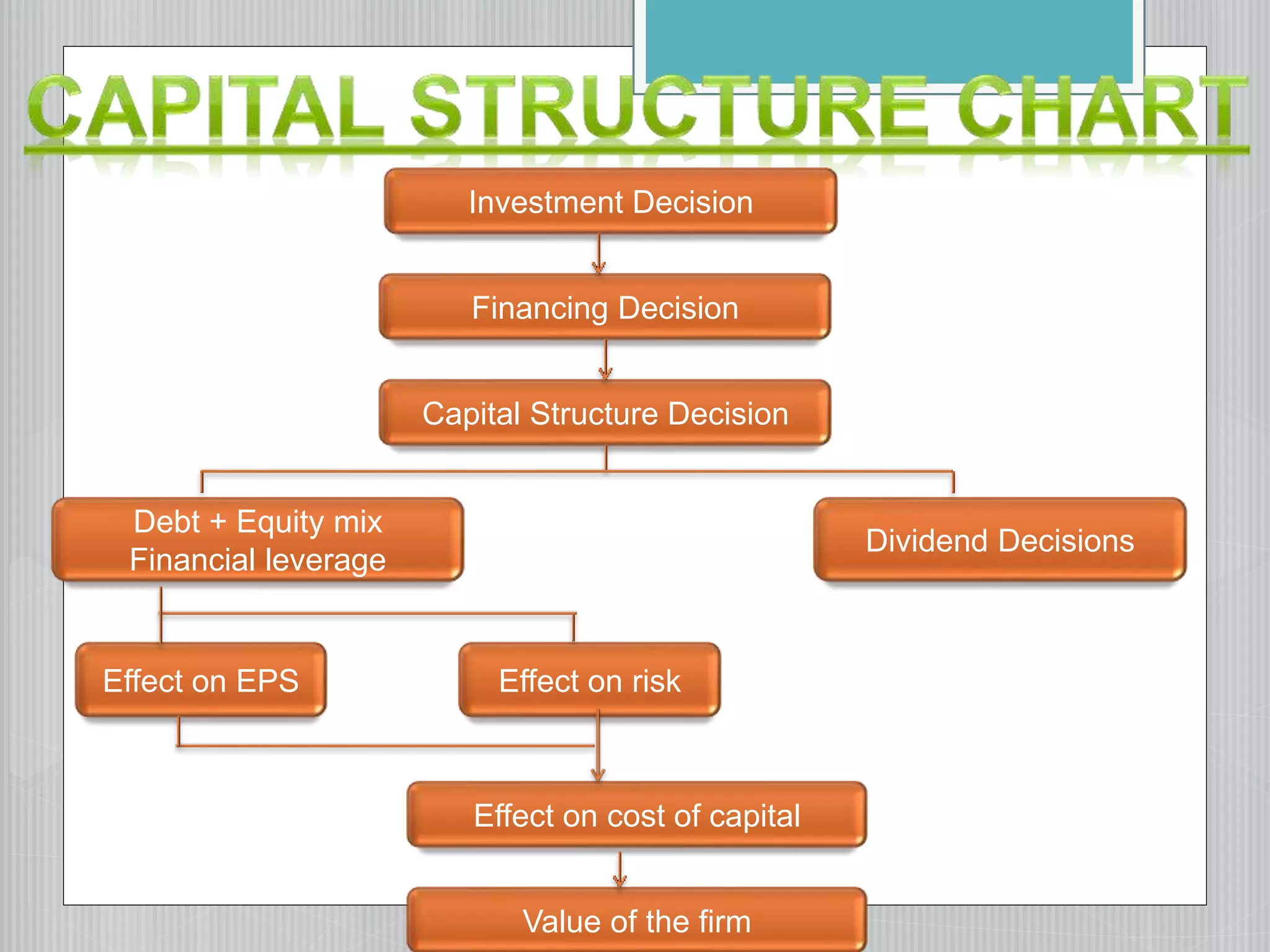
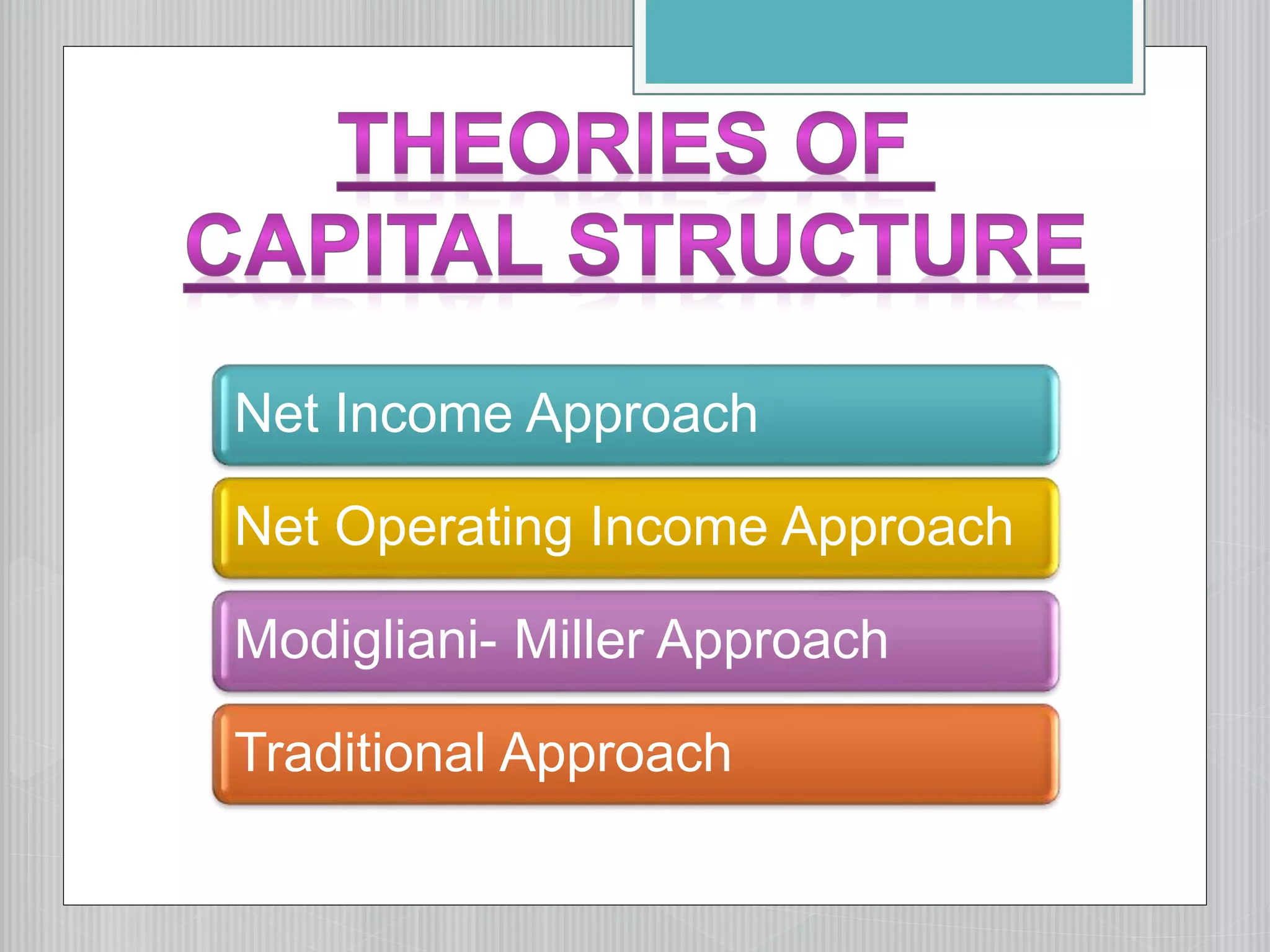
This document discusses capital structure and the factors considered when determining a firm's optimal capital structure. It discusses several approaches to determining the optimal capital structure, including:
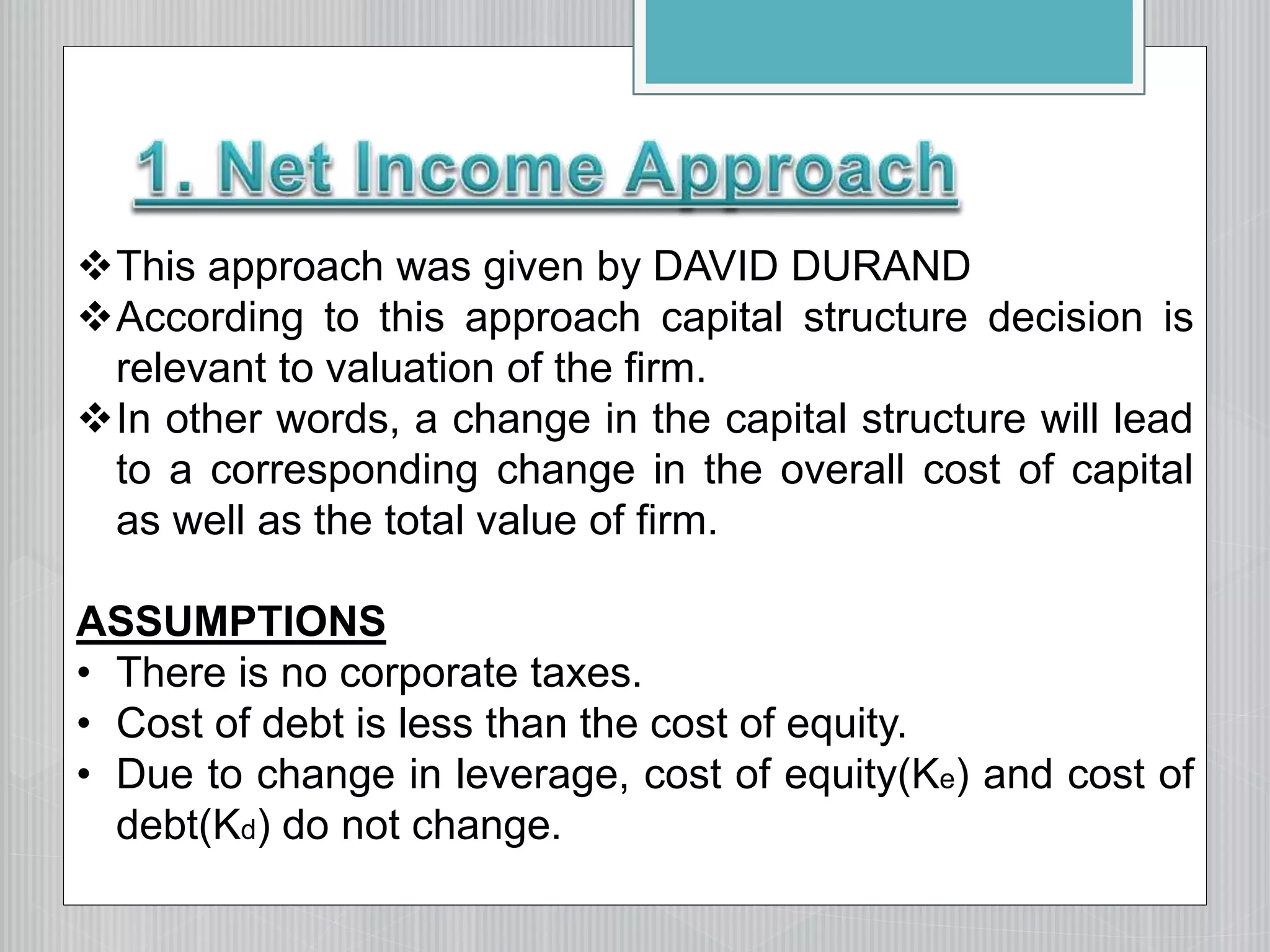
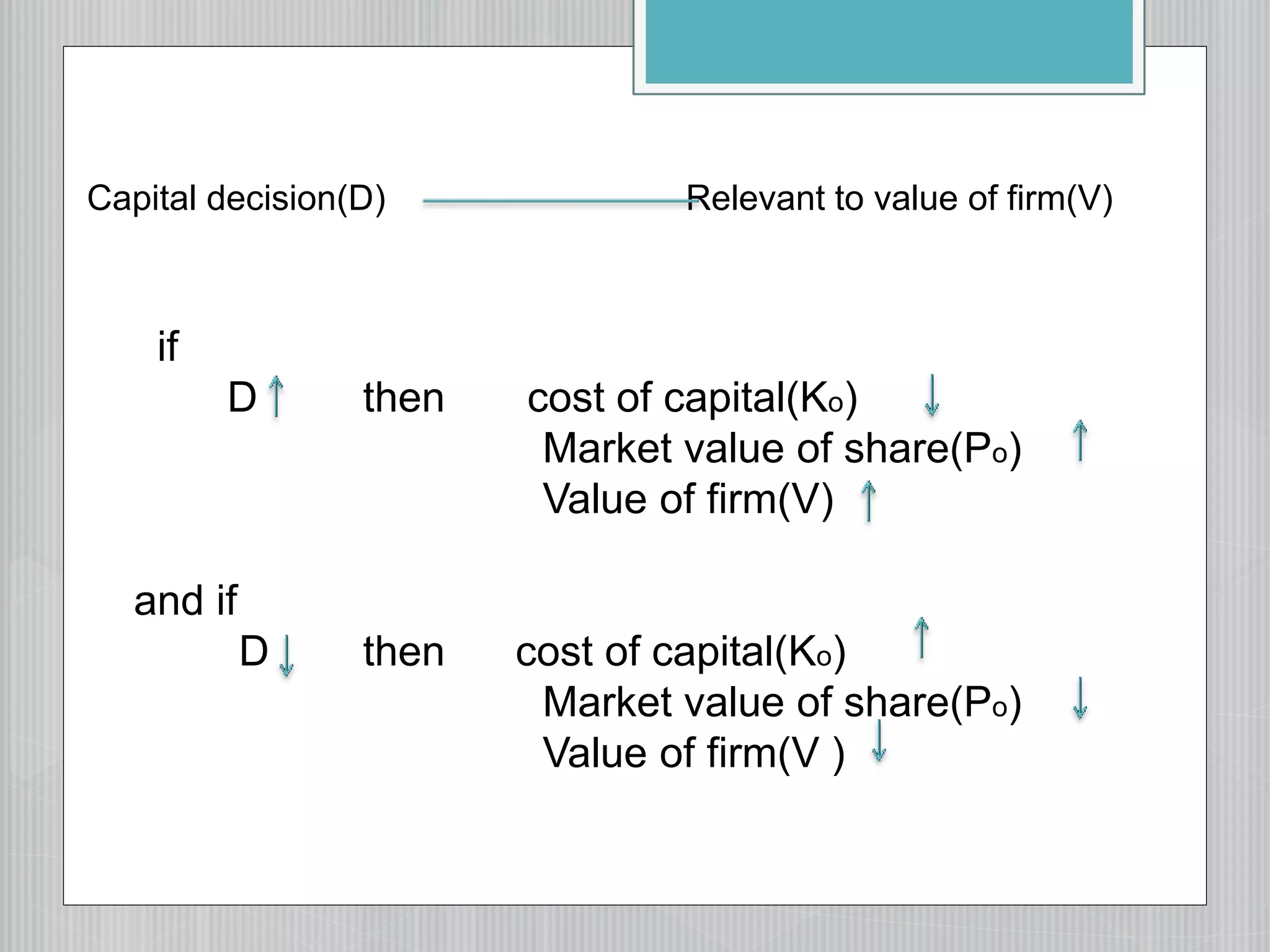
1. The net income approach, which argues that changing capital structure affects overall cost of capital and firm value.
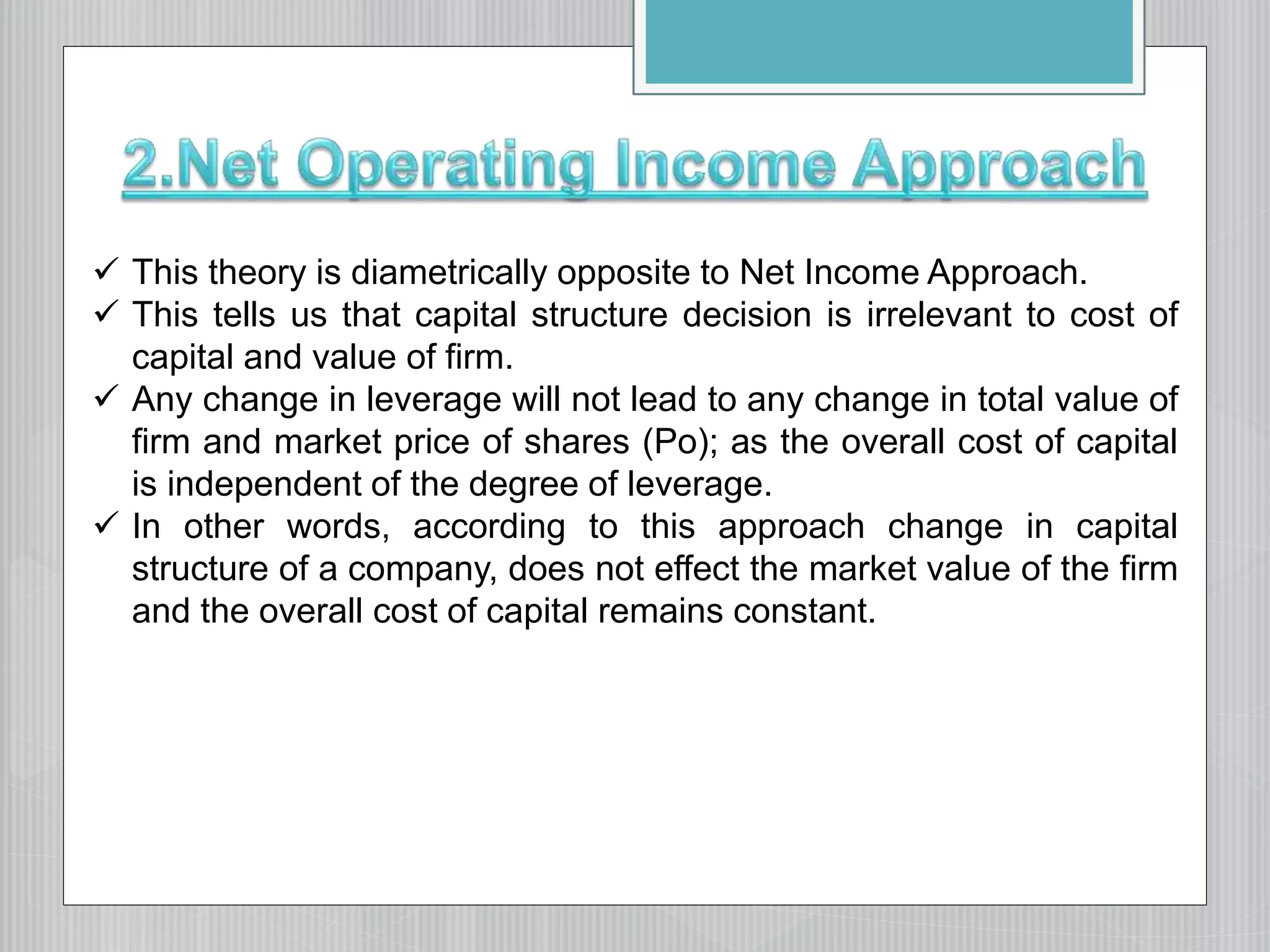
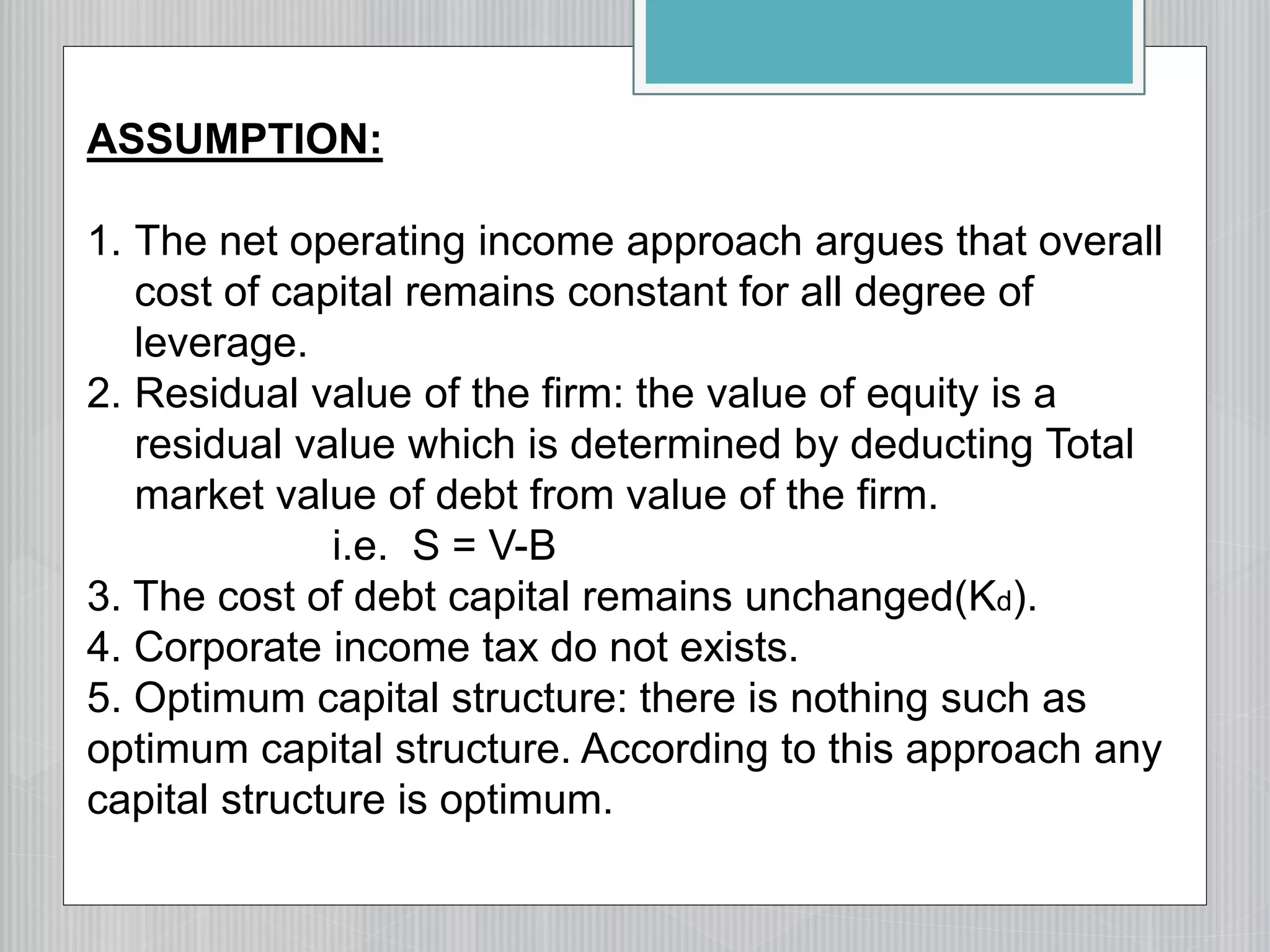
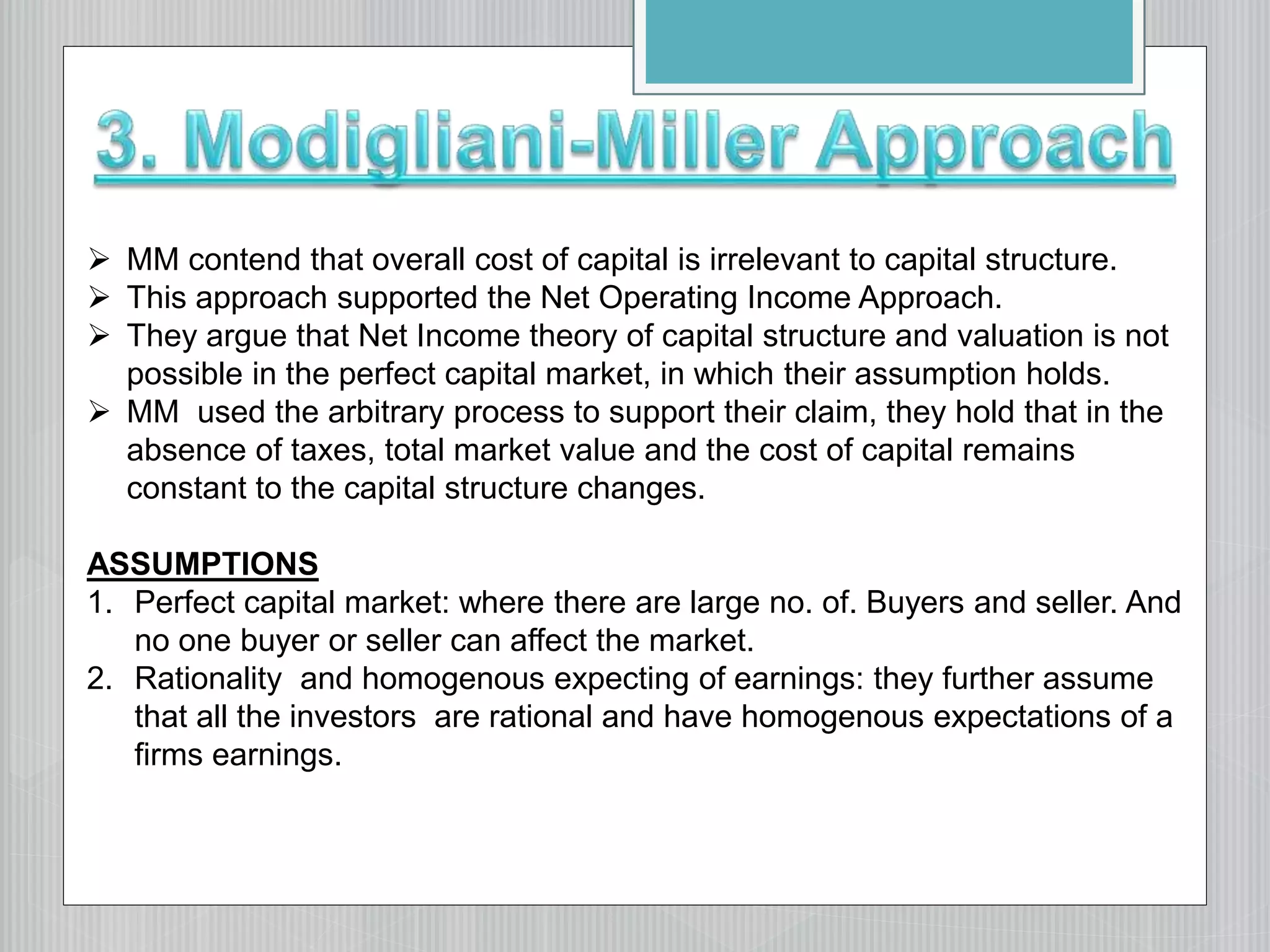
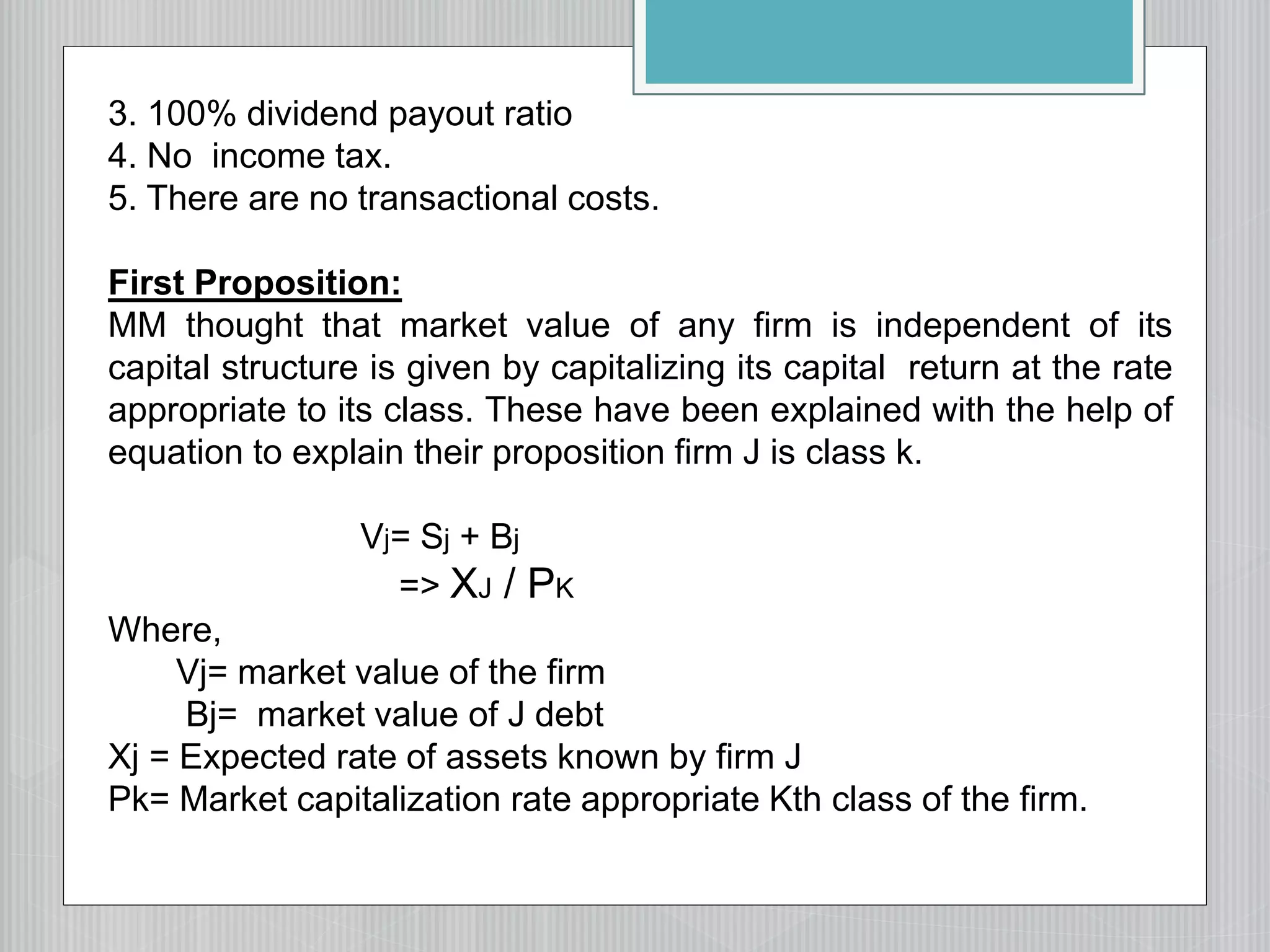
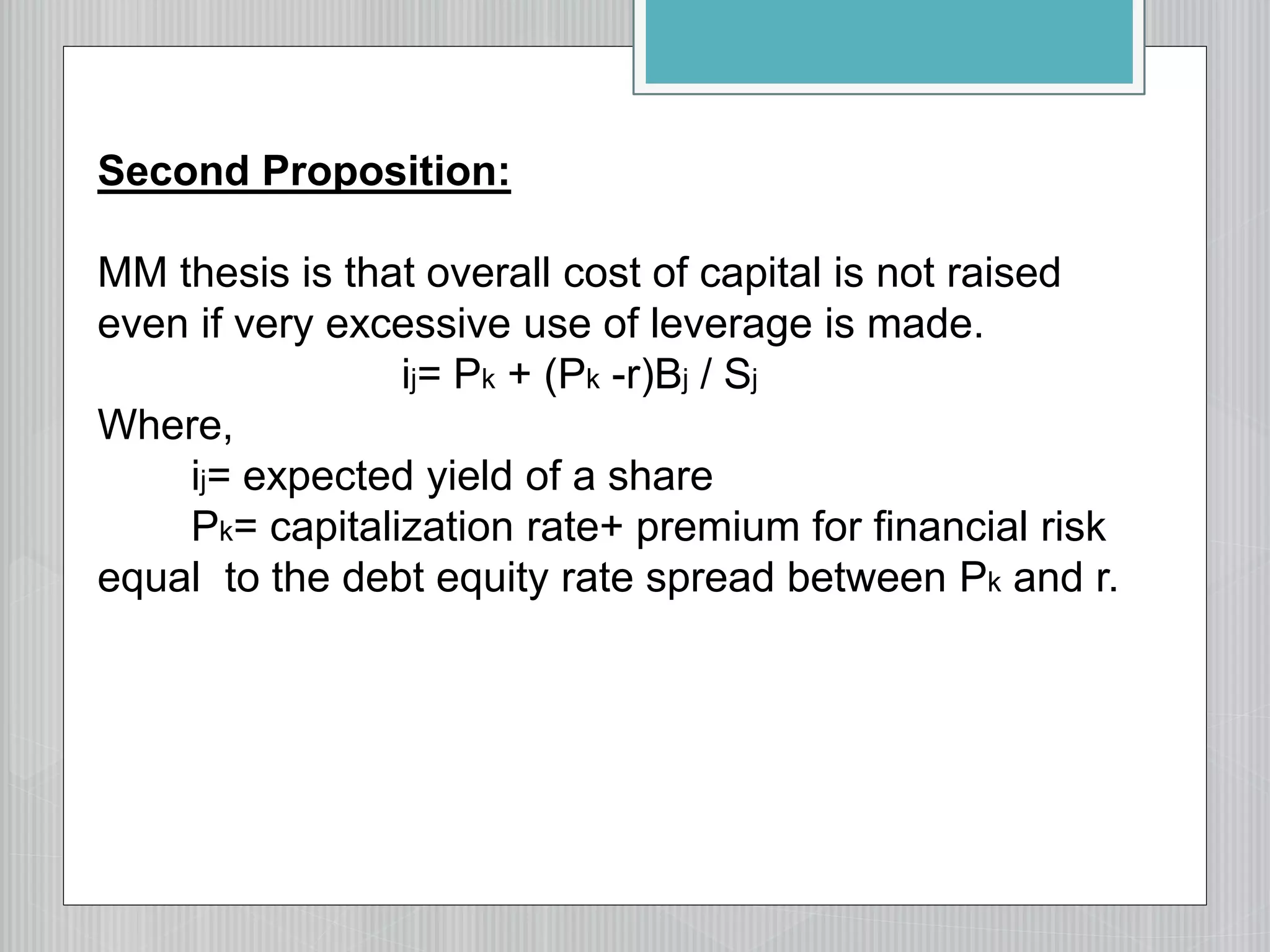
2. The net operating income/Modigliani-Miller approach, which argues that changing capital structure does not affect overall cost of capital or firm value.
3. The traditional/intermediate approach, which argues that increasing debt initially decreases overall cost of capital up to an optimal point, after which further increasing debt increases overall cost of capital.
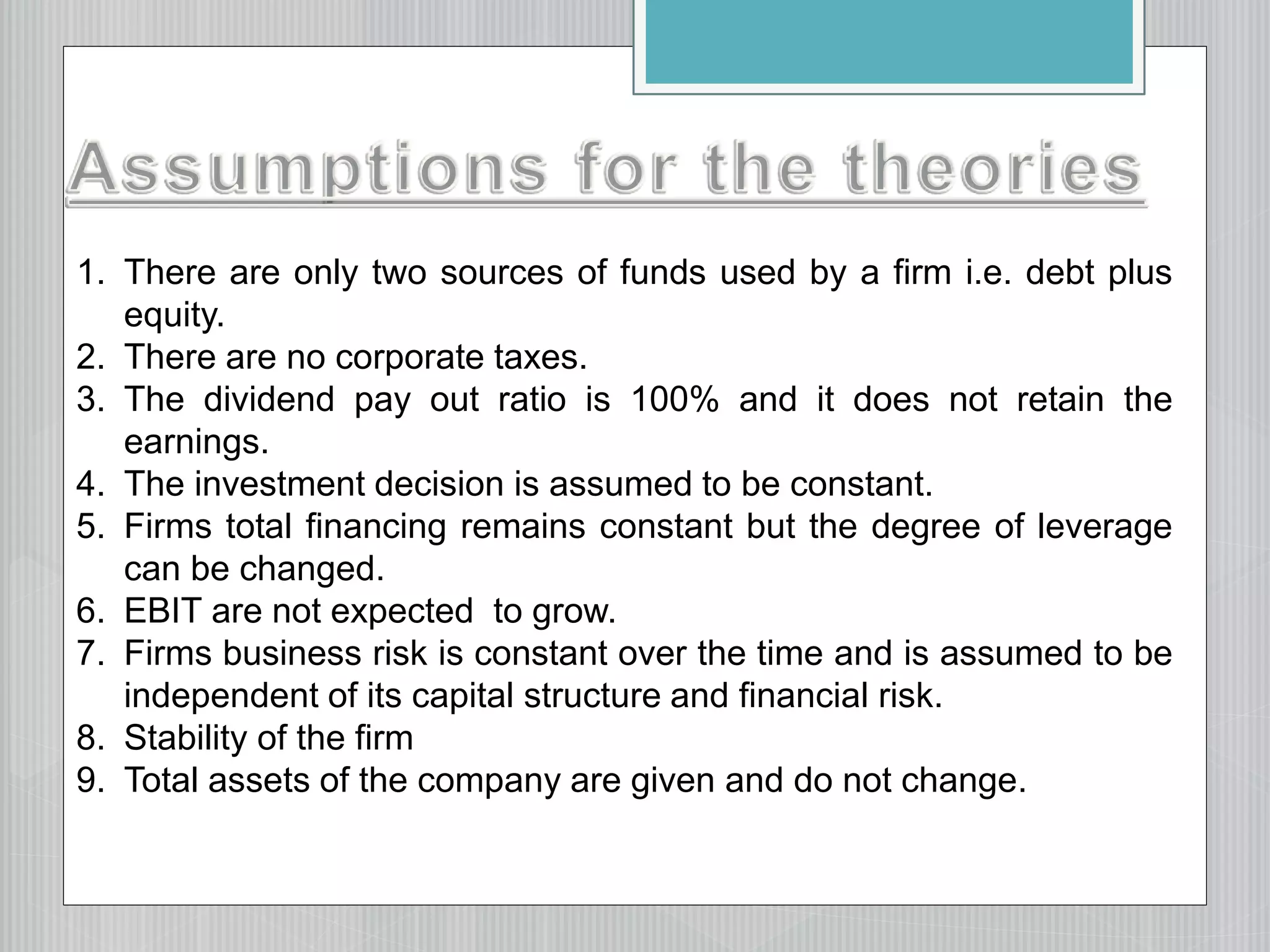
The document analyzes the assumptions and implications of each approach. It also lists factors