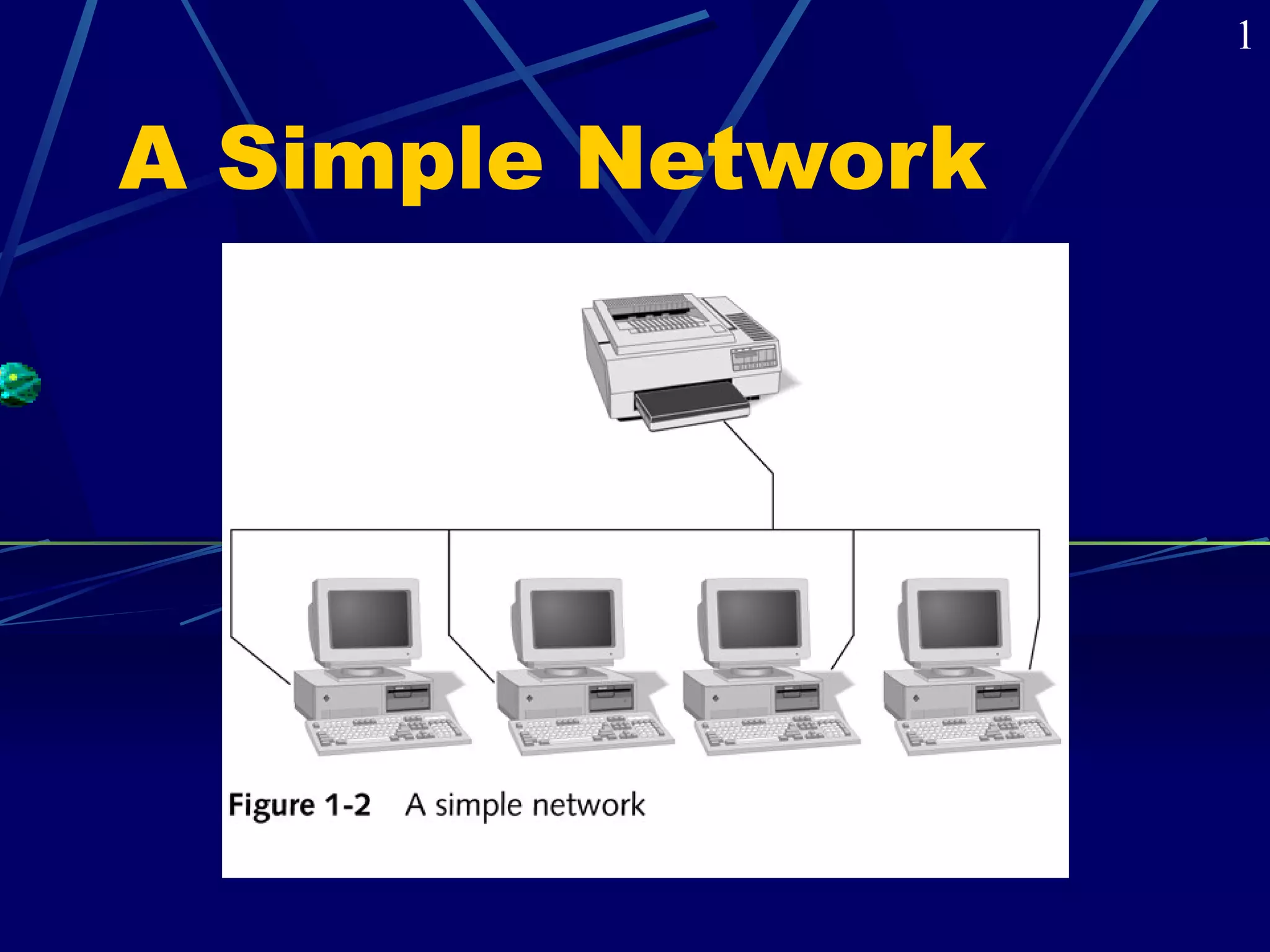
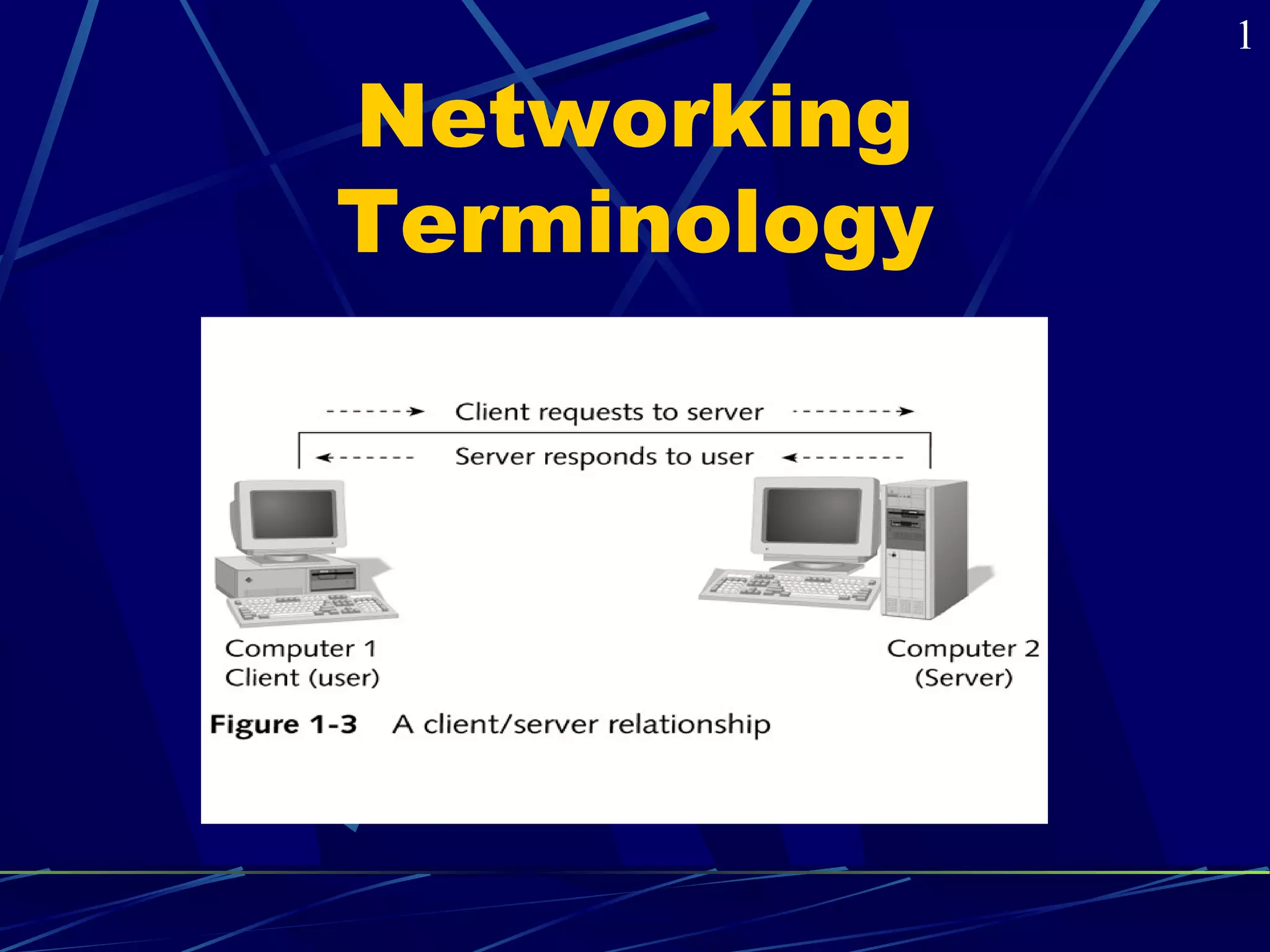
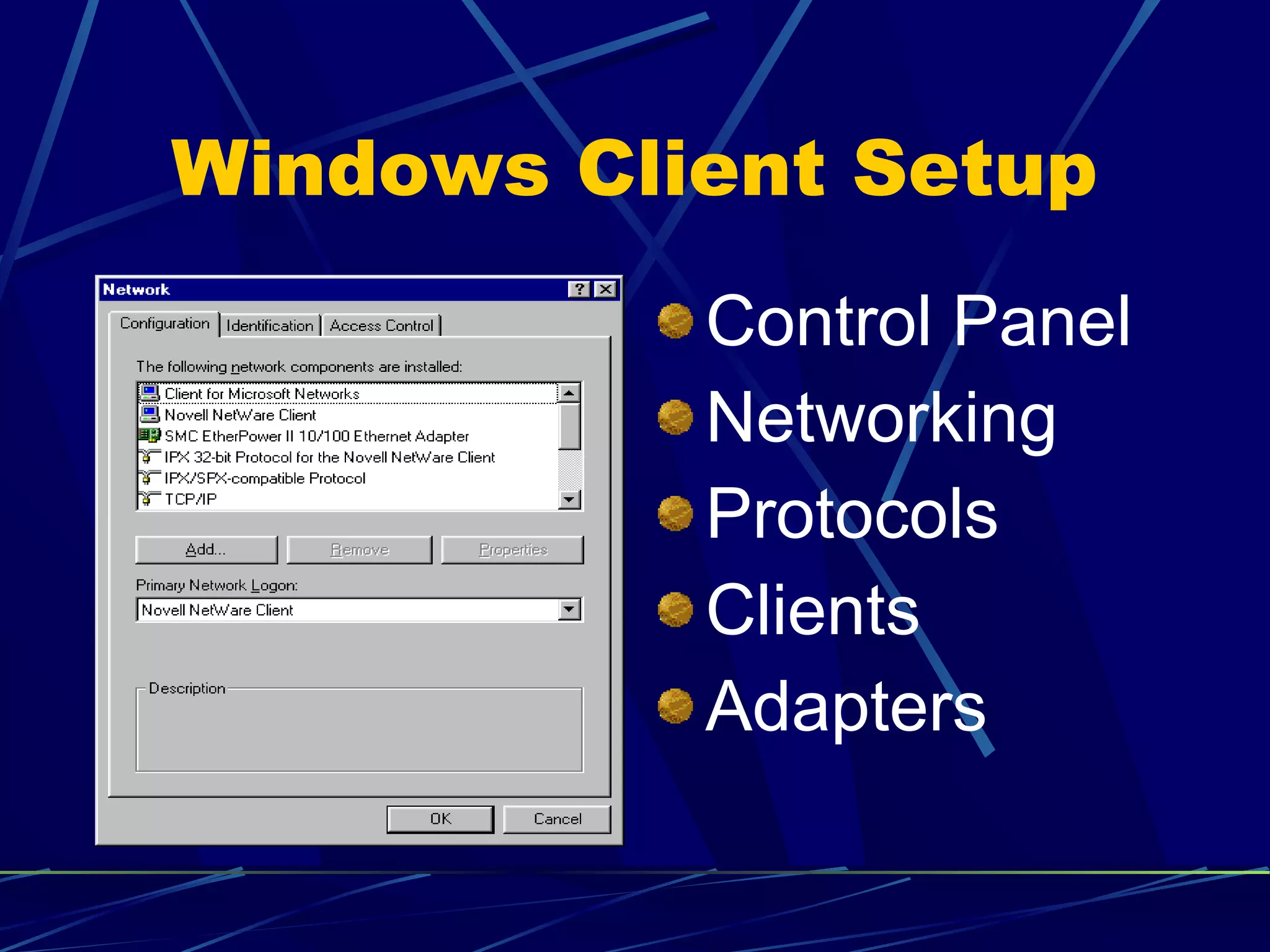
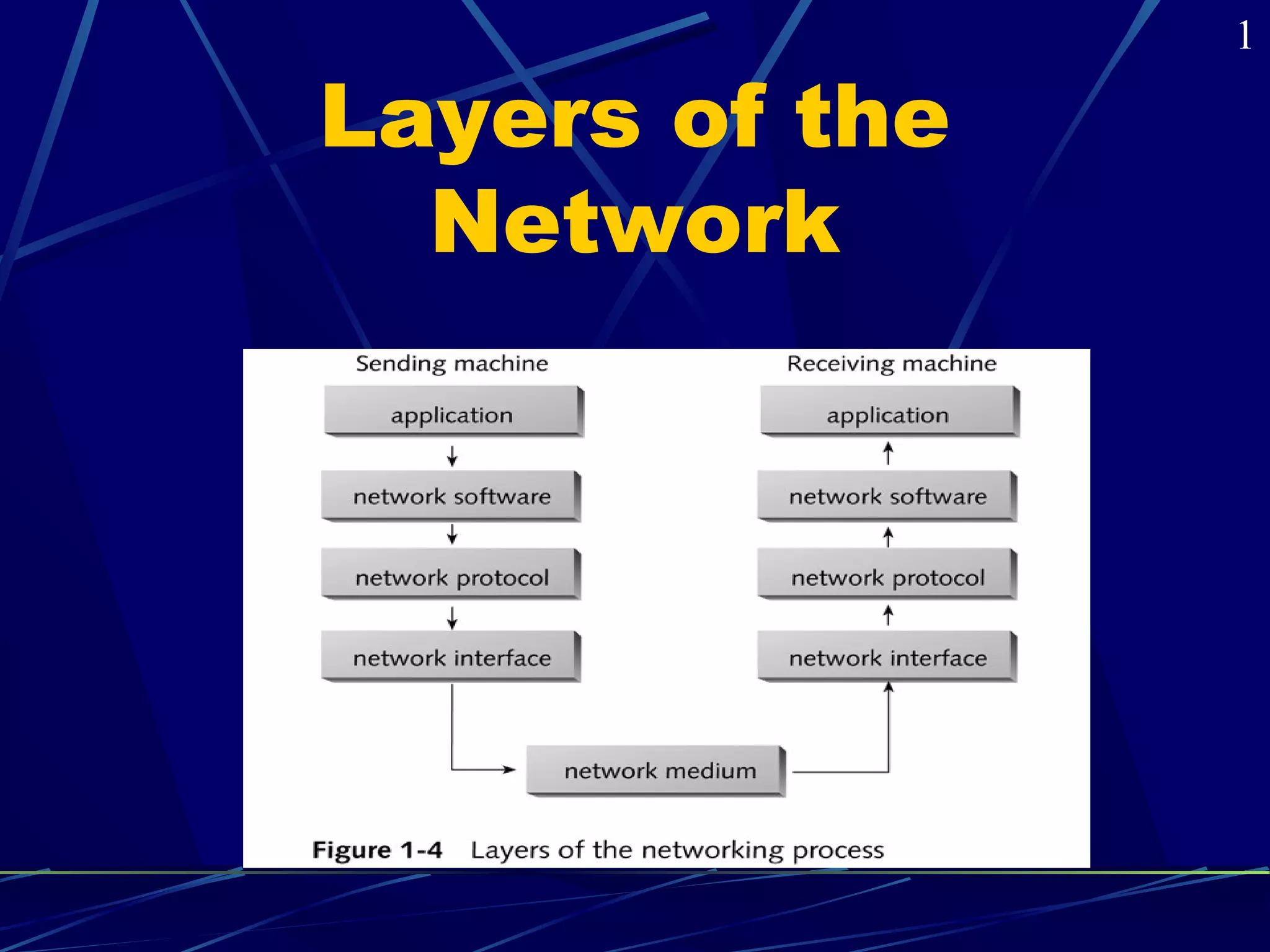
The document covers the fundamentals of networking, defining various types such as local area networks (LAN), wide area networks (WAN), and intranetworks. It details components like network interface cards (NICs), protocols, and server-based vs peer-to-peer networks, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it addresses specialized servers and considerations for selecting an appropriate network based on budget, user numbers, and future growth.