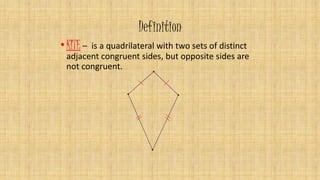
1. A kite is a quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent congruent sides. Kites were historically used for rituals and are now commonly known as children's toys.
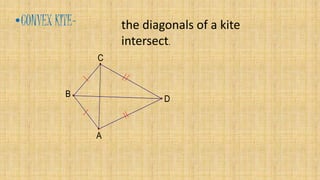
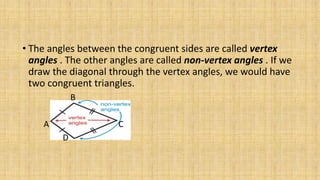
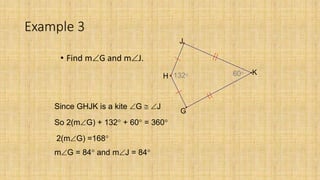
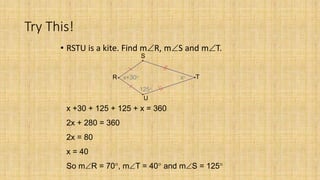
2. A kite has one set of congruent adjacent sides and one set of congruent opposite sides. If a kite's diagonals do not intersect, it is called a dart.
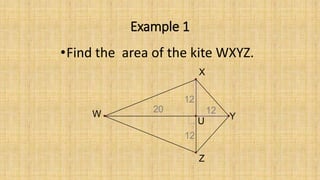
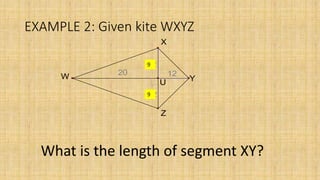
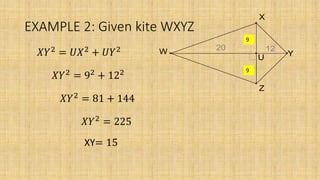
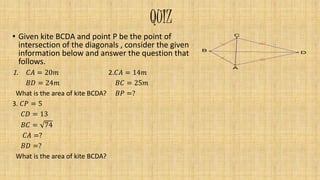
3. The area of a kite is half the product of its diagonals. The diagonals of a kite are perpendicular and bisect the angles between the congruent sides.