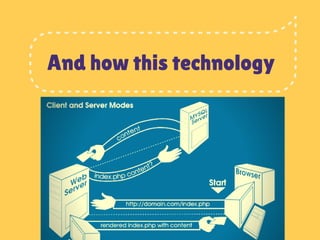
The document introduces the client server model used to access the internet. It discusses how a client like a web browser on a computer or phone connects to an internet server to request and receive webpages or other online resources. It explains that the client sends an HTTP request to the server's IP address, the server then returns the requested page if found or an error message if not found. The document also covers how the client server model revolutionized information transfer and some pros and cons of the model for organizations to consider.