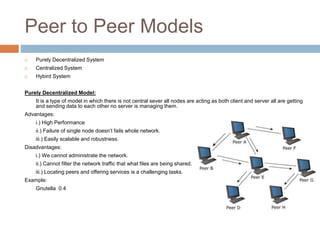
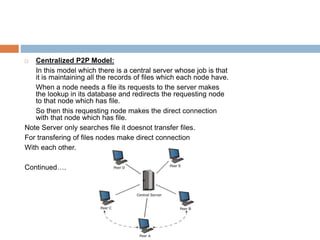
The document provides an overview of peer-to-peer (P2P) architecture, which allows nodes to share resources directly without a central server, facilitating distributed systems and applications like file-sharing and web caching. It contrasts P2P with client-server architecture, highlighting advantages such as ease of installation and cost-effectiveness, as well as disadvantages including security risks and challenges in data backup. Various P2P models, including decentralized, centralized, and hybrid systems, are discussed, alongside a case study on Skype's architecture and terminology associated with P2P systems.











![Overall Architecture
A
B
C
Peer
[Leech]
Downloader
“US”
Peer
[Seed]
Peer
[Leech]
TrackerWeb Server](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peertopeersystem-150117175655-conversion-gate02/85/Peer-to-peer-system-16-320.jpg)
![Overall Architecture
A
B
C
Peer
[Leech]
Downloader
“US”
Peer
[Seed]
Peer
[Leech]
TrackerWeb Server](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peertopeersystem-150117175655-conversion-gate02/85/Peer-to-peer-system-17-320.jpg)
![Overall Architecture
A
B
C
Peer
[Leech]
Downloader
“US”
Peer
[Seed]
Peer
[Leech]
TrackerWeb Server](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peertopeersystem-150117175655-conversion-gate02/85/Peer-to-peer-system-18-320.jpg)
![Overall Architecture
A
B
C
Peer
[Leech]
Downloader
“US”
Peer
[Seed]
Peer
[Leech]
TrackerWeb Server](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peertopeersystem-150117175655-conversion-gate02/85/Peer-to-peer-system-19-320.jpg)
![Overall Architecture
A
B
C
Peer
[Leech]
Downloader
“US”
Peer
[Seed]
Peer
[Leech]
TrackerWeb Server](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peertopeersystem-150117175655-conversion-gate02/85/Peer-to-peer-system-20-320.jpg)
![Overall Architecture
A
B
C
Peer
[Leech]
Downloader
“US”
Peer
[Seed]
Peer
[Leech]
TrackerWeb Server](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peertopeersystem-150117175655-conversion-gate02/85/Peer-to-peer-system-21-320.jpg)
![Overall Architecture
A
B
C
Peer
[Leech]
Downloader
“US”
Peer
[Seed]
Peer
[Leech]
TrackerWeb Server](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peertopeersystem-150117175655-conversion-gate02/85/Peer-to-peer-system-22-320.jpg)

