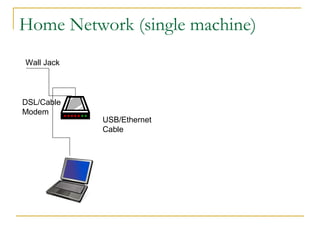
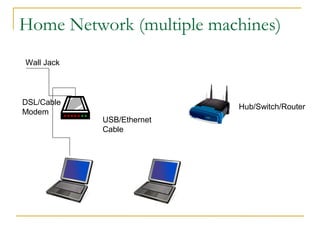
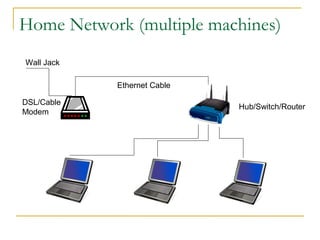
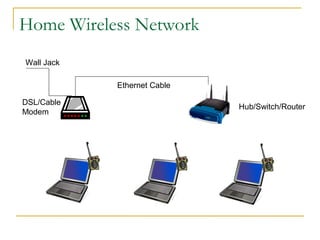
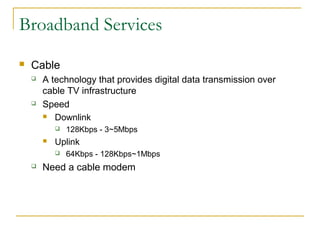
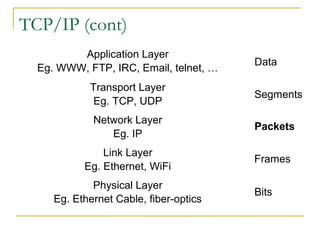
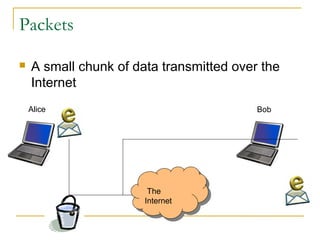
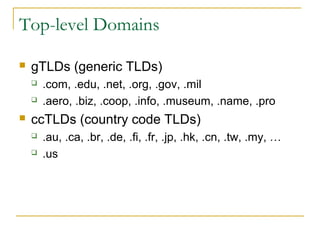
This document discusses networking concepts like bandwidth, connection types, LANs, WLANs, and broadband services. It explains that bandwidth is measured in bits per second and describes common connection standards like Ethernet, Wi-Fi, DSL, cable, and dial-up. It also discusses networking hardware like modems, routers, switches and hubs and how they enable connections within local and wide area networks.