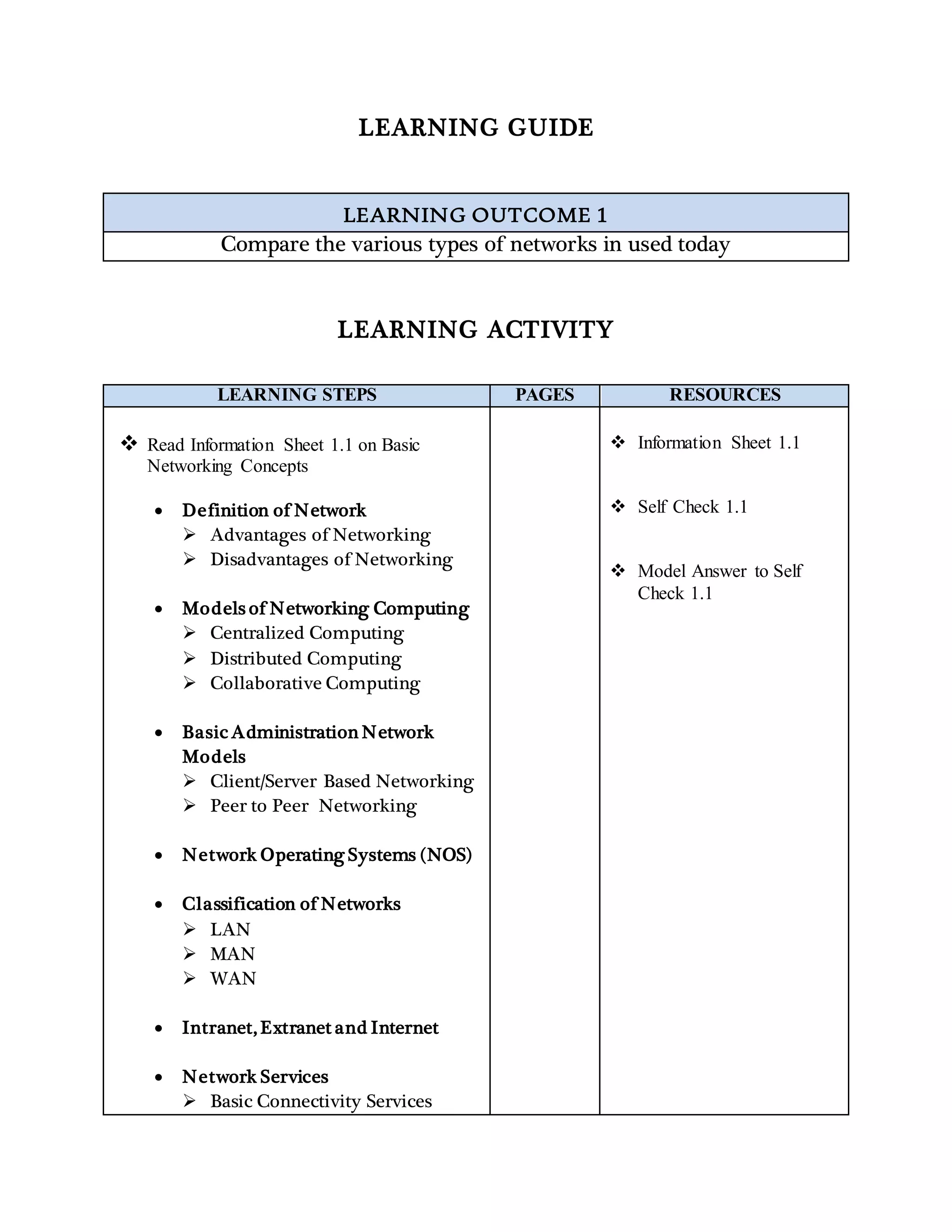
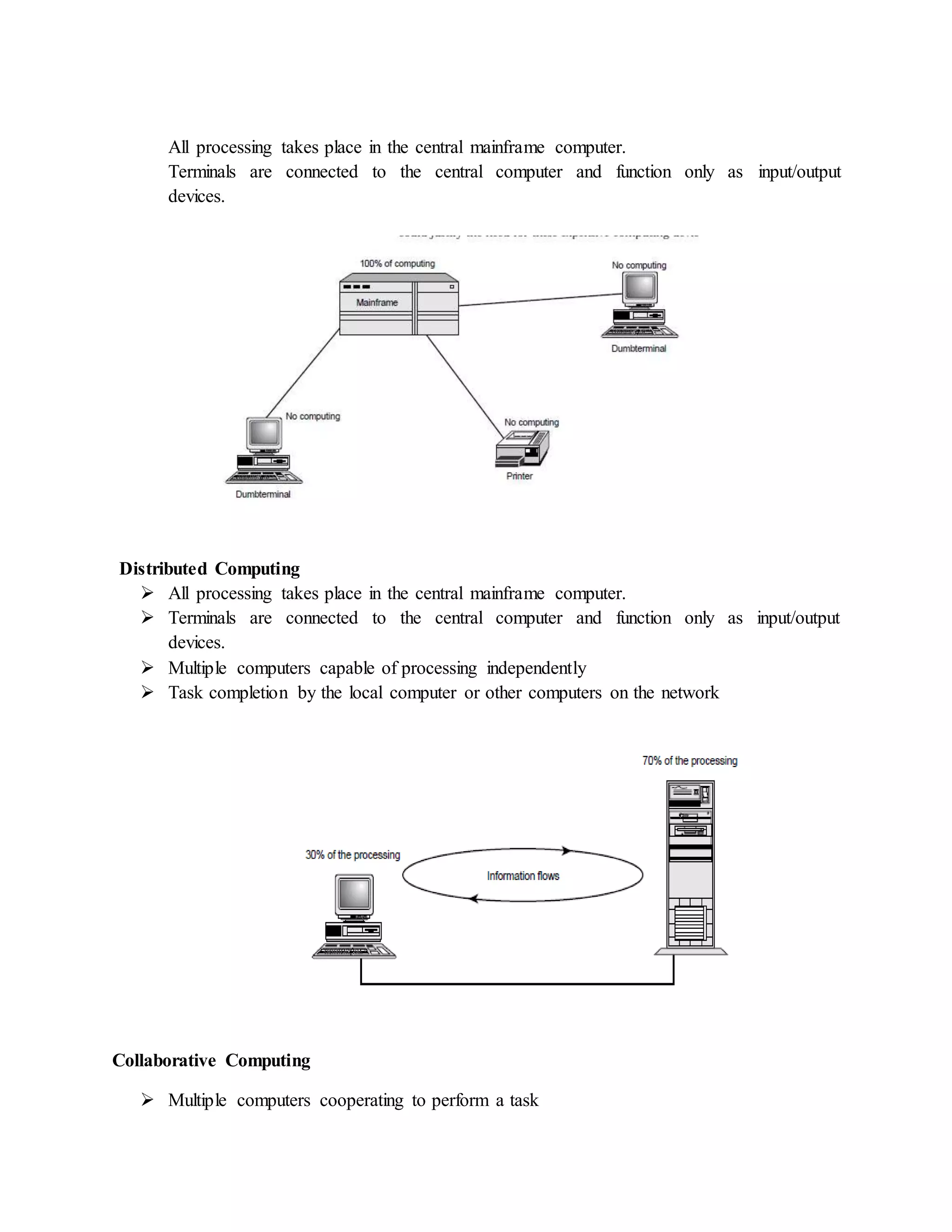
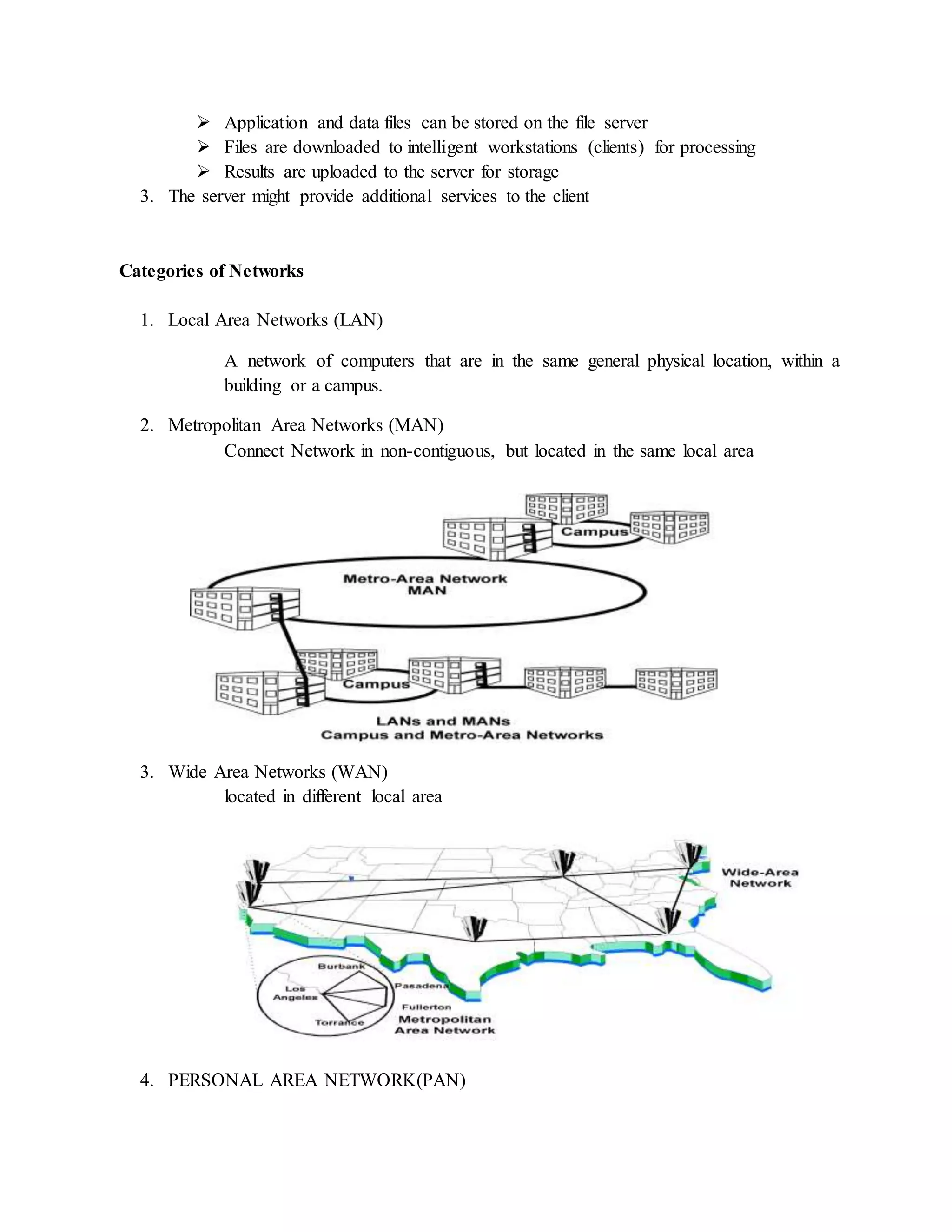
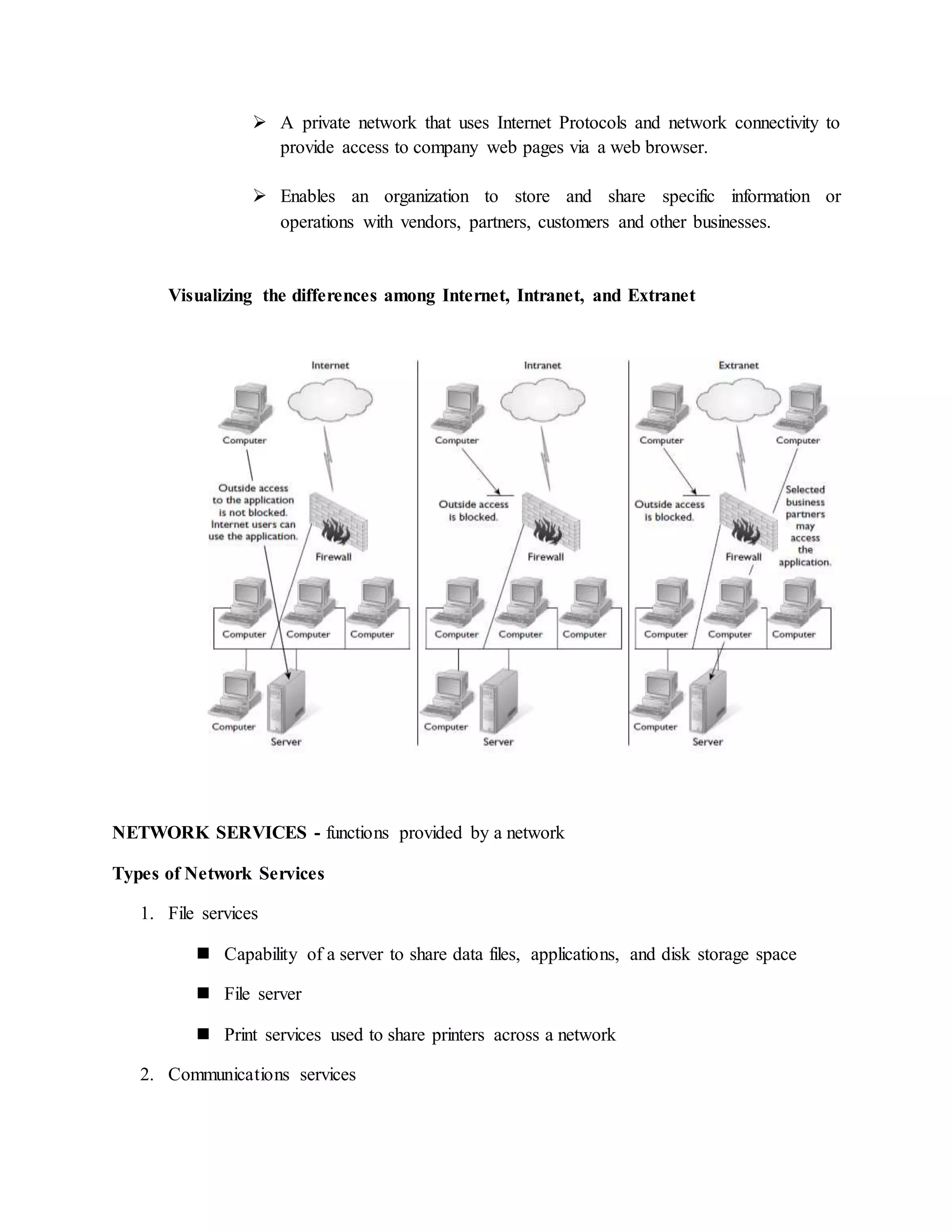
The document provides information about basic networking concepts including different types of networks, models of networking computing, network administration models, network operating systems, categories of networks, and types of network services. It includes an information sheet that defines these key networking terms and concepts. It also includes a self-check questions and model answers to test understanding of the material.