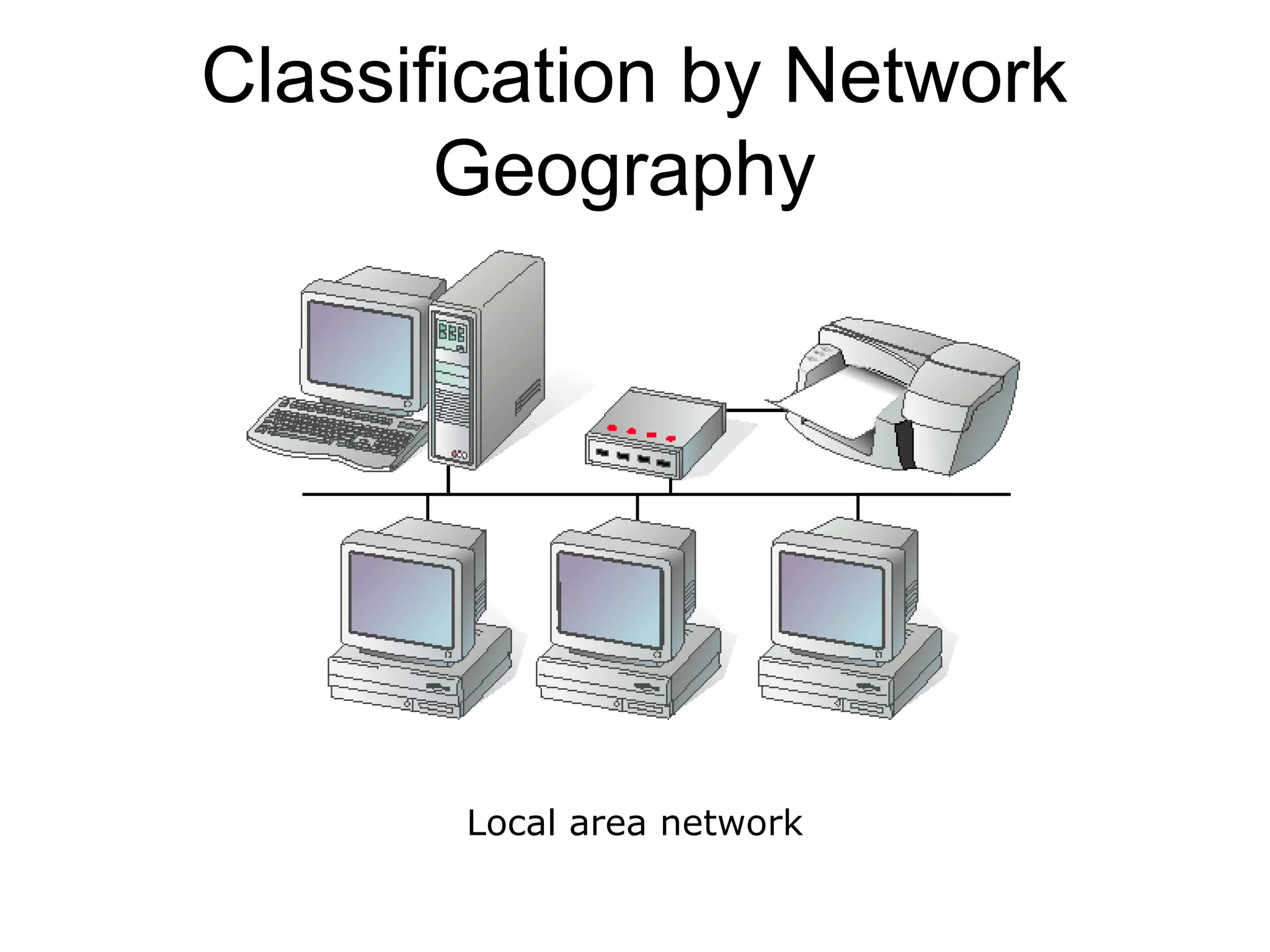
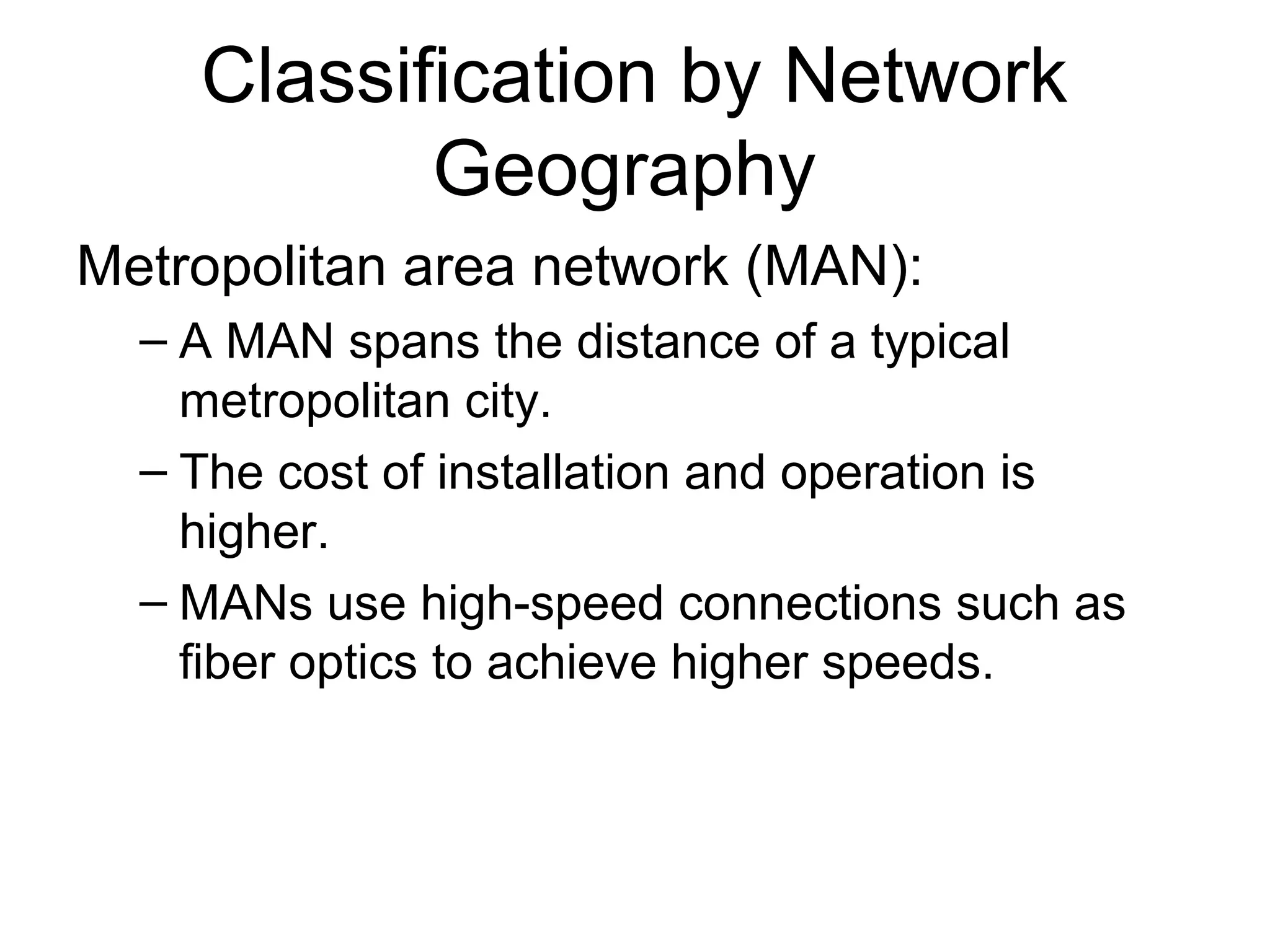
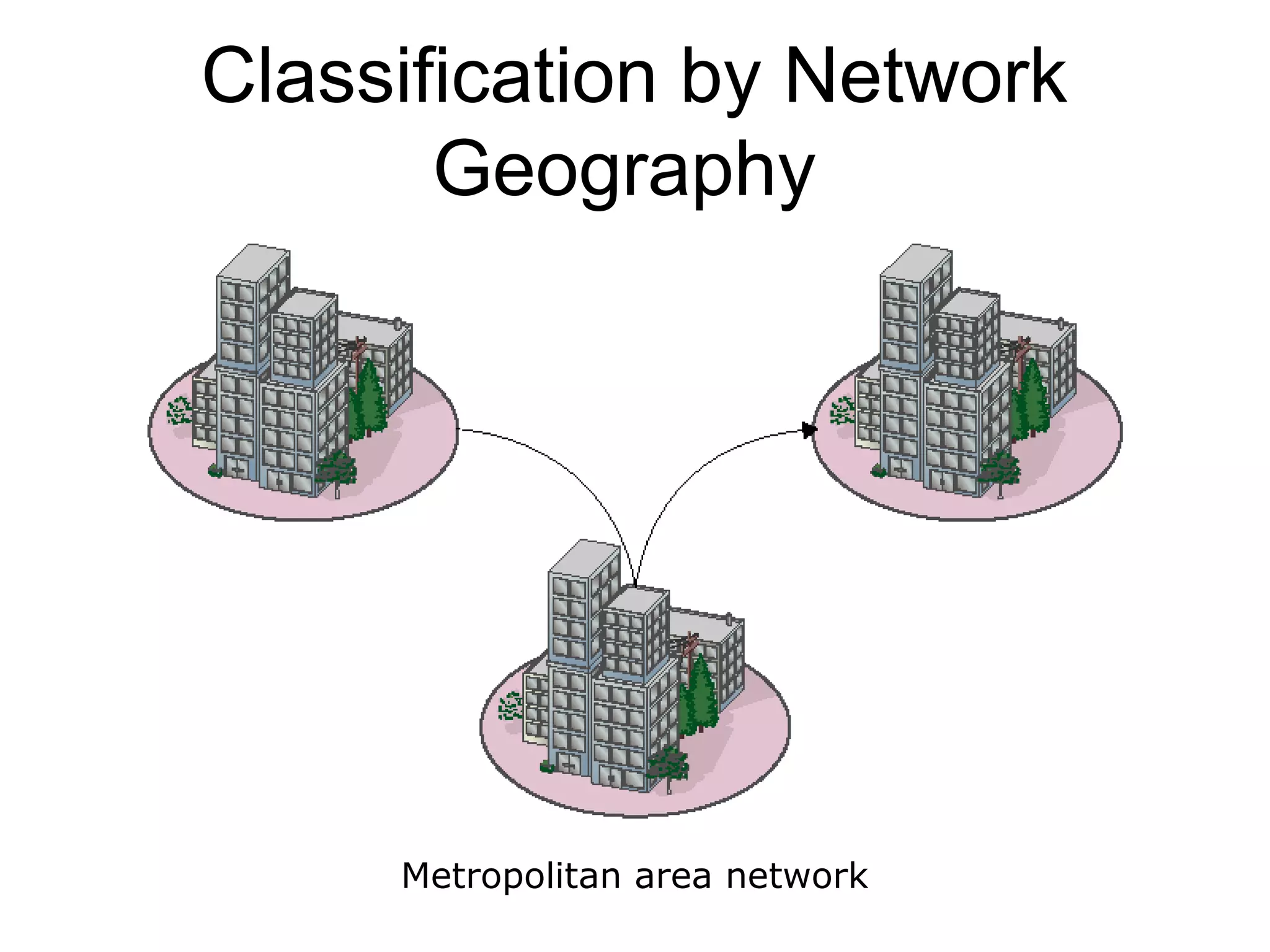
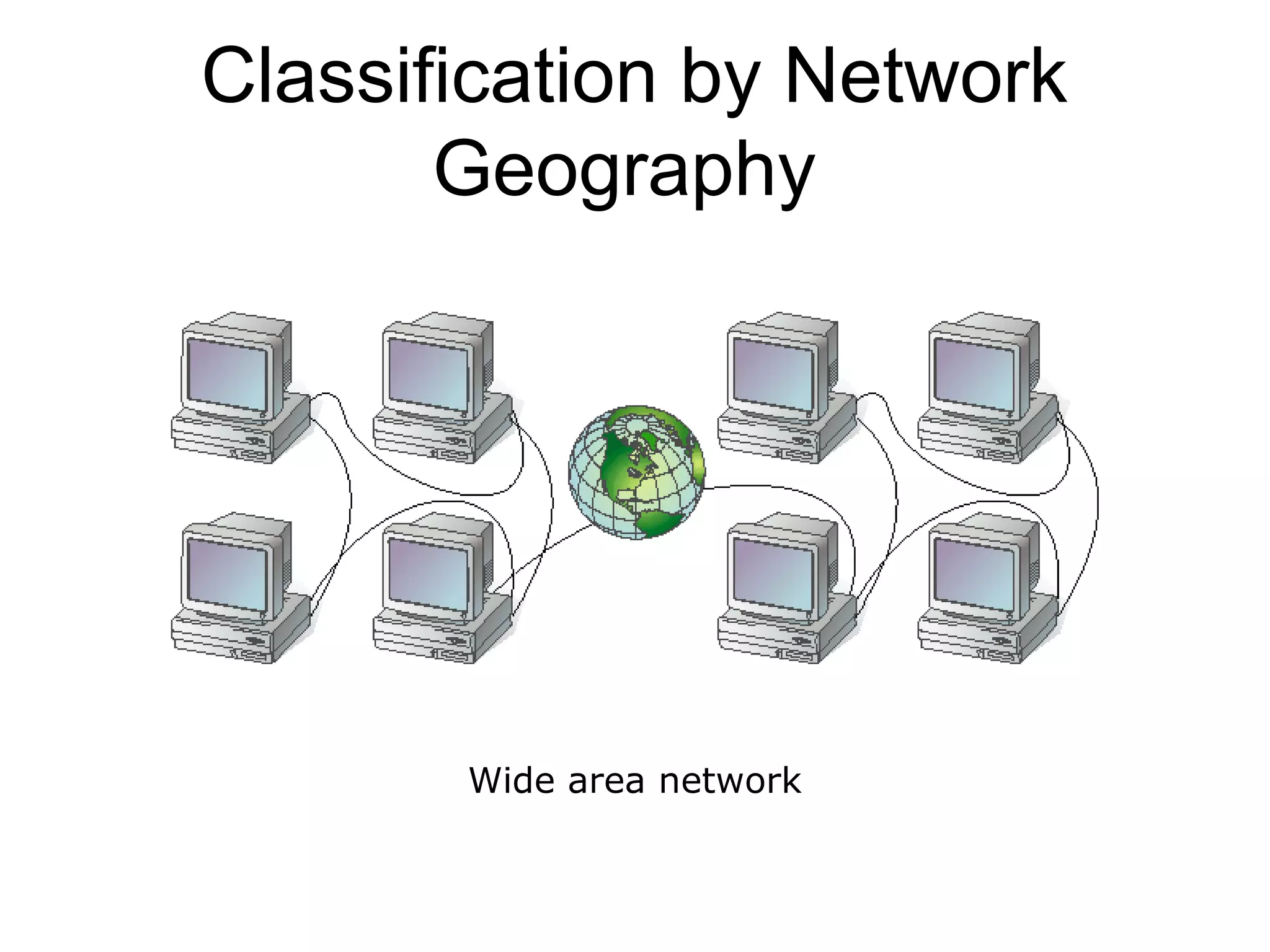
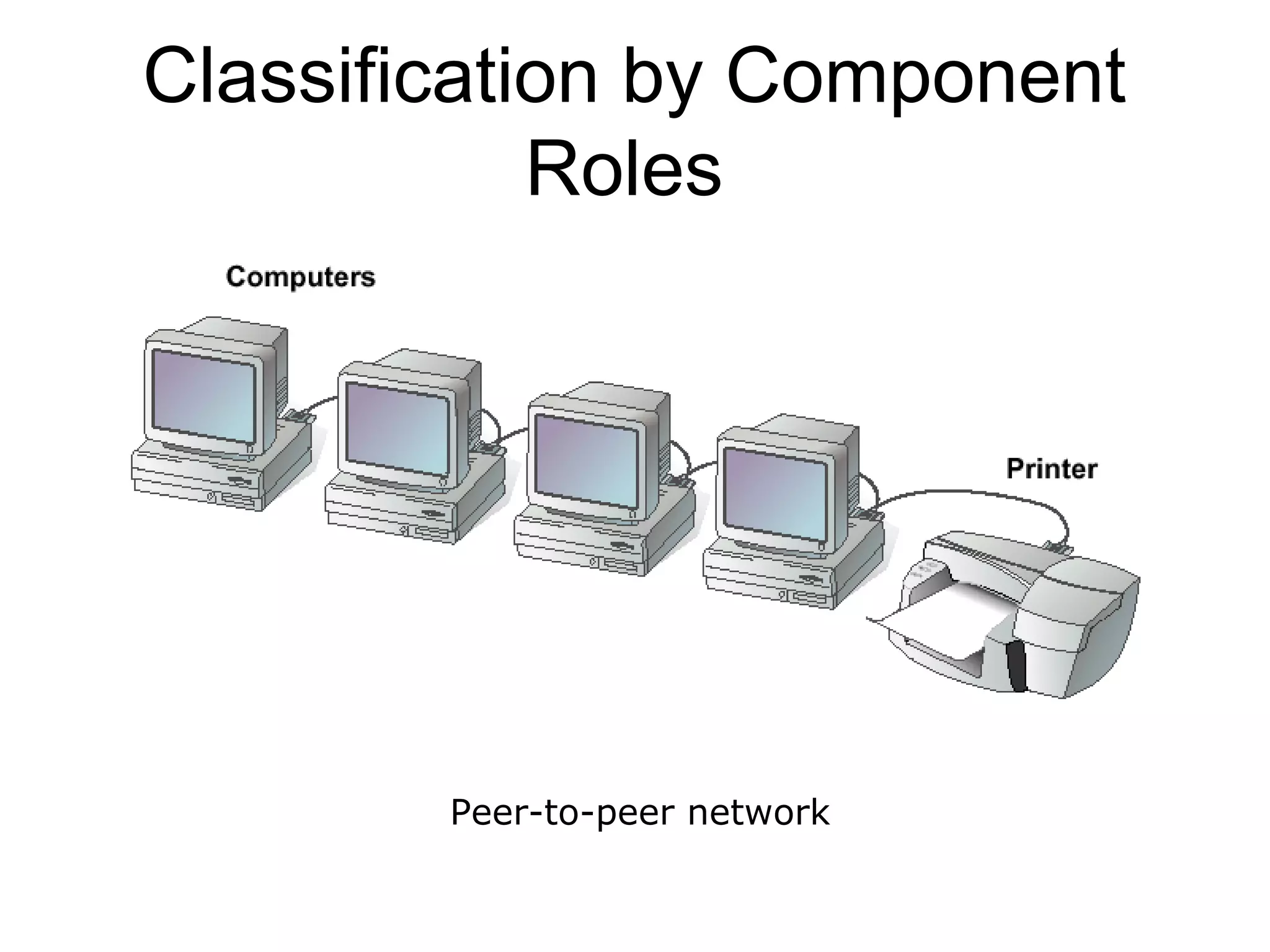
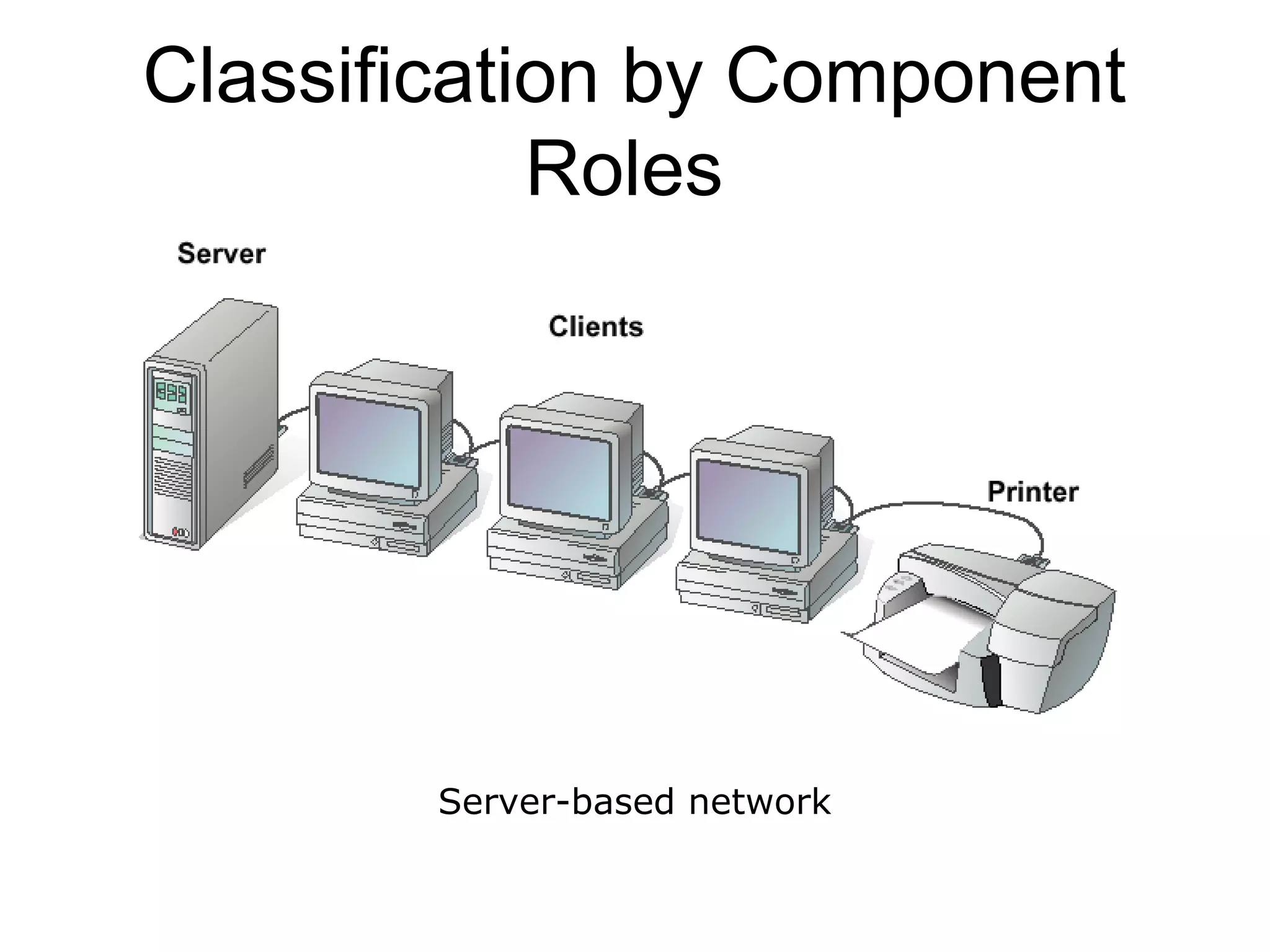
This document provides an overview of computer networks, detailing their definitions, purposes, and classifications. It explains that networks enhance communication, share resources, and facilitate centralized management, with types categorized by geography (LAN, MAN, WAN) and roles (peer-to-peer, server-based, client-based). The fundamental purpose of networks is to enable effective communication among connected computers to share information and resources.