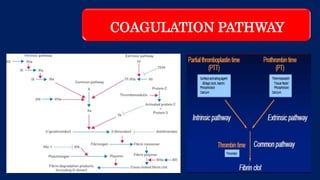
This document discusses the complexities of performing surgery in patients with bleeding diathesis, outlining the physiology of hemostasis, pre-operative evaluations, and cases managed. It details various bleeding disorders, pre-operative assessments, and specific surgical cases involving children, including patients with hemophilia. The text also highlights management strategies for different bleeding conditions and presents clinical vignettes illustrating practical applications.