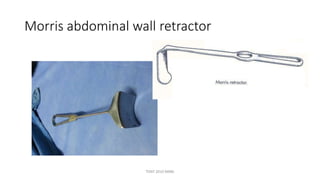
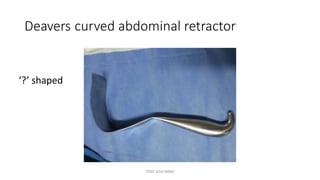
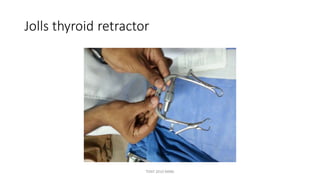
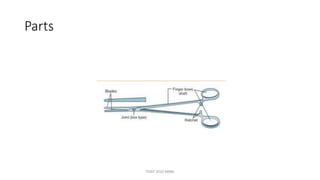
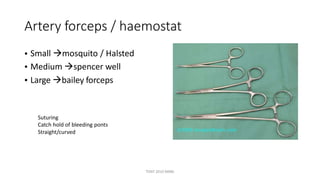
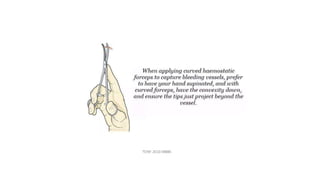
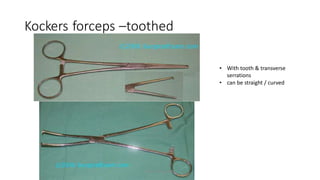
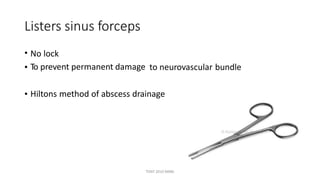
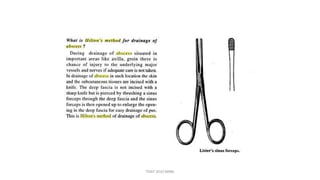
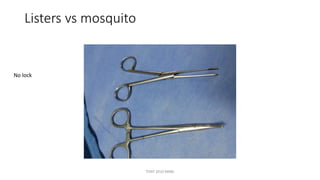
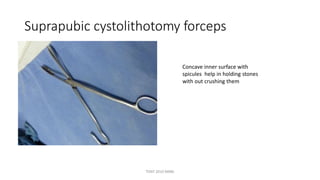
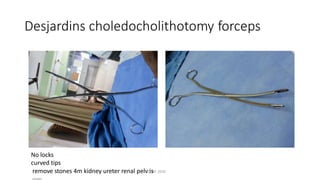
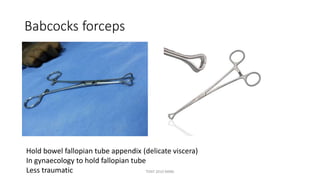
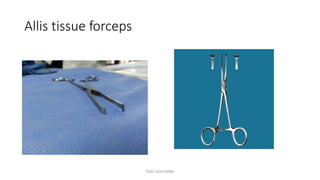
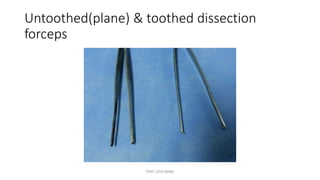
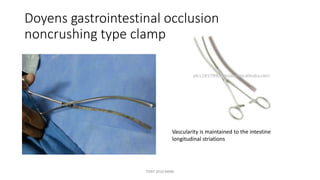
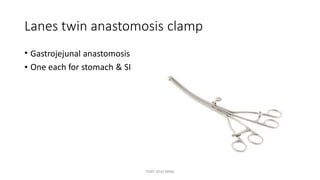
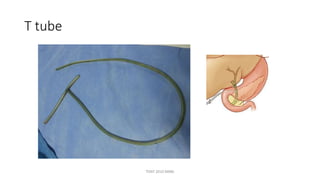
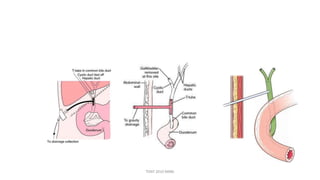
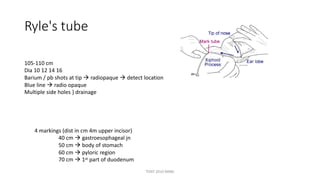
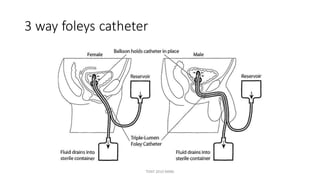
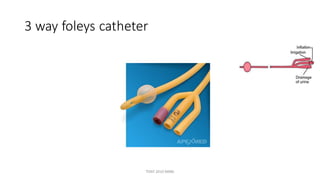
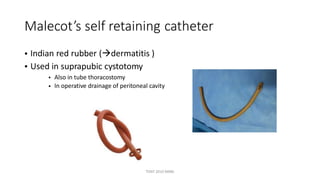
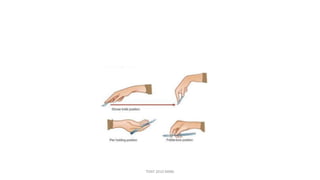
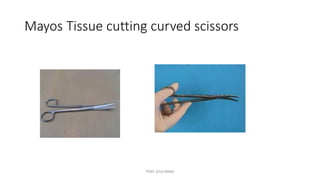
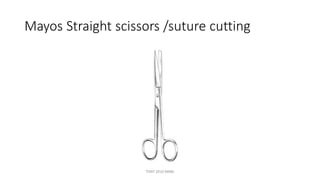
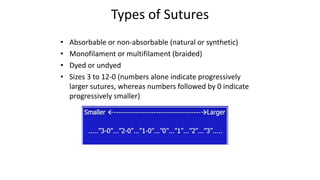
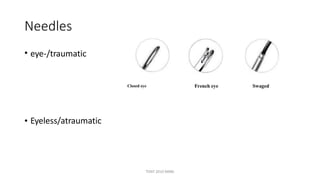
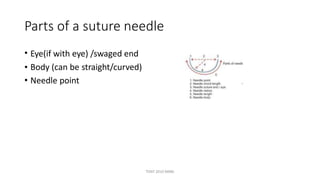
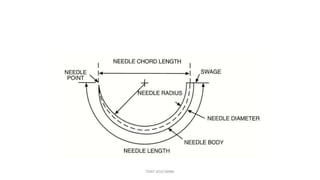
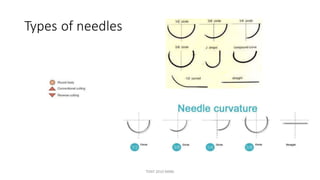
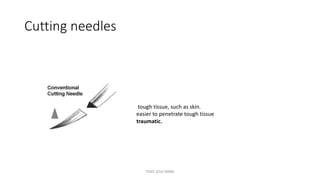
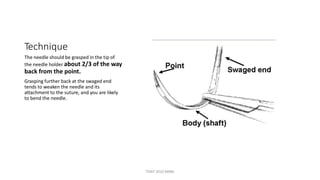
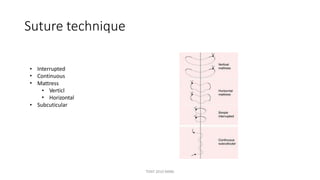
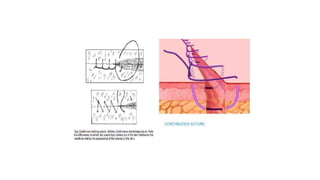
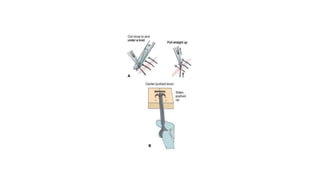
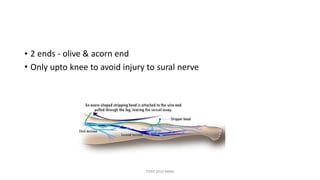
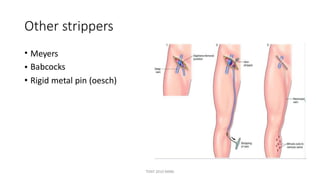
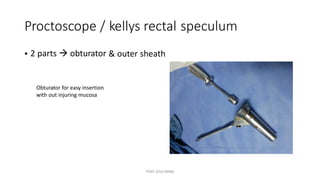
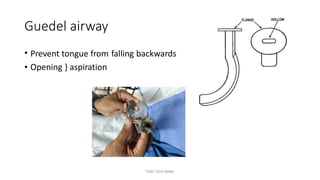
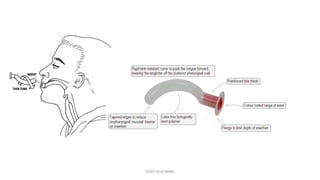
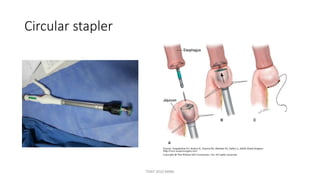
The document outlines various surgical instruments and their uses, including retractors, forceps, clamps, and tubes, along with specific applications in surgeries such as laparotomy, cholecystectomy, and cystolithotomy. Additionally, it details different types of sutures, needles, and catheters, highlighting their characteristics and appropriate usage in medical procedures. Various instruments are specified for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, emphasizing the importance of choosing the right tool for the surgical context.