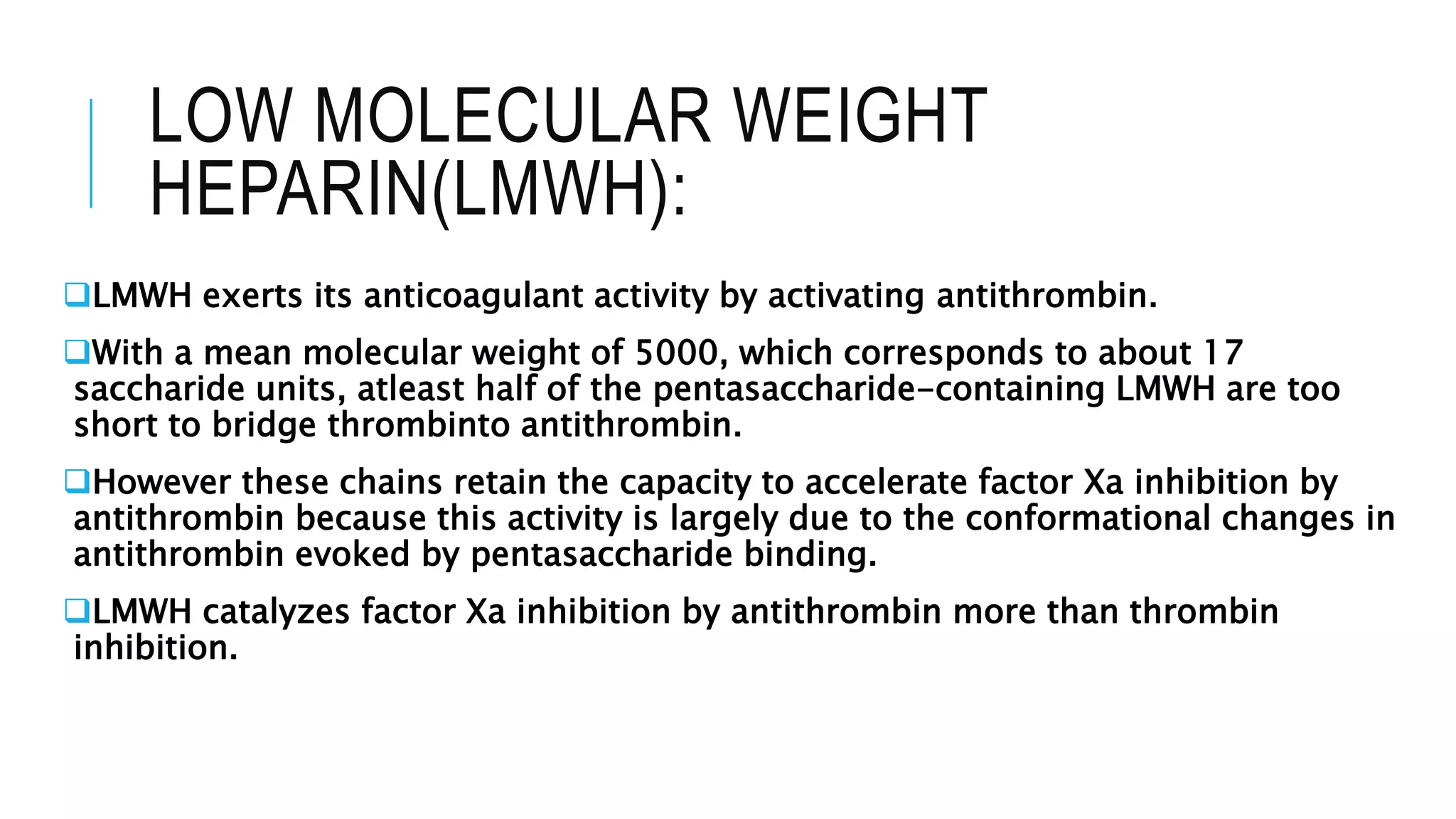
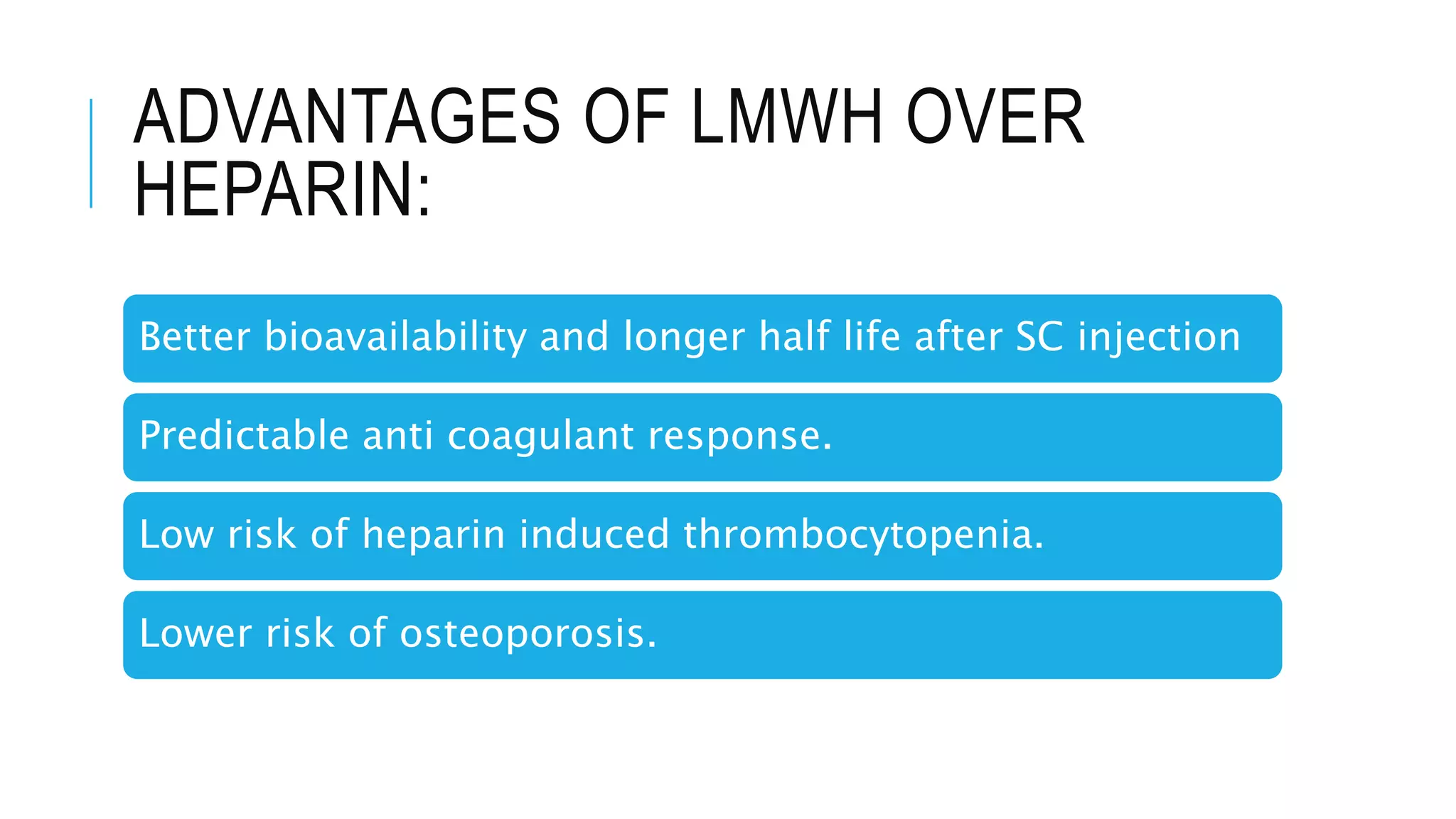
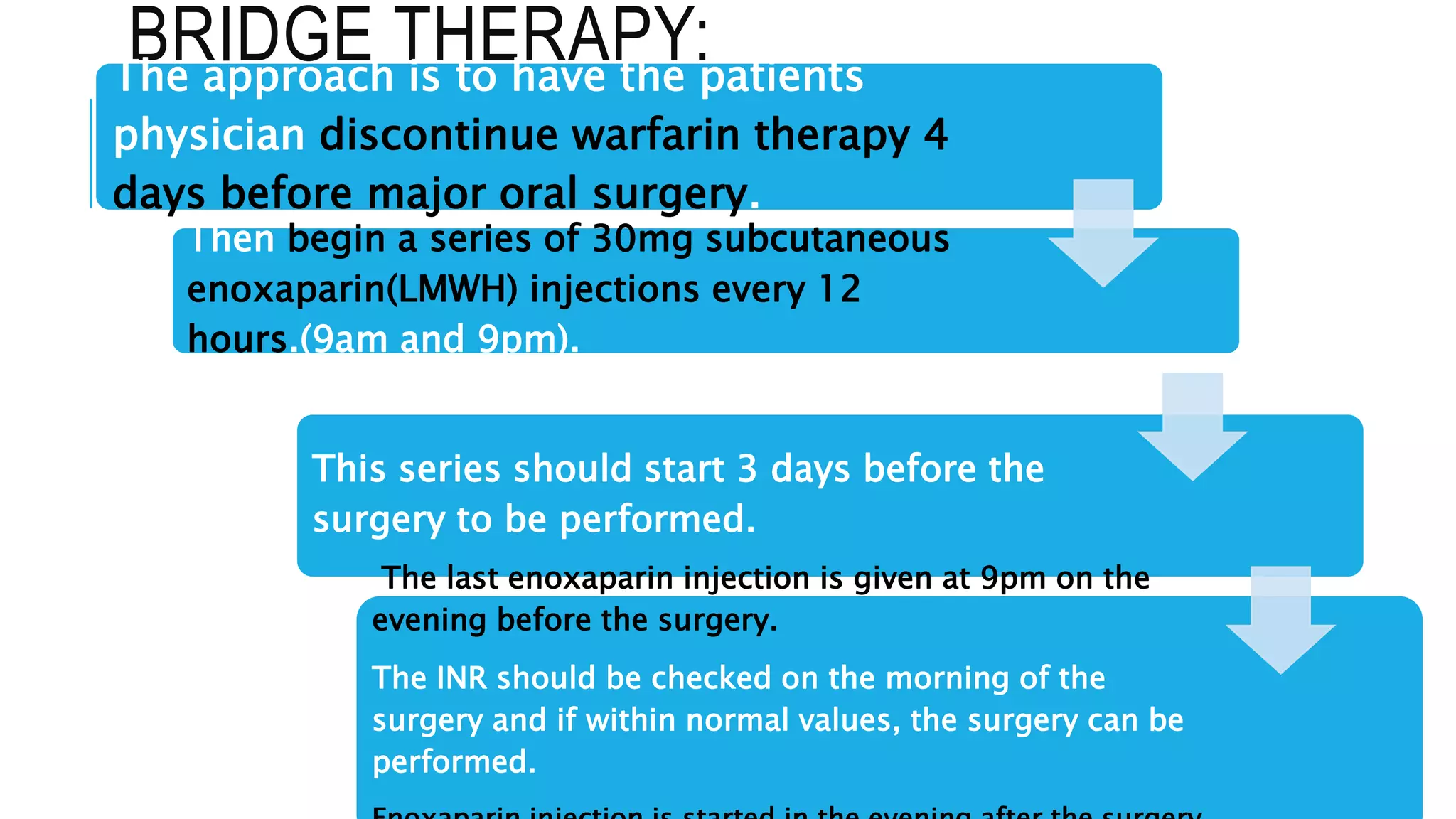
Warfarin and heparin are oral and injectable anticoagulants, respectively, that are used to treat and prevent blood clots. Warfarin works by inhibiting vitamin K epoxide reductase to prevent gamma-carboxylation of clotting factors. Heparin activates antithrombin to inhibit clotting factors such as factor Xa. Low molecular weight heparins like enoxaparin have fewer side effects and more predictable responses than unfractionated heparin. Bridge therapy using enoxaparin is often used when dental or surgical procedures are needed in patients taking warfarin to control their coagulation levels and prevent bleeding complications during and after the procedure