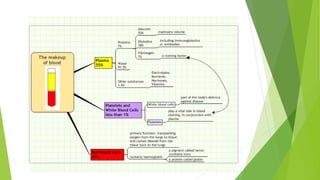
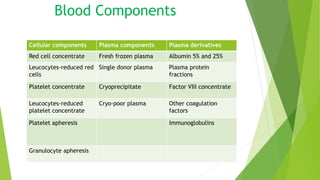
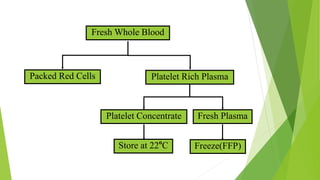
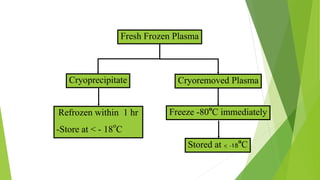
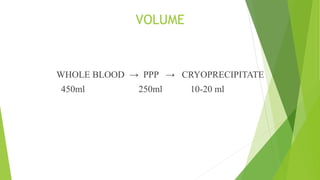
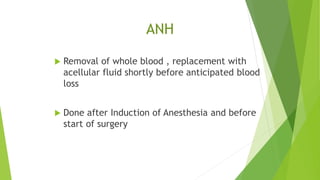
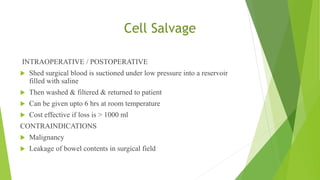
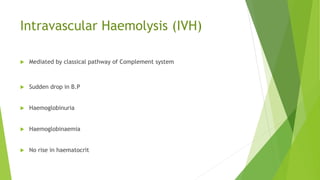
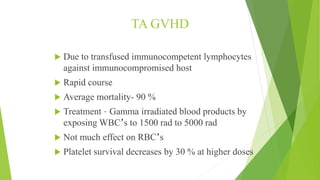
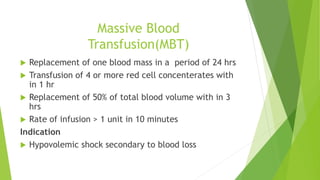
This document provides information about blood transfusion and component therapy. It discusses the need for transfusion when there is inadequate oxygen carrying capacity or coagulation proteins. Whole blood can be separated into components like red blood cells, platelets, plasma, and cryoprecipitate to provide targeted therapy. The storage and indications of various blood components like packed red blood cells, fresh frozen plasma, cryoprecipitate, and platelets are described. The document also covers transfusion triggers, guidelines, blood ordering schedules, and blood sparing strategies like autologous donation and acute normovolemic hemodilution.