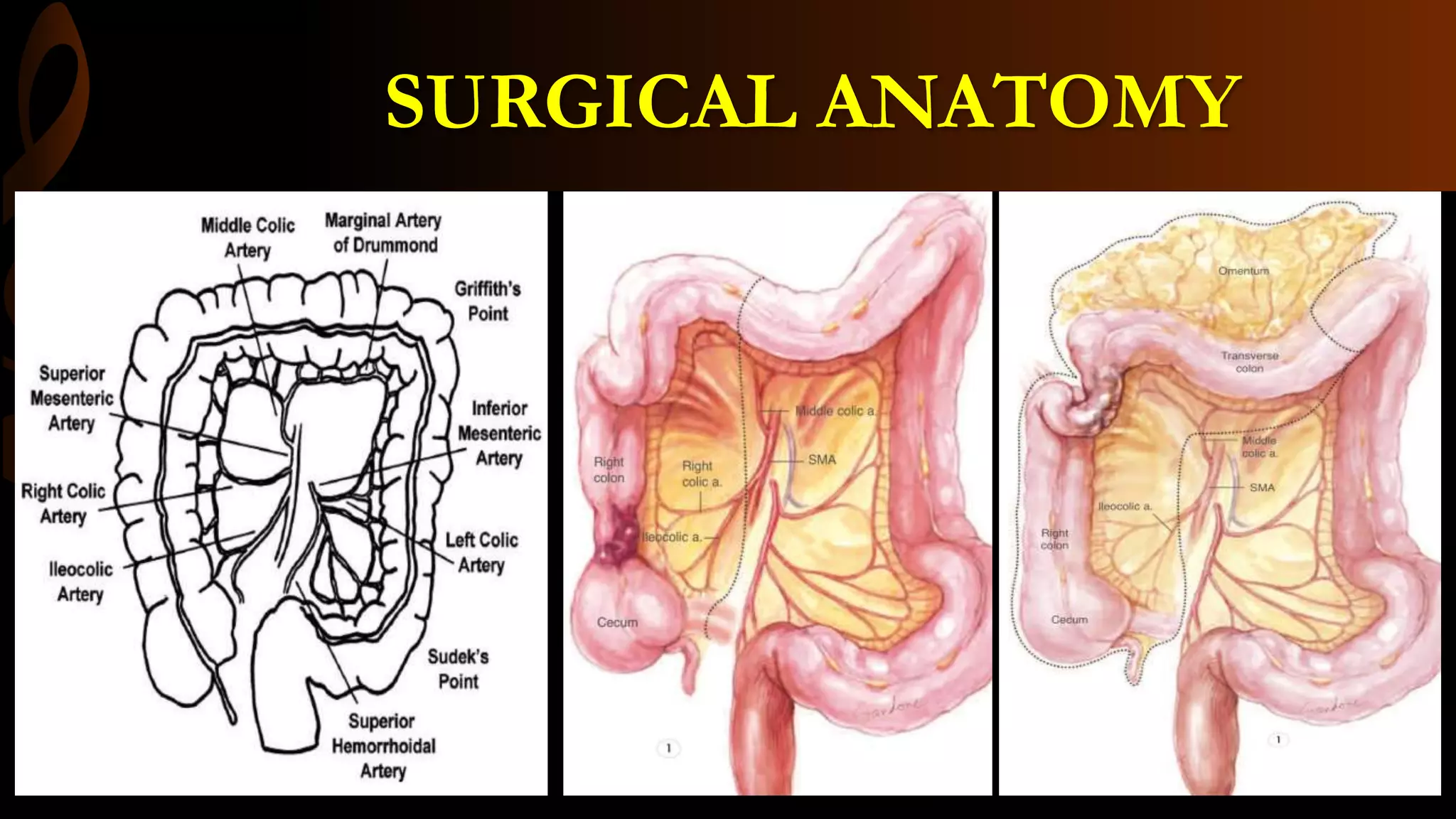
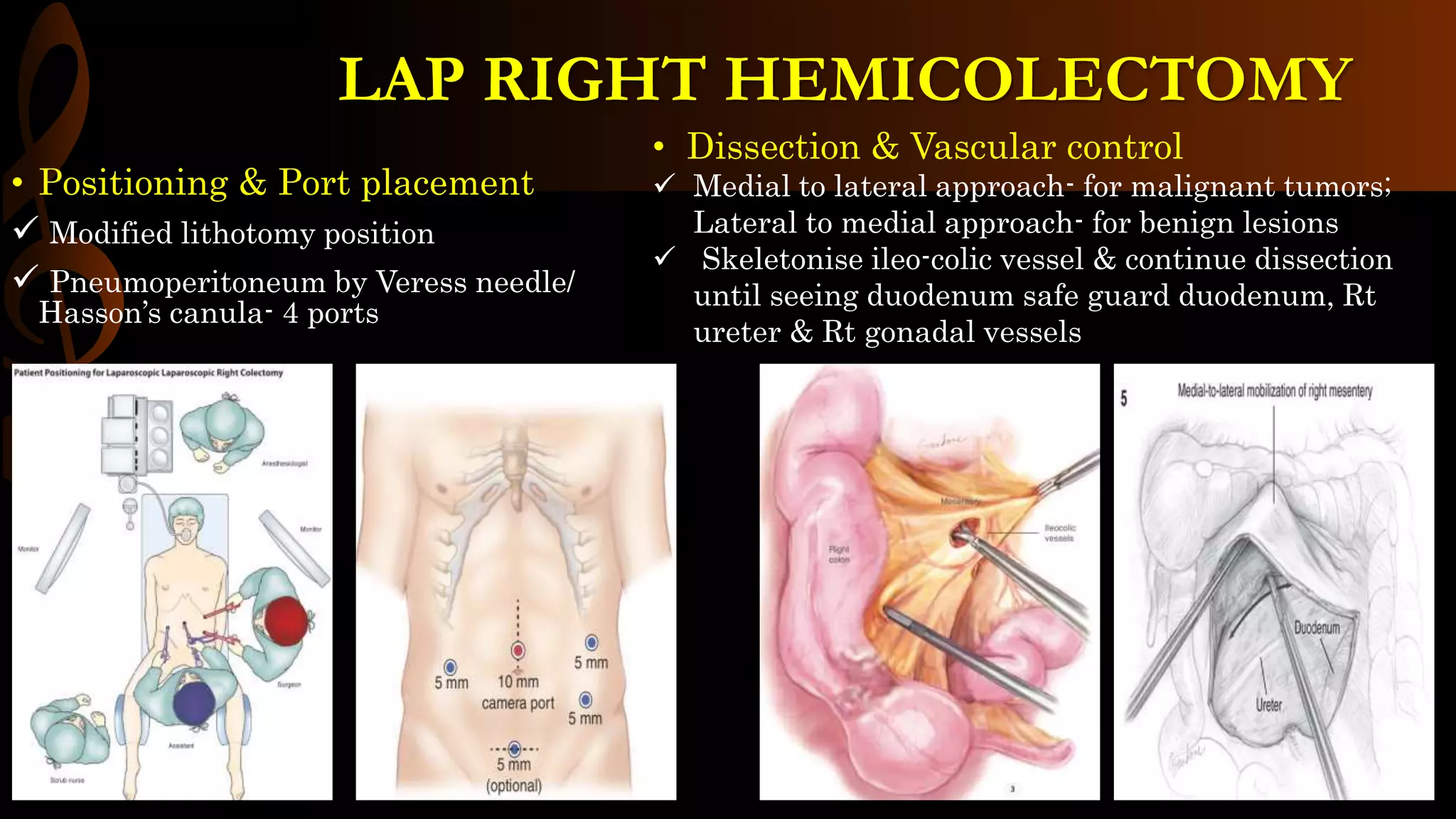
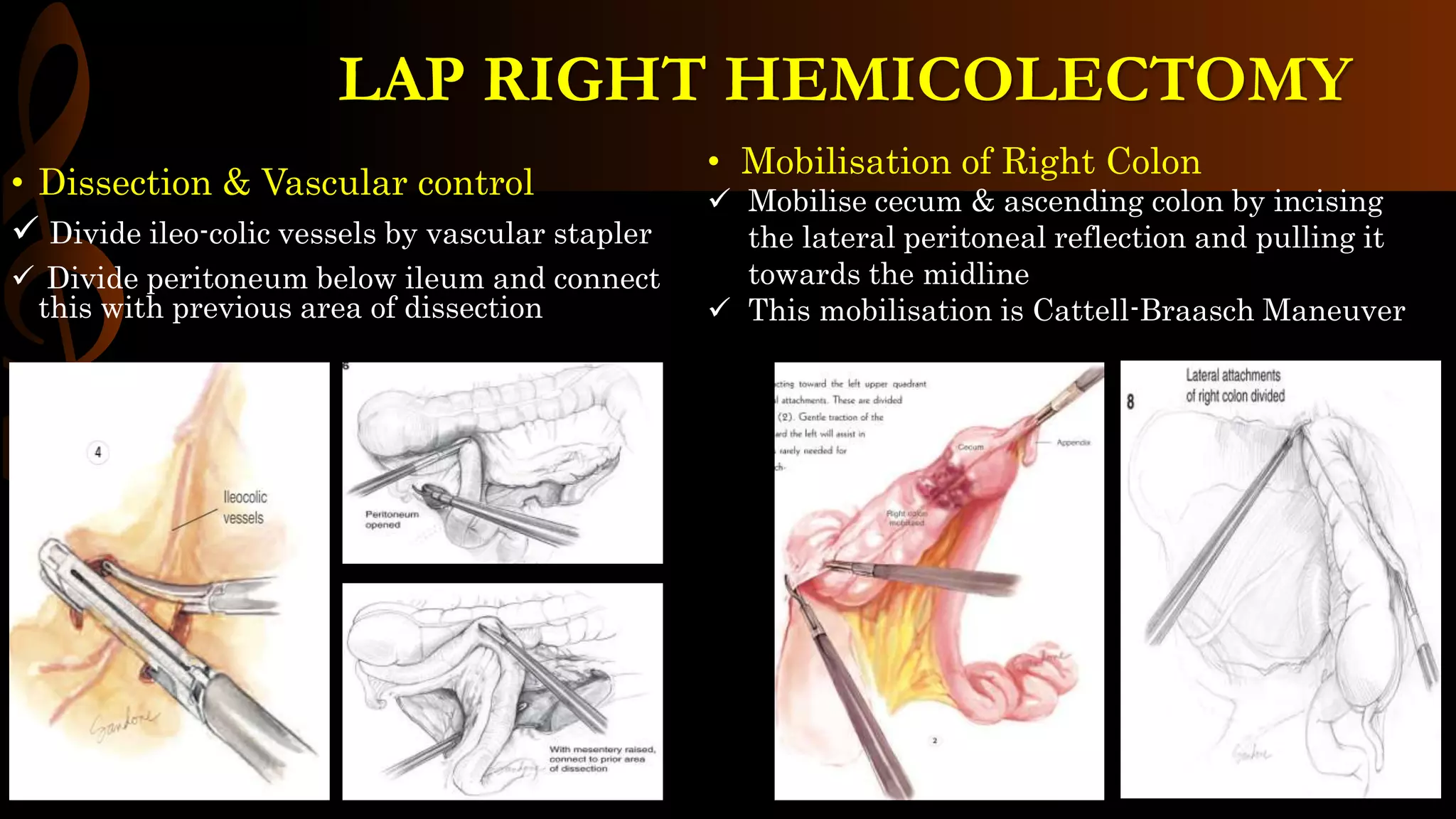
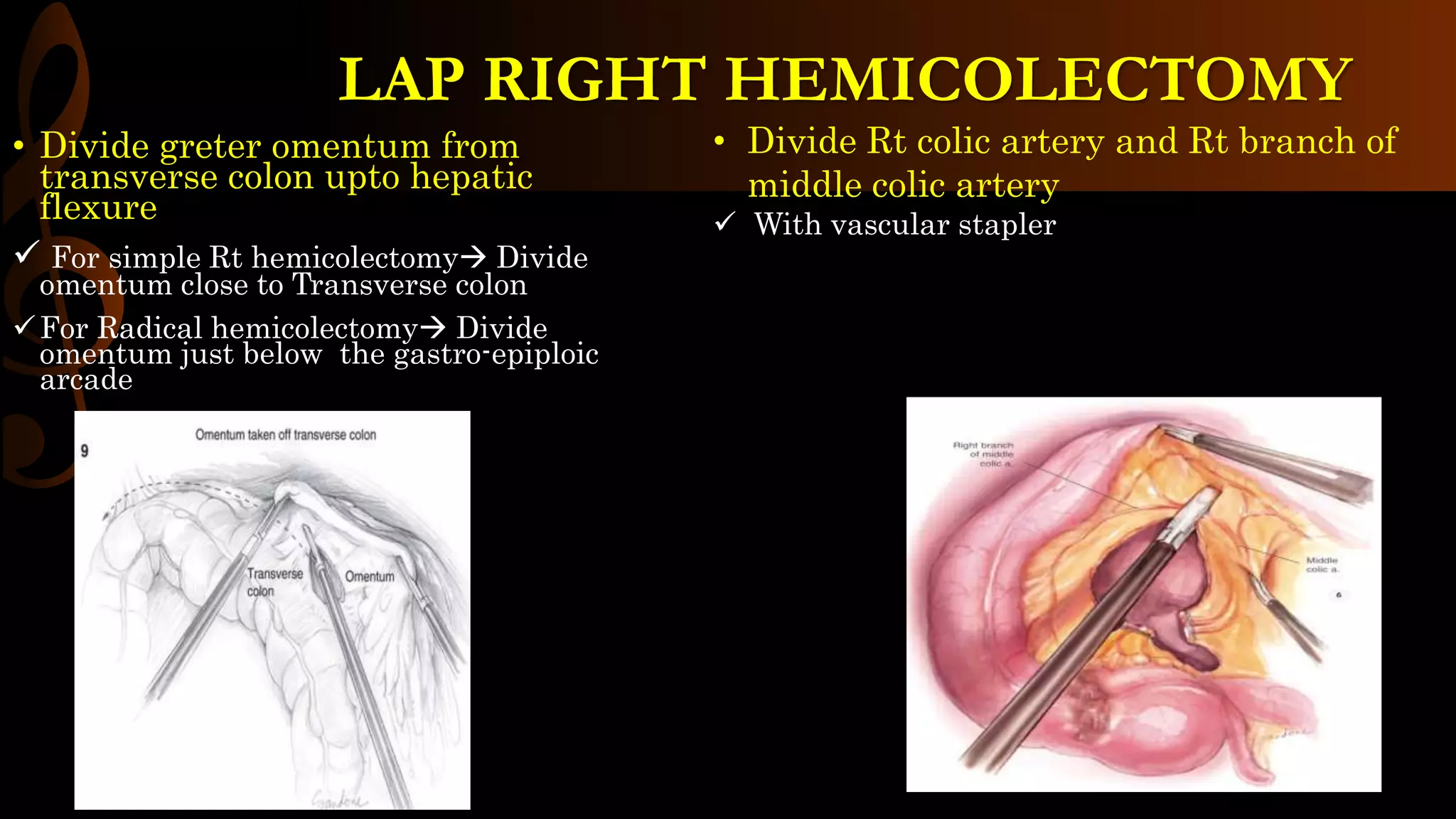
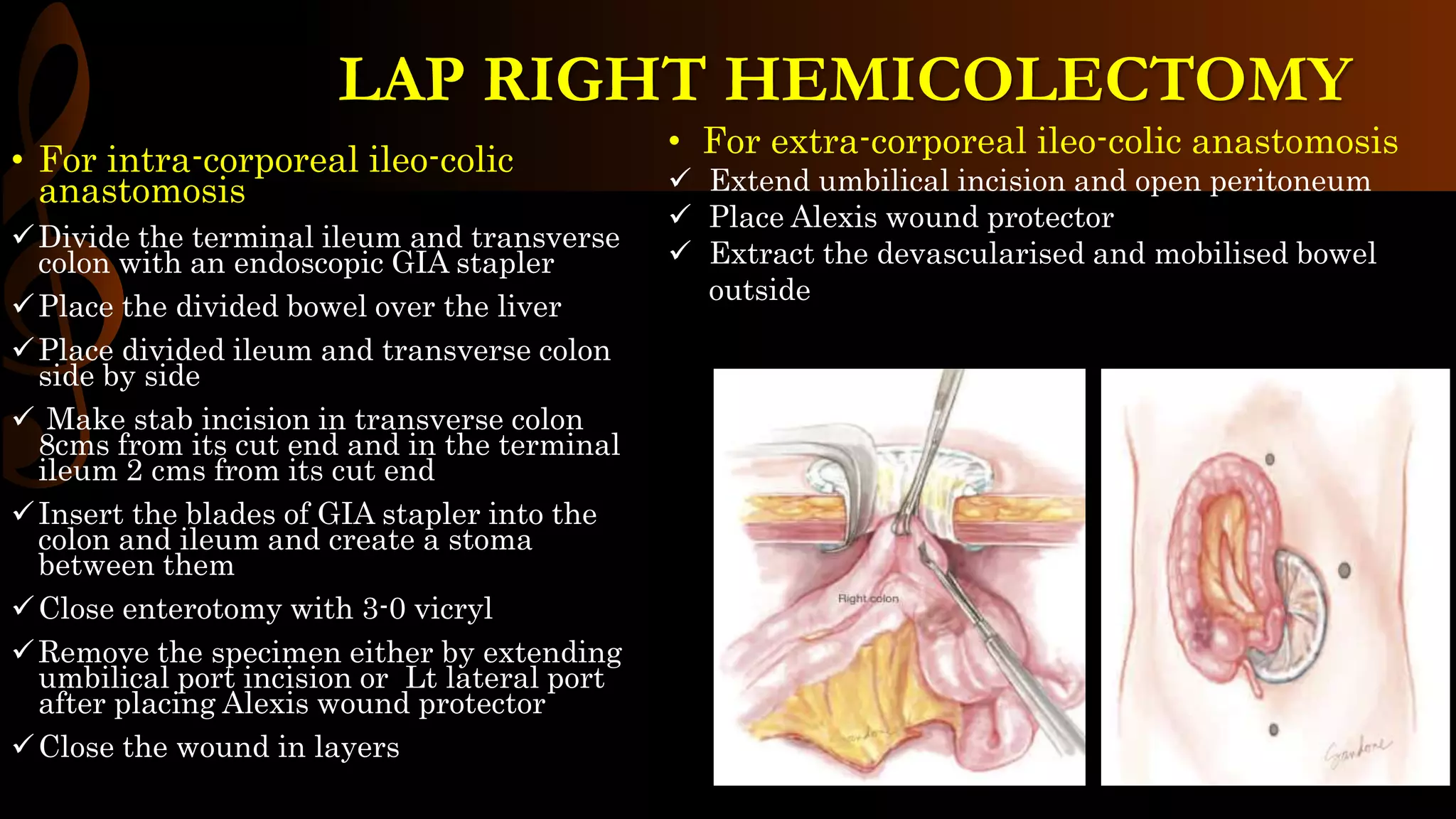
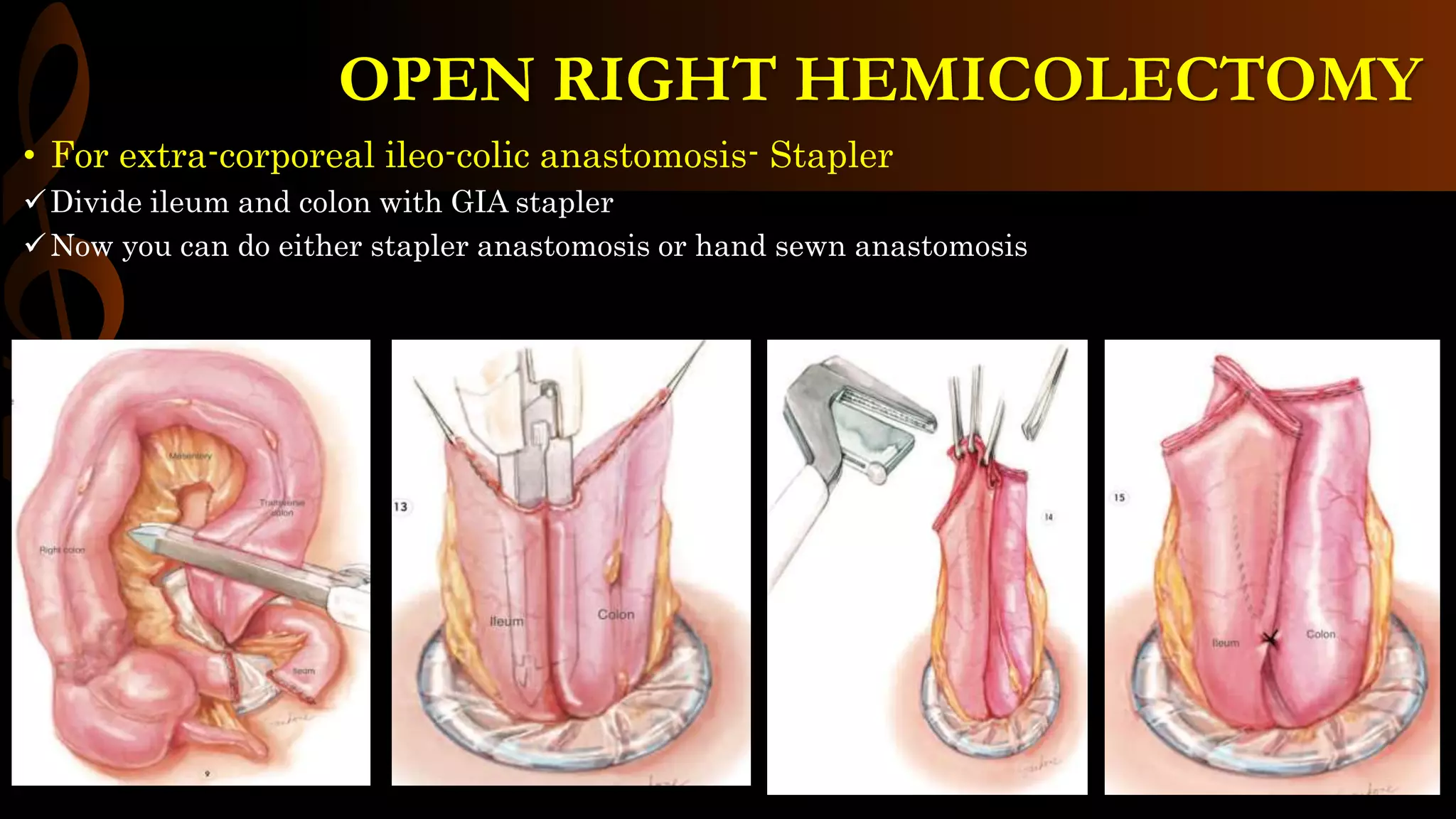
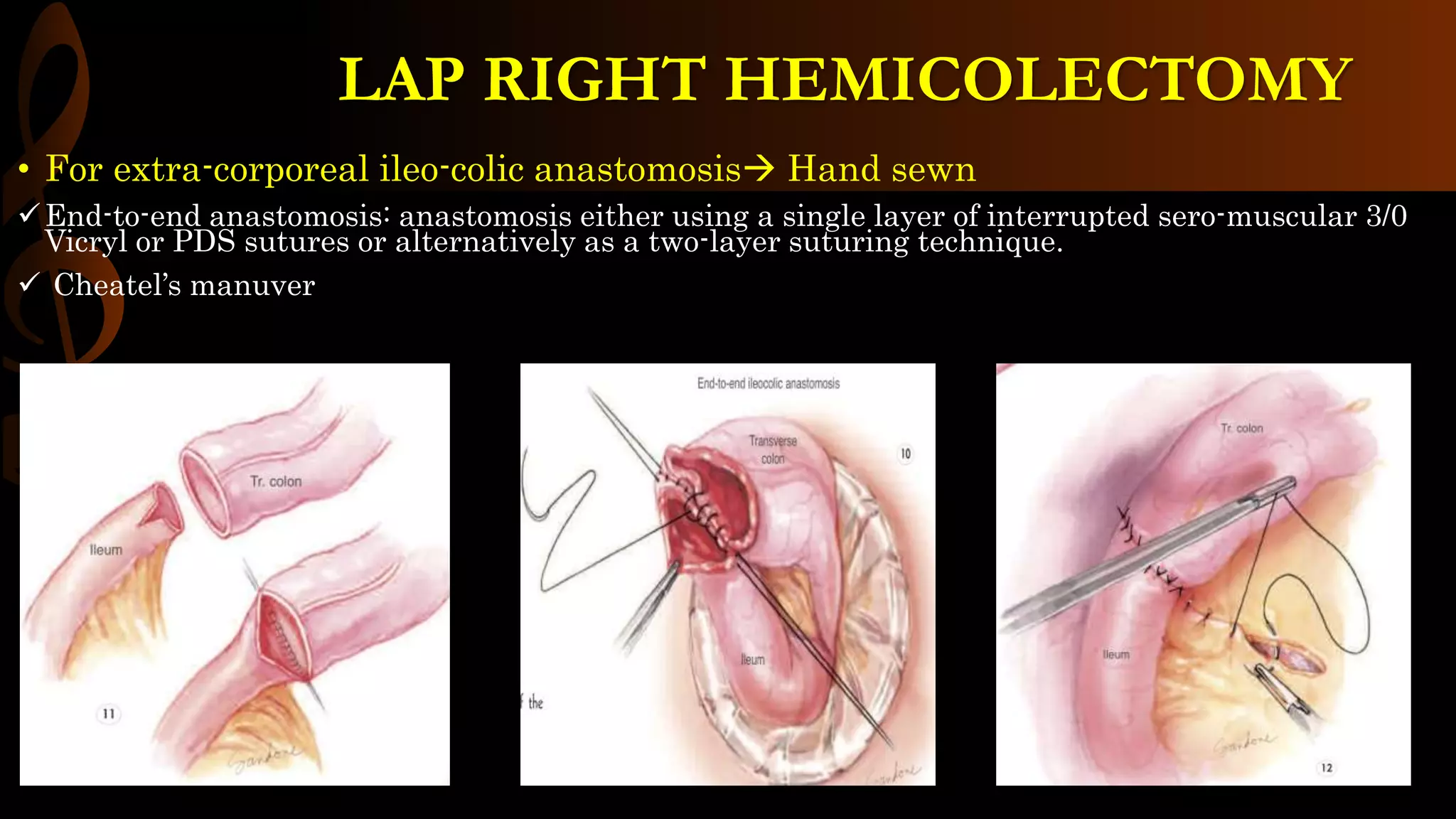
This document describes the procedure for a laparoscopic right hemicolectomy. It discusses the indications, pre-operative preparation including bowel preparation and antibiotic prophylaxis. During the procedure, ports are placed and the ileocolic vessels are divided. The right colon is mobilized and specimens are extracted either intracorporeally or extracorporeally. An ileocolic anastomosis is then performed using a stapler or hand sewing. Post-operative care includes pain control, DVT prophylaxis, and diet advancement. Potential complications are discussed.