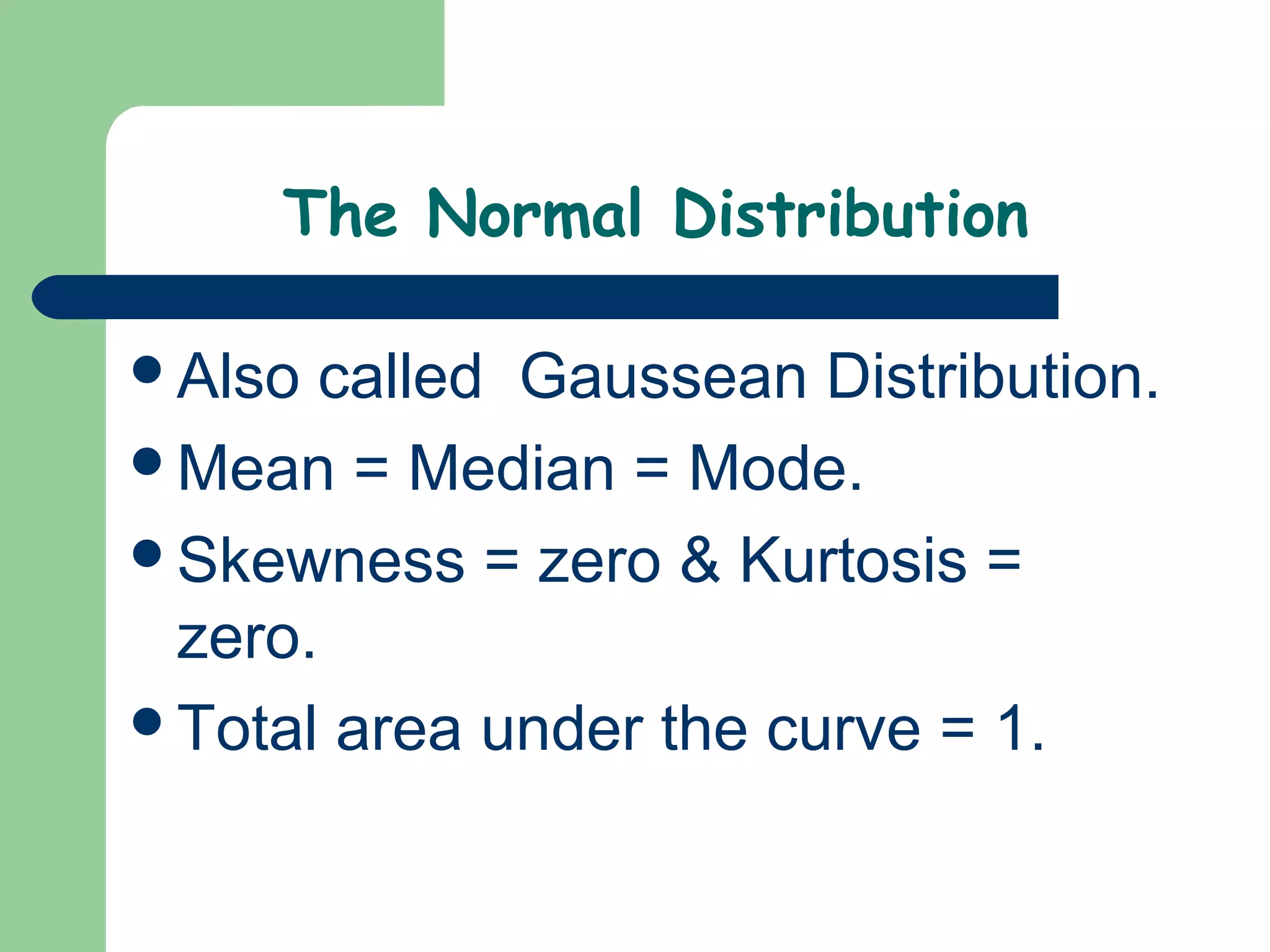
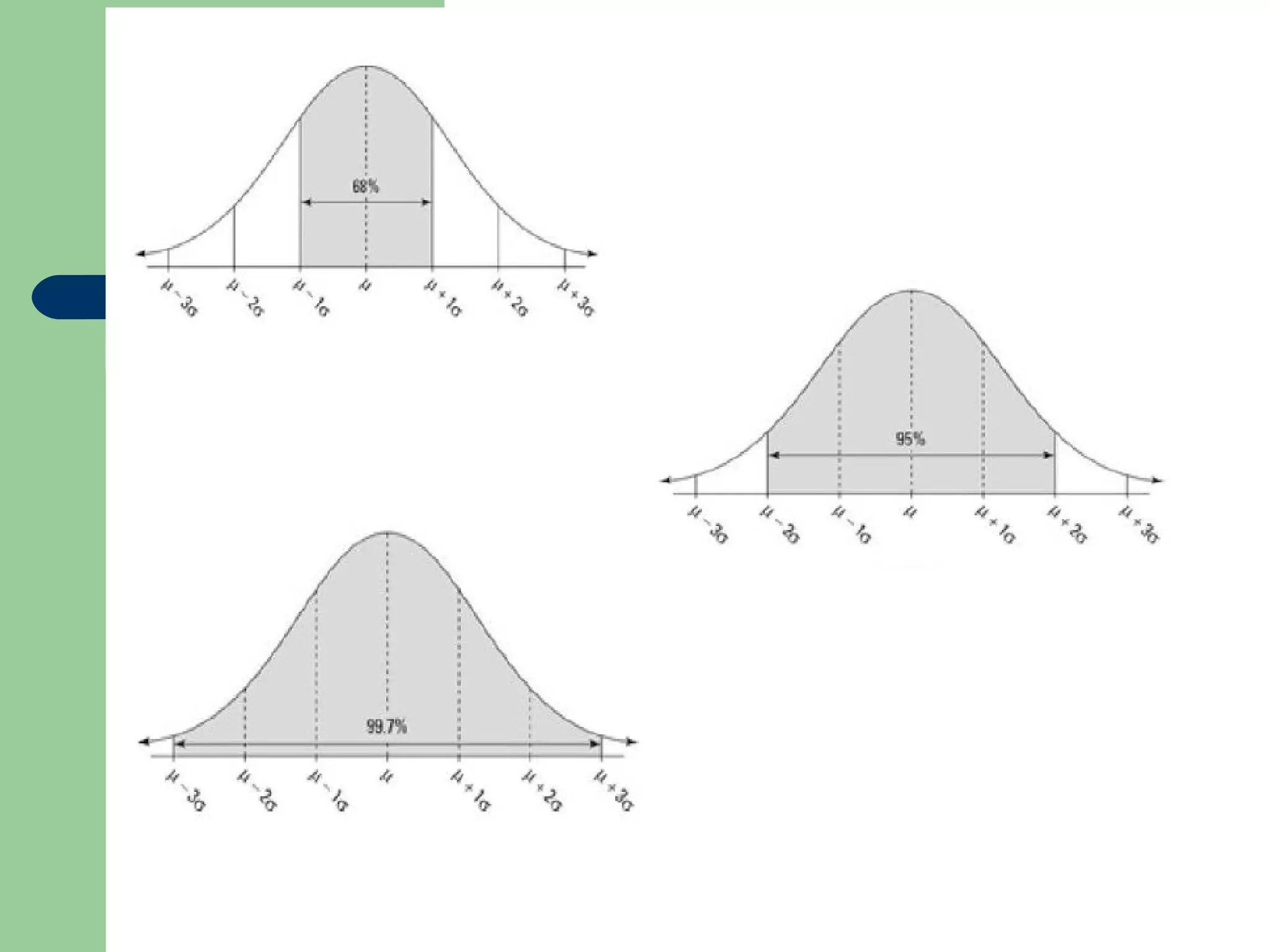
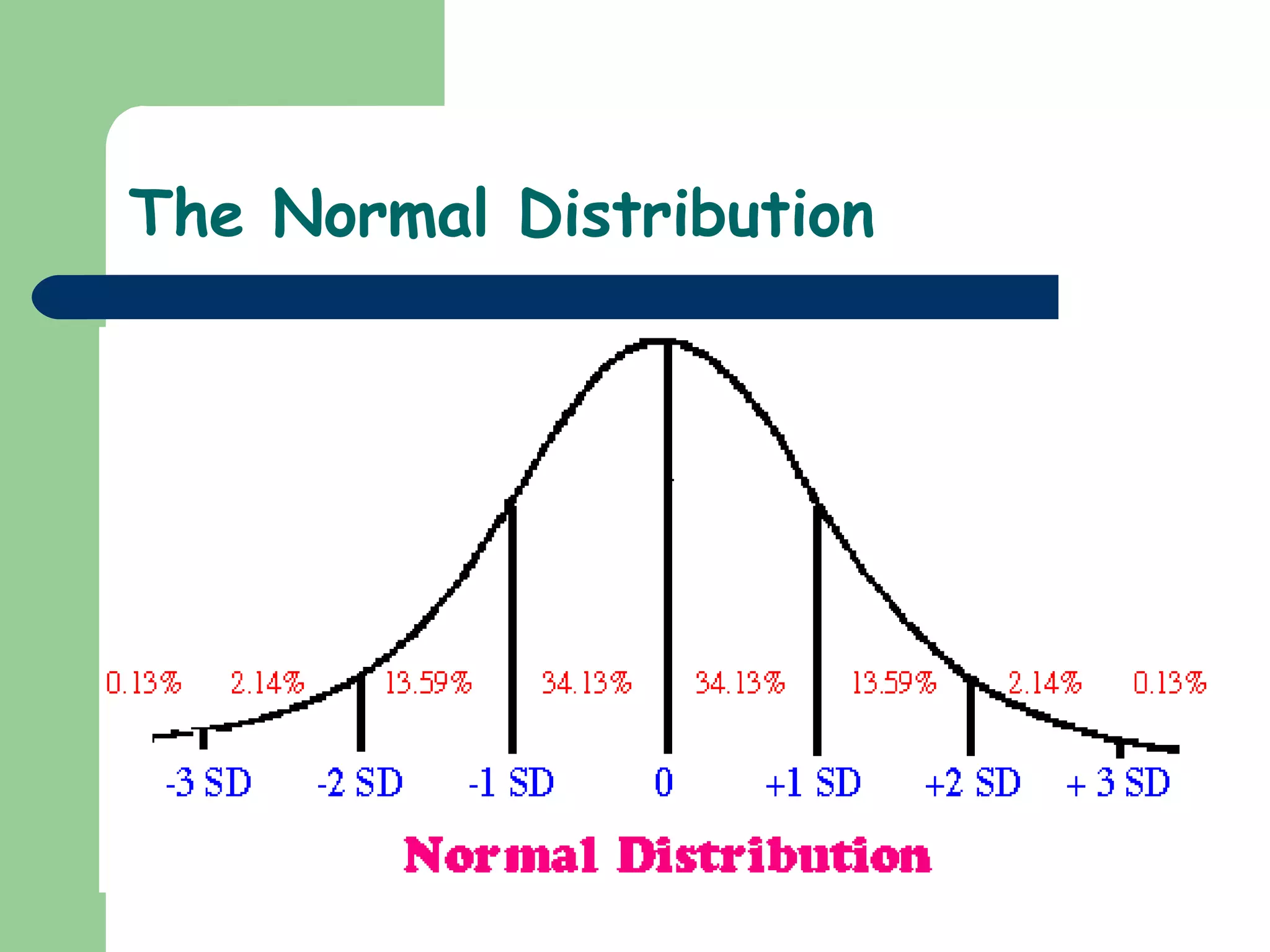
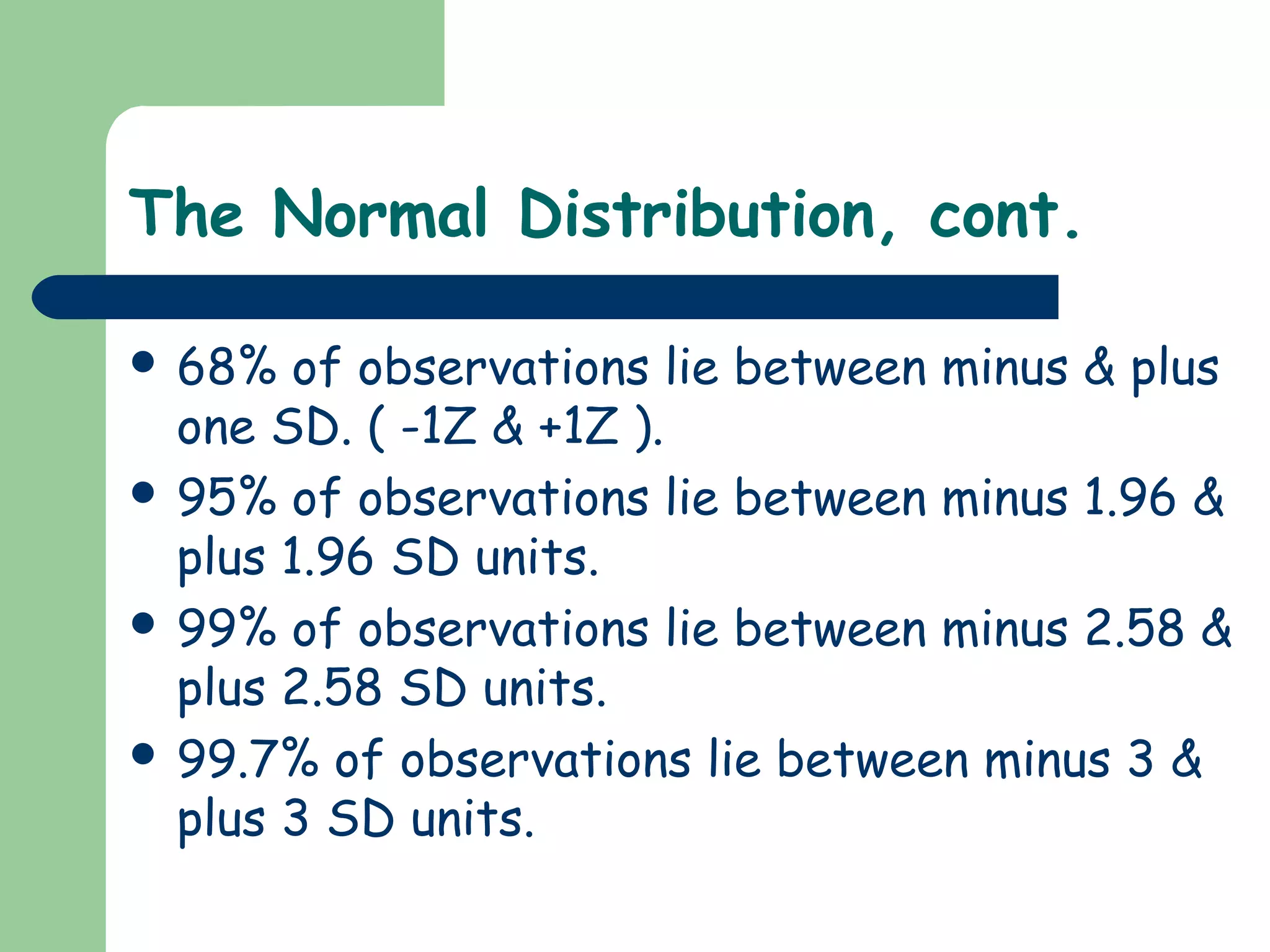
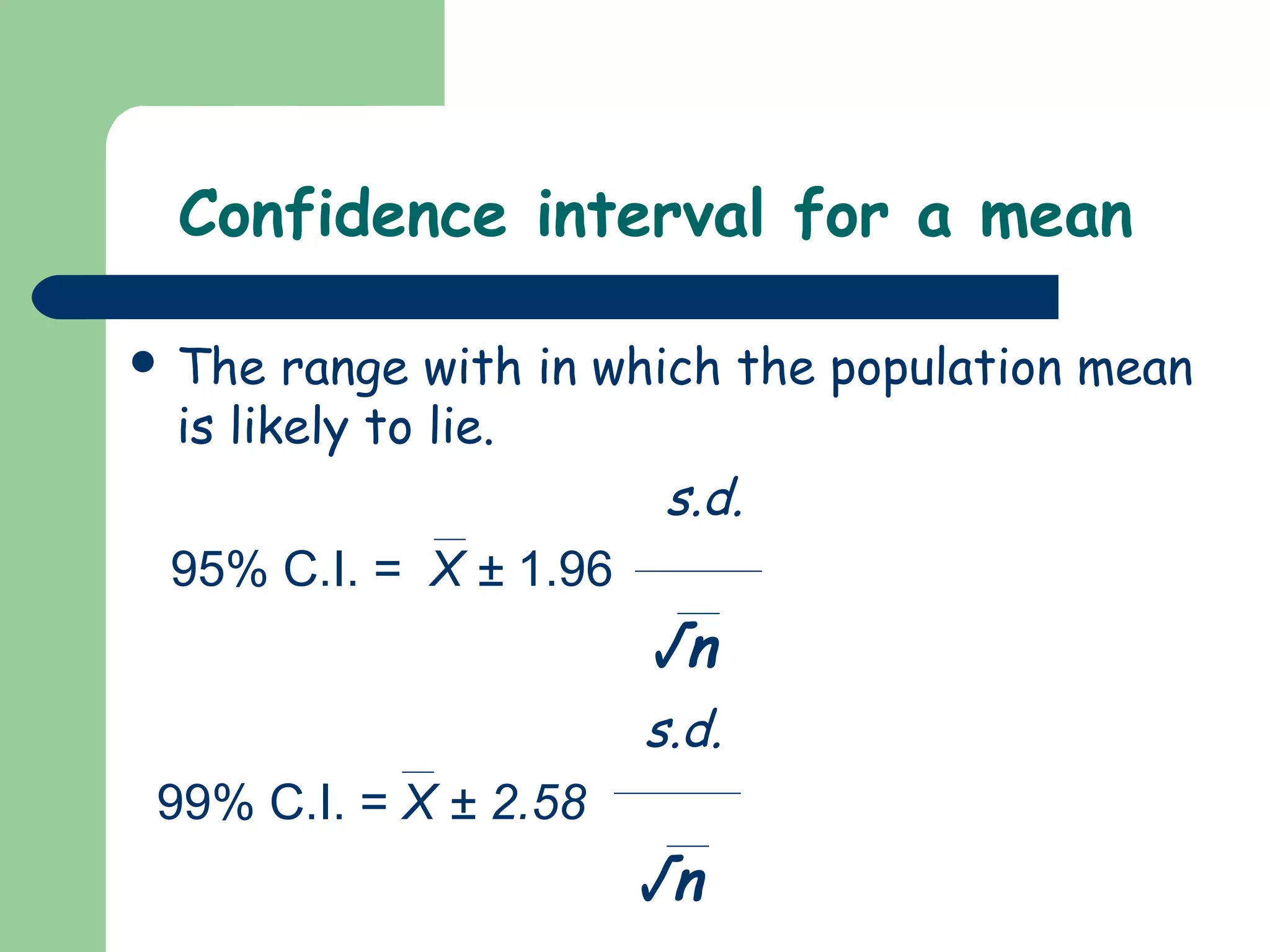
The document discusses the normal distribution and statistical hypothesis testing. It notes that the normal distribution is also called the Gaussian distribution, and has equal mean, median and mode. It then discusses how much of the data falls within standard deviations of the mean for the normal distribution. The document also covers confidence intervals for means, the steps of statistical hypothesis testing including assumptions, hypotheses, significance levels and tests, and different statistical tests used for numerical and categorical data like t-tests, ANOVA, regression and correlation.