This document discusses key concepts in probability theory including:
- Probability is a quantitative measure of uncertainty ranging from 0 to 1.
- Experiments produce outcomes that define events in a sample space.
- There are different approaches to determining probability (classical, relative frequency, subjective).
- Probability can be classified as marginal, union, joint, or conditional depending on the relationship between events.
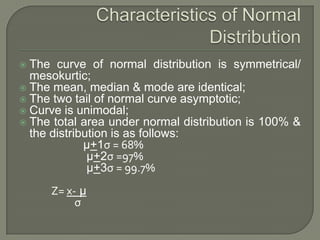
- Common discrete and continuous probability distributions include the binomial, Poisson, and normal distributions.