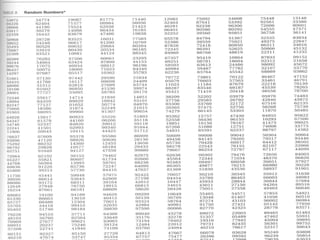
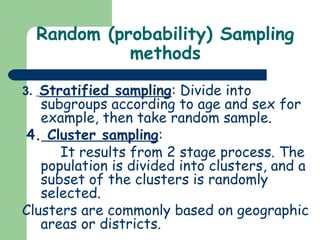
Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, and analyzing data to draw conclusions. There are two main types of data: data from measurements and data from counts. Data can come from various sources like records, surveys, experiments, and external reports. Biostatistics analyzes data from biological sciences and medicine. Variables are characteristics that can take different values and are either quantitative (measured) or qualitative (categorical). Variables can be random, continuous, discrete, independent, or dependent. Samples are subsets of populations used for statistical analysis. Common random sampling methods include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling.