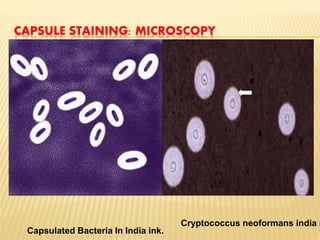
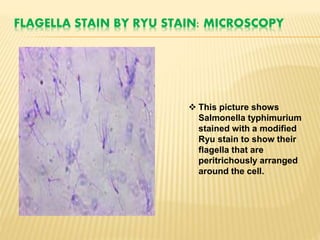
The document discusses various staining techniques used in microbiology, including Gram staining, acid-fast staining, and simple staining techniques. Gram staining differentiates bacteria into gram-positive and gram-negative groups based on differences in their cell wall structure and how they retain or release crystal violet dye. Acid-fast staining uses a carbolfuchsin primary stain to identify acid-fast bacteria that resist decolorization by acid-alcohol, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Simple stains like Loeffler's methylene blue and diluted carbol fuchsin are also discussed, which provide contrast but do not differentiate bacterial types.